Cellular Respiration, Photosynthesis, - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 7
Title:
Cellular Respiration, Photosynthesis,
Description:
Cellular Respiration, Photosynthesis, & Plants I. Cellular Respiration Cellular Respiration the process that releases energy by breaking down glucose & other food – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:172
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Cellular Respiration, Photosynthesis,
1
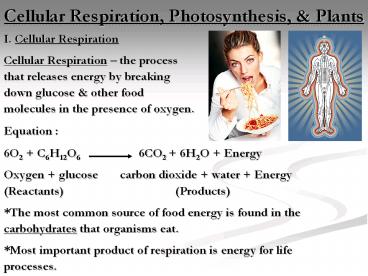
Cellular Respiration, Photosynthesis, Plants
- I. Cellular Respiration
- Cellular Respiration the process
- that releases energy by breaking
- down glucose other food
- molecules in the presence of oxygen.
- Equation
- 6O2 C6H12O6 6CO2 6H2O
Energy - Oxygen glucose carbon dioxide water
Energy - (Reactants) (Products)
- The most common source of food energy is found
in the - carbohydrates that organisms eat.
- Most important product of respiration is energy
for life - processes.
2
Cellular Respiration occurs in 3 steps
- 1. Glycolysis process in which 1
- molecule of glucose is broken in half,
producing 2 molecules of pyruvic acid, a 3-carbon
compound. - -End result of glycolysis is 4 ATP
- molecules.
- ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
- main energy-storing molecule
- used by organisms.
- -In the absence of oxygen,
- glycolysis is followed by
- fermentation production of
- ATP without oxygen (anaerobic
- respiration).
3
2 Main types of fermentation
- A. Alcoholic fermentation produces alcohol
CO2 (bread) as wastes. - B. Lactic acid fermentation produces lactic
acid that builds - up in muscle.
- -Happens when the body cant supply
- enough oxygen to the tissues-
- muscles fatigue, ache, or burn.
- -The last 2 steps of cellular respiration
- are aerobic (need oxygen to happen).
- -Oxygens role in cellular respiration
- is to act as the final hydrogen
- (electron) acceptor in the reaction.
4
The Krebs Cycle
- 2. The Krebs cycle process by which pyruvic
acid is broken down into carbon dioxide. - -The Krebs cycle generates
- high-energy electrons that are
- passed to NADH FADH2.
- -The energy stored in NADH
- FADH2 hydrogen bonds
- are transferred to ATP
- phosphate bonds in the
- electron transport chain.
5
Electron Transport Chain
- 3. Electron transport chain
- series of proteins in which
- high-energy electrons are
- used to convert ADP into
- ATP.
- Most ATP produced by
- cellular respiration is
- formed here.
6
II. Photosynthesis
- Photosynthesis process by which
- plants use the energy of sunlight to
- convert water carbon dioxide into
- carbohydrates (sugar starches)
- oxygen. Equation
- (Light energy)
- 6CO2 6H2O
C6H12O6 6O2 - (Reactants)
(Products) - (Light energy)
- Carbon dioxide water
sugar oxygen - -The most important product of the reaction,
glucose (an - organic molecule), is used by plants to store
energy for the - production of ATP. No glucose no energy for
cells.
7
Photosynthesis happens in 2 stages
- 1. Light-dependent reactions that
- produce oxygen, ATP, NADPH.
- 2. The Calvin cycle that produces sugars
(C6H12O6). - -The separation of carbon from
- carbon dioxide (carbon fixation)
- occurs in the Calvin cycle.
- -The major photosynthetic pigment,
- chlorophyll is needed by plants in
- order to do photosynthesis.
- -Chlorophyll doesnt absorb green
- light, it reflects it. Plants appear to be
- green in color but do not use the green
- wavelength of light for photosynthesis.