Presentazione di PowerPoint - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 30
Title:
Presentazione di PowerPoint
Description:
There are wide disagreements in the literature about the 'ideal' geriatric ... Nursing care and physiotherapy services did not differ. ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:21
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Presentazione di PowerPoint
1
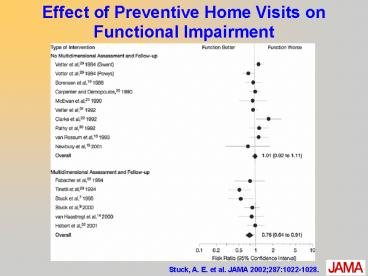
Effect of Preventive Home Visits on Functional
Impairment
Stuck, A. E. et al. JAMA 20022871022-1028.
2
CGA Instruments ?
3
Limits of the traditional assessment instruments
- Descriptive
- No etiology available
- Assessment of a single area
- Individual assembly
- Difficulties in comparisons
4
Second generation instruments
- Omni-comprehensive
- Underline causes and (make possible) etiological
diagnosis - Care planning oriented
- Comparisons
5
ITEM(s)
TRIGGER
PROBLEM IDENTIFICATION and UNDERLYING CAUSES
CARE PLANNING
6
Background There are wide disagreements in the
literature about the ideal geriatric assessment
instrument, despite the shared knowledge of the
relevance of comprehensive geriatric assessment
(CGA) as the core element to attain results.
There are no evidences available about the
cost-effectiveness of different instruments
JAGS 2001491288-1293
7
Bergamo Project
Objectives To test the effectiveness in
standardized home care programs with case
management of the Minimum Data Set for Home
Care (MDS-HC). We wanted to establish whether
such an innovative assessment system would be
able to reduce disability and health care costs
in older disabled patients. In this randomized
controlled trial with 1-year follow-up we
compared patients receiving MDS-HC, with controls
receiving conventional geriatric assessment by
means of the Barthel ADL index, the Instrumental
Activities of Daily Living (IADL) of Lawton and
Brody, and the Mini-Mental State Examination test
(MMSE).
8
Trial profile
Home Care BERGAMO District 1 95
patients District 2 92 patients
Randomisation District 1 and District 2
9
Baseline characteristics of subjects in the
intervention and control groups
At baseline, subjects in the intervention and
control groups did not differ across demographic
variables, clinical characteristics, and
functional measures.
10
Functional outcomes after 1-year follow-up in the
intervention and control groups
Differences between the IG and CG were
statistically significant for functional and
cognitive performance. The adjusted mean score of
ADL index was significantly improved in the IG
with respect to the CG. A similar trend was
observed for cognitive performance, as indicated
by the greater improvement of MMSE score in the
IG than in the CG.
11
Use of community services during 1-year follow-up
in the intervention and control groups
Nursing care and physiotherapy services did not
differ. Conversely, the intervention was
associated with a significant increase in the use
of in-home help services. No differences in the
number of home visits by general practitioners
was observed.
12
Hospital admission during 1-year follow-up in the
intervention and control groups
Fifteen percent of subjects in the intervention
group and 26 of those in the control group were
admitted at least once to acute hospital. The
relative risk of hospital admission was 0.49 (95
CI 0.56-0.97) for the intervention patients as
compared with control group. In addition, the
number of days spent in hospital was reduced in
the intervention group, both at the individual
patient-level and for each admission.
13
Results of survival analyses based upon time to
first hospital
Finally, we calculated total per capital health
care costs over the follow-up. The IG expenditure
was 21 less than the CG
14
Minimum Data Set
Make the physical exam complete Better care plan
Patient level
Comparisons
Outcome measurements
Population level
Database
Quality control indicators
Prognostic factors
15
Developing an evidence-base for community care
services in EuropeThe Aged Home Care project
ADHOC
Carpenter I et al, Aging Clin Exp Res 2004
16
AdHoc study
- 4007 subjects in Home Care in 11 European
countries - Age 65 years
- At each site subjects were selected by
computer-driven randomisation. - Data collected by the Minimum Data Set for Home
Care version 2.0.
17
Objectives
- Description and comparison of the characteristics
of patients in each European HC Service
18
Bernabei R et al International Gerontology in
Hazzards Principles of Geriatric Medicine and
Gerontology, Sixth Edition.
19
Bernabei R et al International Gerontology in
Hazzards Principles of Geriatric Medicine and
Gerontology, Sixth Edition.
20
Relationship between median dependency score
and median hours of all formal care by country
Carpenter I et al, Aging Clin Exp Res 2004
21
(No Transcript)
22
Objectives
- Description and comparison of the characteristics
of patients in each European HC Service - Identification at the patient-level and at the
system-level of the independent predictors of
positive or negative outcomes
23
Longitudinal analysis Pain and risk of
disability
- All sample RR (95 CI)
- No pain 1
- Pain less than daily 1.01 (0.74-1.39)
- Daily pain 1.36 (1.05-1.78)
- Men
- No pain 1
- Pain less than daily 1.21 (0.66-2.20)
- Daily pain 1.56 (0.89-2.74)
- Women
- No pain 1
- Pain less than daily 1.01 (0.70-1.47)
- Daily pain 1.40 (1.04-1.88)
Adjusted for age, gender, CPS, living alone,
site, number of medications, depression, cad,
hypertension, chf, pad, diabetes, arthritis,
COPD, stroke.
Onder G et al. Pain in press
24
Case manager and NH admission
Case Manager
No Case Manager
Log rank lt 0.001
Onder G et al. JAGS 2007
25
Objectives
- Description and comparison of the characteristics
of patients in each European HC Service - Identification at the patient-level and at the
system-level of the independent predictors of
positive or negative outcomes - Evaluation of quality control indicators in each
European HC Service.
26
Prevalence Quality Indicators
- Nutrition
- Inadequate Meals
- Weight Loss
- Dehydration
- Pain
- Disruptive/Intense Pain
- Unmanaged Pain
- Physical function
- No Assistive Device for Clients with Difficulty
in Locomotion - ADL/Rehabilitation Potential and No Therapies
- Psychosocial function
- Social Isolation with Distress
- Delirium
- Negative mood
- Medication
- No medication review
- Safety/Environment
- Falls
- Any injuries
- Neglect/Abuse
- Other
- No Influenza Vaccination
- Hospitalization
- Caregiver distress
27
Incidence Quality Indicators
- Psychosocial function
- Failure to improve/ incidence of cognitive
decline - Failure to improve/ incidence of difficulty in
communication - Other
- Increased health instability
- Incontinence
- Failure to improve/ incidence of bladder
continence - Ulcers
- Failure to improve/ incidence of skin ulcers
- Physical function
- Failure to improve/ incidence of decline in ADL
- Failure to improve/ incidence of impaired
locomotion in the home
28
Prevalence of Potentially Inappropriate
Medication Use Considering All Explicit Criteria
Combined (Beers 1997, Beers 2003, and McLeod
1997)
Fialova, D. et al. JAMA 2005
29
Prevalence of vaccination
vaccination
Landi, F. et al Vaccine 2005
30
Prevalence of pain by country
Onder G et al. J Clin Psychiatry 2005