The Plasma Membrane - - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 94
Title: The Plasma Membrane -
1
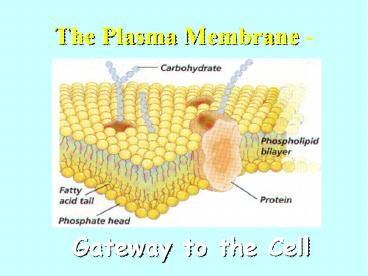
The Plasma Membrane -
Gateway to the Cell
2
Photograph of a Cell Membrane
3
Types of Transport Across Cell Membranes
4
Simple Diffusion
- Requires NO energy
- Molecules move from area of HIGH to LOW
concentration
5
DIFFUSION
- Diffusion is a PASSIVE process which means no
energy is used to make the molecules move, they
have a natural KINETIC ENERGY
6
Diffusion of Liquids
7
Diffusion through a Membrane
Cell membrane
Solute moves DOWN concentration gradient (HIGH to
LOW)
8
Osmosis
Diffusion across a membrane
- Diffusion of water across a membrane
- Moves from HIGH water potential (low solute) to
LOW water potential (high solute)
Semipermeable membrane
9
Diffusion of H2O Across A Membrane
High H2O potentialLow solute concentration
Low H2O potentialHigh solute concentration
10
Cell in Isotonic Solution
10 NaCL90 H2O
ENVIRONMENT
CELL
NO NET MOVEMENT
10 NaCL 90 H2O
What is the direction of water movement?
equilibrium
The cell is at _______________.
11
Cell in Hypotonic Solution
10 NaCL90 H2O
CELL
20 NaCL 80 H2O
What is the direction of water movement?
12
Cell in Hypertonic Solution
15 NaCL85 H2O
ENVIRONMENT
CELL
5 NaCL 95 H2O
What is the direction of water movement?
13
Cells in Solutions
14
Isotonic Solution
Hypotonic Solution
Hypertonic Solution
NO NET MOVEMENT OF H2O (equal amounts entering
leaving)
CYTOLYSIS
PLASMOLYSIS
15
Cytolysis Plasmolysis
Plasmolysis
Cytolysis
16
Osmosis in Red Blood Cells
Isotonic
Hypertonic
Hypotonic
17
isotonic
hypotonic
hypertonic
hypertonic
isotonic
hypotonic
18
Three Forms of Transport Across the Membrane
19
Passive Transport
- Simple Diffusion
- Doesnt require energy
- Moves high to low concentration
- Example Oxygen or water diffusing into a cell
and carbon dioxide diffusing out.
20
Passive Transport
- Facilitated diffusion
- Doesnt require energy
- Uses transport proteins to move high to low
concentration - Examples Glucose or amino acids moving from
blood into a cell.
21
Proteins Are Critical to Membrane Function
22
Active Transport
- Requires energy or ATP
- Moves materials from LOW to HIGH concentration
- AGAINST concentration gradient
23
Active transport
- Examples Pumping Na (sodium ions) out and K
(potassium ions) in against strong concentration
gradients. - Called Na-K Pump
24
Sodium-Potassium Pump
3 Na pumped in for every 2 K pumped out
creates a membrane potential
25
Moving the Big Stuff
Exocytosis- moving things out.
Molecules are moved out of the cell by vesicles
that fuse with the plasma membrane.
This is how many hormones are secreted and how
nerve cells communicate with one another.
26
Exocytosis
27
Moving the Big Stuff
Large molecules move materials into the cell by
one of three forms of endocytosis.
28
Pinocytosis
Most common form of endocytosis.
Takes in dissolved molecules as a vesicle.
29
Pinocytosis
- Cell forms an invagination
- Materials dissolve in water to be brought into
cell - Called Cell Drinking
30
Example of Pinocytosis
mature transport vesicle
pinocytic vesicles forming
Transport across a capillary cell (blue).
31
Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis
Some integral proteins have receptors on their
surface to recognize take in hormones,
cholesterol, etc.
32
Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis
33
Endocytosis Phagocytosis
Used to engulf large particles such as food,
bacteria, etc. into vesicles
Called Cell Eating
34
Phagocytosis About to Occur
35
Phagocytosis - Capture of a Yeast Cell (yellow)
by Membrane Extensions of an Immune System Cell
(blue)
36
Exocytosis The opposite of endocytosis is
exocytosis. Large molecules that are manufactured
in the cell are released through the cell
membrane.
Inside Cell
Cell environment
37
OSMOSIS
http//www.biology4kids.com/files/cell_main.html
38
Diffusion
http//lhs.lps.org/staff/sputnam/Biology/U3Cell/di
ffusion_1.png
39
- See a video clip about
- DIFFUSION-7A
40
Animatioin from http//www.biologycorner.com/reso
urces/diffusion-animated.gif
- Molecules move
- _______where theres _______
- ____where theres _______
FROM
A LOT
to
NOT
41
DIFFUSION across a space
- Happens anytime there is a __________ in
concentration in one place compared to another - ________________________
DIFFERENCE
Concentration gradient
42
DIFFUSION across a SPACE
DOWN
- Molecules move automatically _______ the
concentration gradient _______ an area of _______
concentration ____ an area of ________
concentration - EXAMPLES
from
Higher
to
Lower
Blue dye in beaker demo, Someone making
popcorn/grilling out Strong perfume, Bad smell in
room
http//www.swapmeetdave.com/Humor/Farts.htm
http//leighhouse.typepad.com/blog/images/kool_aid
.jpg
43
DIFFUSION across a space
- Diffusion continues until the concentration is
________________ in space - ________________________
equal everywhere
Equilibrium
http//lhs.lps.org/staff/sputnam/Biology/U3Cell/di
ffusion_1.png
44
Molecules need to move across membranes in cells
Image modiified from http//www.accessexcellence.
org/AB/GG/importProt.html
45
Diffusion can happen ________ a _____________ in
a cell, too
across
membrane
- as long as membrane will let the molecule
_________________
pass through
46
SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE(Semi-permeable)
Video from http//www.southtexascollege.edu/tdehn
e/BC_ShockwaveAnimations/08SWF-MembraneStructureAn
dFunct/08-02-MembraneStructure.swf
See a movie
http//life.nthu.edu.tw/d857401/advance.html
47
CELL EXAMPLE
- DIFFUSION automatically moves oxygen from
HIGHER concentration (in lungs) to a LOWER
concentration (in blood)
CO2 automatically movesfrom where there is
a HIGHER concentration (in blood) to where
there is a lower concentration (in lungs)
http//www.le.ac.uk/pa/teach/va/anatomy/case2/2_2.
html
48
BUT.What if a cell needs to move _____ or
______ molecules?
LARGE
POLAR
http//www.d.umn.edu/sdowning/Membranes/membraneI
mages/jpegimages/diffusionmedium.jpg
49
What if cell needs to move a molecule _________
the CONCENTRATION GRADIENT?_______________
AGAINST
(LOWER ? HIGHER)
- Cell example
- Want to put MORE glucose
- into mitochondria when there is
- already glucose in there
Image from http//www.biologyclass.net/mitochondr
ia.jpg
50
What if cell needs to move molecules really
_______? (cant wait for it to diffuse)
FAST
- Cell example
Movement of Na K ions required to send
nerve signals
http//www.steve.gb.com/images/science/neuron.png
51
We need a ____ to ____ molecules across cell
membranes that _______ across by ___________
WAY
HELP
cant go
themselves
52
Kidspiration by Riedell
53
Kinds of ________ Transport
PASSIVE
__________________________________ _____________
______________________ __________________________
_________
- Diffusion
- Osmosis
- Facilitated Diffusion
54
DIFFUSION across a membrane
DIFFERENCE
- Happens anytime there is a __________ in
_____________ on one side of the membrane
compared to the other
concentration
Molecules that move by diffusion across
membranes in cells ______________ ______________
OXYGEN
CARBON DIOXIDE
See diffusionanimation
http//www.lionden.com/cell_animations.htm
55
OSMOSIS
SPECIAL KIND OF DIFFUSION
IMAGE by RIEDELL
OSMOSIS
____________
See osmosis animation
DIFFUSION
__________
Movement of molecules across a_________________
membranefrom ______ concentration to _____
Semi-permeable
lower
Higher
56
See a video about Passive transport 7-C
57
Facilitated Diffusion_______ proteins help
diffusion go faster
Carrier
58
FACILITATED DIFFUSION
PASSIVE
- No energy required __________________
- Moves _________ concentration gradient
- from ________________________
- _____________________ grab molecule, change
shape, and flip to other side (Like a
revolving door) - Molecules that move this way in cells
- _______________________
DOWN
HIGHER to LOWER
Membrane proteins
GLUCOSE
59
Facilitated Diffusion
Animation from http//bio.winona.edu/berg/ANIMTNS
/facdifan.gif
60
Kidspiration by Riedell
61
Kinds of ________Transport
ACTIVE
________________________________________ _______
____________________________ ____________________
________________
- Sodium-Potassium Pump
- Endocytosis
- Exocytosis
62
- See a video clip about
- Na-K pump -7D
63
Sodium (Na)- Potassium (K) Pump
Animation from http//www.lionden.com/cell_anima
tions.htm
See a movie about Na - K pump
64
Sodium-Potassium pump
ACTIVE
- ___________ transport
- (requires energy from ______)
- Special just for Na and K ions
- Uses integral ___________________ to move
molecules - Examples in nerve cells Na is pumped out of
cells at same time K is taken into
cells
ATP
Carrier Proteins
65
- See a video clip about
- Endo/exocytosis -7E
66
ENDOCYTOSISTakes substances into cell
ACTIVE
- _____________transport
- (requires __________ from ______)
- Uses small membrane sacs called ______________ to
carry substances
energy ATP
VESICLES
http//www.sirinet.net/jgjohnso/cell.html
67
2 KINDS of ENDOCYTOSISTakes substances into cell
- If taking in
- fluid or small molecules _________________
- large particles or whole cells ______________
- Examples in cells
- one celled organisms eat this way
- white blood cells get rid of bacteria this way
PINOCYTOSIS
PHAGOCYTOSIS
68
Pinocytosis
- Called Cell Drinking
69
ENDOCYTOSIS
Animation from http//academic.brooklyn.cuny.ed
u/biology/bio4fv/page/cell-movement.html
http//www.accs.net/users/kriel/chapter20nine/
70
PHAGOCYTOSIS
Called Cell Eating
germs
White blood cell
___________ destroying _______
71
EXOCYTOSISSubstances released outside of cell
ACTIVE
- __________ transport (requires __________)
- Substances move in____________
- Examples in cells
- _________ release packaged proteins this way
energy
VESICLES
GOLGI
72
Exocytosis
http//www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/BIOBK/
BioBooktransp.html
73
GOLGI BODIES USE EXOCYTOSIS
Video http//www.southtexascollege.edu/tdehne/BC
_ShockwaveAnimations/07SWF-TourOfTheCell/07-16-End
omembraneSystem.swf
- Animation from http//www.franklincollege.edu/bio
web/APfiles/week04.html
See a Golgi movie
74
Endocytosis Exocytosis
Videos from http//www.pleasanton.k12.ca.us/avhs
web/thiel/apbio/notes/chp8/exocytosis_endocytosis.
mov http//trc.ucdavis.edu/biosci10v/bis10v/week2/
endocytosis.mov
Watch a video clip about endo/exocytosis Watch
a video clip about endo/exocytosis
Choose Screen/Switch programs to view
75
INSULIN being released by pancreas cells using
exocytosis
http//fig.cox.miami.edu/cmallery/255/255ion/fig1
4x26.jpg
76
What if there is a difference in concentration
but solute molecules cant move across a membrane?
WATER will move until concentration reaches
equilibrium
77
VOCAB
- _____________ substance that is dissolved in a
solvent to make a solution - _____________ substance in which a solute is
dissolved
SOLUTE
SOLVENT
EX Koolaid powder solute Water
solvent Koolaid drink solution
http//www.makash.ac.il/h_school/hst/hstsb/chem/lu
ach/dissolve.jpg
78
Images by Riedell
- __________________ mass of a solute in a given
volume of solution
CONCENTRATION
MORE
The _______ molecules there are in a given
volume the ____________the concentration
GREATER
79
- See a video clip about
- OSMOSIS -7B
80
Animation http//www.ouhscphysio.org/humanphys/an
imations/osmosis1.swf
See an animation Osmosis1
http//faculty.etsu.edu/currie/images/osmosis1.jpg
81
OSMOSIS
Animation from http//www.ouhscphysio.org/humanph
ys/animations/osmosis4.swf
See an animation OSMOSIS 4
- HYPERTONIC Concentration outside cell is
____________________ inside cell - More water leaves cell than enters so cell
____________
GREATER THAN
shrinks
82
Cell in Hypertonic Solution
15 NaCL85 H2O
ENVIRONMENT
CELL
5 NaCL 95 H2O
What is the direction of water movement?
83
OSMOSIS
Animation from http//www.ouhscphysio.org/humanph
ys/animations/osmosis3.swf
See an animationOsmosis3
- HYPOTONIC Concentration outside cell is
________________ inside the cellMore water
enters than leaves cell so cellwill
___________________
LESS THAN
Swell and possibly burst
84
Cell in Hypotonic Solution
10 NaCL90 H2O
CELL
20 NaCL 80 H2O
What is the direction of water movement?
85
OSMOSIS
- ISOTONIC
- Concentration outside cell __________
- concentration inside cell
- Water entering water leavingso cell
_____________________
EQUALS
STAYS THE SAME SIZE
86
Cell in Isotonic Solution
10 NaCL90 H2O
ENVIRONMENT
CELL
NO NET MOVEMENT
10 NaCL 90 H2O
What is the direction of water movement?
equilibrium
The cell is at _______________.
87
Isotonic Solution
Hypotonic Solution
Hypertonic Solution
NO NET MOVEMENT OF H2O (equal amounts entering
leaving)
Cell Swells may burst
Cell shrivels up
88
Animal cells
http//www.stchs.org/science/courses/sbioa/metener
gy/bloodcells.gif
89
Osmosis in Red Blood Cells
Isotonic
Hypertonic
Hypotonic
90
Plant cells
http//www.stchs.org/science/courses/sbioa/metener
gy/aplantturgor.gif
CELL WALL
_____ keeps Plant cells from bursting
91
VACUOLES store WATER
http//www.biology4kids.com/files/cell_vacuole.htm
l
OSMOTIC PRESSURE
_____________________________ Pressure exerted
by water during osmosis
92
SO WHAT?
Bath water is ________________ compared to you
hypotonic
- Sitting in the bathtub causes your fingers and
toes to wrinkle up when water ________ your skin
cells by osmosis
enters
93
Grocery stores spray water on their veggies to
plump them up
- http//www.painetworks.com/photos/gt/gt0461.JPG
94
SO WHAT?