Cell Membranes - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Cell Membranes
Description:
Cell Membranes The Cell Membrane Cell Membrane: Phospholipid Molecule Model Membrane Structure Cell Membrane Every cell is encircled by a membrane and most cells ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:1521
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Cell Membranes
1
Cell Membranes
- Cell vs. virus A battle for health
- Insights into cell membranes via dish detergent
2
The Cell Membrane
3
Cell Membrane
At Very High Magnification in color
4
Membrane Structure
Form a Bilayer
HydroPhilic/philiaPhobic/phobiaPolarsoluble
in water
5
Cell Membrane
- Every cell is encircled by a membrane and most
cells contain an extensive intracellular membrane
system. Membranes fence off the cell's interior
from its surroundings. Membranes let in water,
certain ions and substrates and they excrete
waste substances. They act to protect the cell. - Without a membrane the cell contents would
diffuse into the surroundings, information
containing molecules would be lost and many
metabolic pathways would cease to work - The cell would die!
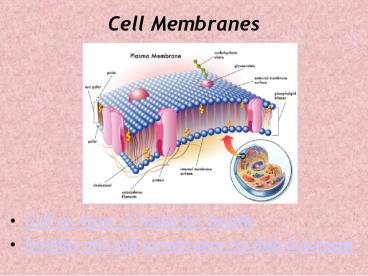
6
Cell Membranes
- Surround all cells
- Fluid-like compositionlike soap bubbles
- Composed of
- Lipids in a bilayer
- Proteins embedded in lipid layer (called
transmembrane proteins) - And, Proteins floating within the lipid sea
(called integral proteins) - And Proteins associated outside the lipid bilayer
(called peripheral proteins).
7
Membrane Lipids
- Composed largely of phospholipids
- Phospholipids composed of.glycerol and two fatty
acids PO4 (phosphate) group - Phospholipids are polar molecules
P-Lipids are represented like this
8
Membrane Proteins
- Integral embedded within bilayer
- Peripheral reside outside hydrophobic region of
lipids
How many integral proteins are in the
picture? How many peripheral proteins are in the
picture?
9
Membrane Models
- Fluid Mosaic Model - lipids arranged in bilayer
with proteins embedded or associated with the
lipids.
What color are the lipids? What color are the
integral proteins? What color are the peripheral
proteins?
10
Fluid Mosaic Model of the Cell Membrane
11
Evidence for the Fluid Mosaic Model (Cell Fusion)
- Frey and Edidin
12
Membrane Functions
- allows for different conditions between inside
and outside of cell - subdivides cell into compartments with different
internal conditions - allows release of substances from cell via
vesicle fusion with outer membrane
13
Membrane Permeability
- Biological membranes are physical barriers..but
which allow small uncharged molecules to pass - And, lipid soluble molecules pass through
- Big molecules and charged ones do NOT pass
through - Semi-permeable / selectively permeable
14
Solution solute solventSolute-- the thing
being dissolvedSolvent--does the
dissolvingkool-aid chocolate milkTerms that
refer to soluteHyperHypoIso
15
How to get other molecules across membranes??
- There are two ways to move through the membrane
- passive transport and active transport
- Active transport requires energy (that the cell
has obtained from food to move the molecules
through the cell membrane) - Passive transport does not require energy
16
Membrane Transport MechanismsI. Passive Transport
- Diffusion- simple movement from regions of high
concentration to low concentration - Osmosis- diffusion of water across a
semi-permeable membrane - Facilitated diffusion- protein transporters which
assist in diffusion
How Osmosis works
17
Membrane Transport MechanismsII. Active Transport
- Active transport- proteins which transport
against concentration gradient. - Requires energy input (uses ATP)
- - Endocytosis
- Exocytosis
- Receptor mediated endocytosis
18
- 1.What is the solute?
- 2. What diffuses?
- 3.Why?
- 4.Is this diffusion or osmosis?
- 5.Which side is hypertonic?
- 6.Which side is hypotonic?
- 7.Why doesnt the sugar diffuse?
19
Osmosis
- Movement of water across a semi-permeable
barrier. - Example Salt in water, cell membrane is
barrier. Salt will NOT move across membrane,
water will.
This is why you will die if you try to drink sea
water on a desert island This is why lunch salad
gets soggy when you put dressing on at home. This
is why over fertilizing your plants will kill
them This is why salting slugs turns them to
slime This is why, adding sugar to strawberries,
makes strawberry soup. Use terms hypertonic,
hypotonic, solute, solvent, diffusion, osmosis
20
Osmosis in Hypertonic medium
Hypertonic solutions- shrink cells Plasmolysis in
Plant Cells Crenation in Animal Cells What
happens when you eat salty chips?
21
Osmosis in Hypotonic medium
Hypotonic solutions- swell cells Hypos make
hippos Cytolysis in Animal Cells Turgor Pressure
in Plant Cells http//www.kscience.co.uk/animation
s/turgor.htm
22
(No Transcript)
23
For more animations view http//www.tvdsb.on.ca/w
estmin/science/sbi3a1/Cells/Osmosis.htm
24
For Osmosis in Action
- View frozen frogs at
- http//www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/sciencenow/3209/05.ht
ml - How did the frog use the principles of osmosis
and diffusion to survive the winter? Make sure
you use the following terms appropriately in your
description hypertonic, hypotonic, solute,
solvent, diffusion, osmosis, cytolysis,
crenation, isotonic and semi-permeable membrane.
25
Osmosis Food Preservation
- Food can be preserved by causing any
microorganism that comes in contact with it to
become plasmolysed and, therefore, shrivel and
die. To do this food is placed in a high salt or
sugar medium. The salt or sugar concentration is
higher than the cytoplasm of bacteria or fungi.
Bacteria or fungi, that contaminate the food,
will lose water by osmosis and their metabolism
will decline. Many will die but some bacteria may
survive by forming dormant resistant endospores.
Meat and fish are often preserved in salt. Fruit
is commonly preserved in sugar as in jam or syrup.
26
Endocytosis
- Transports macromolecules and large particles
into the cell. - Part of the membrane engulfs the particle and
folds inward to bud off.
27
Phagocytosis
- Pseudo pods
- Phago cytes
- Macro phages (phage)_
28
Putting Out the Garbage
- Vesicles (lysosomes, other secretory vesicles)
can fuse with the membrane and open up the the
outside
29
Sodium-Potassium Pump
30
Resources
- http//users.rcn.com/jkimball.ma.ultranet/BiologyP
ages/C/CellMembranes.html - www.biologie.uni-hamburg.de/b-online/e22/22.htm
- More Animations http//www.kscience.co.uk/animati
ons/anim_1.htm - http//fig.cox.miami.edu/cmallery/150/memb/membra
nes.htm - Pictures http//biologycorner.com/resources/
- 1st Semester Final Review