Hypotonicity PowerPoint PPT Presentations
All Time
Recommended
provides evidence of adherence to standards of care. ... hypotonicity, spasm, inflammation, tautness, rigidity, flaccidity, etc., can ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Down's syndrome may be 108 kcal/kg. Correction for Gestational Age ... Di George Syndrome. Down Syndrome. Trisomy 21. Sucking problems due to hypotonicity ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Enhancing Services For Students With. Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) ... Hypotonicity: Low muscle tone of trunk or limbs. Rigidity: Resistance to movement in any range. ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
OLIGOHYDRAMNIOS * Dr Mona Shroff www.obgyntoday.info * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * PHYSIOLOGY OF AMNIOTIC FLUID * INFLOW ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
... R/O IUGR ,IUFD when suspected Amniocentesis if chromosomal anomalies suspected early symmetric IUGR Tests for APLA Syndrome , ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Hypotonic, good diluent, and can be administered via USN ... Can usually NOT be used as a diluent for drugs. Has same side effects as hypertonic saline ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Cell Transport Taking a look at the plasma membrane
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
CP affects body movement and muscle coordination ... http://www.burke-eisner.com/media/cerebral-palsy-Small.JPG. Spastic CP Continued...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Hyponatremia Anthony R Mato, MD Remember the basics of the body s fluid compartments. TBW = WEIGHT x .5 (women) or .6 (men) TBW x 1/3 = ECF TBW x 2/3 = ICF ECF x 2 ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
What test would you order? Case Study #4 Differential diagnosis Polyuria 1) ... +urea/2.8+glucose/18 Serum osmolarity is 280-300 mOsm/L 280-300 mOsmol/L- Isotonic ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
... entire extra (or deficient) gene: Down Syndrome (trisomy 21) ... Down syndrome: 24 23 = 47 chromosomes in every cell (since all derived from first cell) ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Global electrolyte drinks market size is expected to reach $41.12 Bn by 2028 at a rate of 6.9%, segmented as by type, isotonic, hypotonic, hypertonic
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Global electrolyte drinks market size is expected to reach $41.12 Bn by 2028 at a rate of 6.9%, segmented as by type, isotonic, hypotonic, hypertonic
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Cell Membrane, Cell Transport & Cell Division Chapter 7: Membrane Structure and Function Chapter 12: The Cell Cycle Plasma Membrane Plasma Membrane ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Intravenous Therapy IV Infusion Preparations Fluid and Electrolytes Sasha A. Rarang, RN, MSN Intravenous (IV)Therapy : Definition: Infusion of a fluid into a vein to ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Cell Membranes The Cell Membrane Cell Membrane: Phospholipid Molecule Model Membrane Structure Cell Membrane Every cell is encircled by a membrane and most cells ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Title: PowerPoint Presentation Author: PYLUSD Last modified by: custom Created Date: 10/14/2004 4:29:11 AM Document presentation format: On-screen Show
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Dr. NervanaMostafaMB BS, MD, PhD (UK)Associate Professor of Physiology Consultant Molecular BiologyDirector of Academic Quality UnitCollege of Medicine, KKUH, KSU
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
EOCT Biology Content Review *
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
... Nursing Interventions Replace fluids by PO route first SLOW admin. of salt-free IV solutions Monitor S/S cerebral & pulmonary edema Monitor accurate I/O, ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Chapter 7 Cellular Structure and Function 7.1 Cell Discovery and Theory * * Cells in Solutions Isotonic Solution = same solutes Hypotonic Solution = lower solutes ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Homeostasis the steady-state physiological condition of the body Ability to regulate the internal environment important for proper functioning of cells
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Cellular Transport And the Cell Cycle Identify the stage of mitosis Anaphase Metaphase Prophase Telephase Results of Mitosis So what s the point?
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Cell Transport: The Plasma Membrane The Gateway to the Cell Photograph of a Cell Membrane Cell Membrane The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Chapter 3: The Cellular Level of Organization * * Stage 2: Metaphase Chromosomes align in a central plane (metaphase plate) Figure 3 25 (Stage 2) * Stage 3 ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
HOMEOSTASIS and the PLASMA MEMBRANE Chapter 7-3 Hypertonic, Hypotonic, Isotonic Passive Transport Facilitated diffusion Movement of specific molecules through a cell ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Title: talaroch07 Author: Laraine Powers Last modified by: LONNIE Created Date: 10/12/2003 3:06:06 PM Document presentation format: On-screen Show (4:3)
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Scientific Method
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
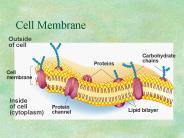
Cell Membrane Outside of cell Carbohydrate chains Proteins Cell membrane Inside of cell (cytoplasm) Protein channel Lipid bilayer
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Moving through the Plasma Membrane Environment outside cell Water moves Effect on ANIMAL cell Effect on PLANT cell Hypotonic In Swells, then bursts (cytolysis ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Transport Flip n Go
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Chapter 7 Cell Structure: A Tour of the Cell
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Title: Plasma Membrane Author: Biology Computer User Last modified by: Teacher Created Date: 1/21/2001 11:07:55 PM Document presentation format: On-screen Show (4:3)
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
The Cell Membrane
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Homeostasis & Transport Chapter 5 Passive Transport Section 5.1 Homeostasis? How do cell membranes help maintain homeostasis within a cell? By controlling what goes ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Title: Pediatric Painless EMG Author: M. Mohammadi Last modified by: PARAND Created Date: 5/2/2003 2:28:31 PM Document presentation format: On-screen Show (4:3)
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Cell Membrane & Cell Transport
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Title: PowerPoint Presentation Last modified by: sanaa tork Created Date: 1/1/1601 12:00:00 AM Document presentation format: On-screen Show Other titles
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Cell Membrane Outside of cell Carbohydrate chains Proteins Cell membrane Inside of cell (cytoplasm) Protein channel Lipid bilayer
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Title: PowerPoint Presentation Author: DOE Last modified by: e2009657 Created Date: 8/28/2003 2:24:07 AM Document presentation format: On-screen Show (4:3)
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Active and Passive Transport Chapter 5 1. Passive Transport Movement of materials in and out of the cell Requires no energy to happen Two Types of Passive Transport ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Passive Transport (moving particles in with the concentration gradient) Diffusion Movement of molecules from areas of high concentration to areas of lower concentration.
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Gateway Biology Content Review Biology Exercises 5. In terms of the carbon cycle, explain how a carbon atom of one of your cells could have at one time been in George ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
How do you think materials move in and out of the cell?
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Cell Membranes Diffusion, Osmosis & Osmotic Pressure Functions of Membranes 1. Protect cell 2. Control incoming and outgoing substances 3. Maintain ion concentrations ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Title: PowerPoint Presentation Last modified by: Hank Dueck Created Date: 1/1/1601 12:00:00 AM Document presentation format: On-screen Show (4:3) Other titles
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Passive Transport
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
The Cell Membrane What do you notice about the picture below? What parts can you name? Do you know their functions?
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
The Cell Membrane Overview Cell membrane separates living cell from nonliving surroundings thin barrier = 8nm thick Controls traffic in & out of the cell selectively ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Chapter 3 Sections 3, 4,& 5 Movement through the membrane
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Title: PowerPoint Presentation Author: Mark Last modified by: Effingham County Created Date: 1/1/1601 12:00:00 AM Document presentation format: On-screen Show
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
The Cell Membrane
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Cell Processes S. Burnham HHS Biology
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view