Circulatory System - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Circulatory System
Description:
Circulatory System & Respiration System By: Jordan Monfort, April Quijano & Christopher Siess – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:232
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Circulatory System
1
Circulatory System Respiration System
- By Jordan Monfort, April Quijano Christopher
Siess
2
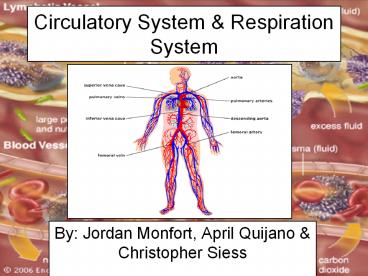
Circulatory System
- Circulatory system is responsible for
transporting materials throughout the entire
body. It transports nutrients, water, and oxygen
to your billions of body cells and carries away
wastes such as carbon dioxide that body cells
produce. It is an amazing highway that travels
through your entire body connecting all your body
cells. - The Circulatory System is divided into three
major parts - The Heart
- The Blood
- The Blood Vessels
3
The Heart
- The heart is located roughly in the center of the
chest cavity. It is covered by a protective
membrane, the pericardium. - It's job is to pump your blood and keep the blood
moving throughout your body.
- Deoxygenated blood enters the right atrium of the
heart through the superior vena cava. - The right atrium contracts and pushes the blood
cells through the tricuspid valve into the right
ventricle. - The right ventricle then contracts and pushes the
blood through the pulmonary valve into the
pulmonary artery, which brings it to the lungs. - In the lungs, the blood cells exchange carbon
dioxide for oxygen. This oxygenated blood returns
to the heart by way of the pulmonary vein and
enters the left atrium. - The left atrium contracts and pumps the blood
through the mitral valve into the left ventricle.
Then, the left ventricle contracts and pushes the
blood into the aorta. - The aorta branches off into several different
arteries that pump the oxygenated blood to
various parts of the body.
4
The Blood
- The heart pumps blood which is consisting of red
blood cells, white blood cells, platelets and
plasma
- Red Blood Cells
- - Red Blood Cells are responsible for carrying
oxygen and carbon dioxide. Red Blood Cells pick
up oxygen in the lungs and transport it to all
the body cells. After delivering the oxygen to
the cells it gathers up the carbon dioxide and
transports carbon dioxide back to the lungs where
it is removed from the body when we exhale - White Blood Cells
- - White Blood Cells help the body fight off
germs. White Blood Cells attack and destroy germs
when they enter the body. When you have an
infection your body will produce more White Blood
Cells to help fight an infection. Platelets are
blood cells that help stop bleeding
- Platelets
- - the platelets start to stick to the opening of
the damaged blood vessels. As the platelets stick
to the opening of the damaged vessel they attract
more platelets, fibers and other blood cells to
help form a plug to seal the broken blood vessel.
When the platelet plug is completely formed the
wound stops bleeding - Plasma
- - Plasma is the liquid part of the blood.
Approximately half of your blood is made of
plasma. The plasma carries the blood cells and
other components throughout the body. Plasma is
made in the liver.
5
The Blood Vessels
- The blood is pump through tubes known as blood
vessels. There are three types of blood vessels
arteries, capillaries and veins
- Arteries
- - Arteries are blood vessels that carry oxygen
rich blood away from the heart. It has three
layers of thick walls. - Veins
- - Veins carry blood back toward your heart.
- Capillaries
- - Capillaries are tiny blood vessels as thin or
thinner than the hairs on your head. Capillaries
connect arteries to veins. Food substances,
oxygen and wastes pass in and out of your blood
through the capillary walls.
6
Respiration System
- The main purpose is to supply the blood with
oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen
to all parts of the body. - The mouth, nose, trachea, lungs, and diaphragm
are used in Respiration.
- Nose and Mouth - Oxygen enters the respiratory
system. - Trachea - is a tube that enters the chest cavity.
In the chest cavity, the trachea splits into two
smaller tubes called the bronchi. Each bronchus
then divides again forming the bronchial tubes. - Lungs - The bronchial tubes lead directly into
the lungs where they divide into many smaller
tubes which connect to tiny sacs called alveoli.
The inhaled oxygen passes into the alveoli and
then diffuses through the capillaries into the
arterial blood. Meanwhile, the waste-rich blood
from the veins releases its carbon dioxide into
the alveoli. - Diaphragm - help pump the carbon dioxide out of
the lungs and pull the oxygen into the lungs. The
diaphragm is a sheet of muscles that lies across
the bottom of the chest cavity. As the diaphragm
contracts and relaxes, breathing takes place.
When the diaphragm contracts, oxygen is pulled
into the lungs. When the diaphragm relaxes,
carbon dioxide is pumped out of the lungs.
7
Feedback
- Homeostasis is the maintenance of a stable
internal environment. Homeostasis is a term
coined in 1959 to describe the physical and
chemical parameters that an organism must
maintain to allow proper functioning of its
component cells, tissues, organs, and organ
systems. - For example, when a person is exercising the
body needs more oxygen as an result the heart
beats faster and the person breathes faster and
harder in order to meet the body oxygen demands. - Classic negative feedback
- If there is drop in Red Blood Cell (RBC) count
causes hypoxemia to kidneys - Erythropoietin production increases
- stimulation of bone marrow
- RBC count increases in 3-4 days
- Classic Positive feedback
- - The plugging or sealing of damaged vessels
by the platelets
8
Now, that you know the importance of the
circulatory and respiratory system, do these
three activities on the circulatory and
respiratory system!
Circulatory and Respiratory System Activity 1
Circulation
9
- Situation
- A single working mother of 4 has
mysteriously gotten ill. So thinking it is a
minor common cold or flu, she takes the day off
to go see her doctor. Her doctor can not figure
out what is the cause of her ill so she is sent
home for some rest. However, later that night,
she is awaken to the fact that she is spiting a
large quantity of blood. Highly alarm she is take
to your hospital. While testing her blood it was
realized that her blood platelet levels are low.
10
- Task
- You are the world leading diagnostician and
you have been presented with one of your toughest
class ever. - Find what disease is making her sick.
- What is the primary treatment for her disease?
- Use these links to help you find what you are
looking for - http//www.diagnose-me.com/cond/C271923.html
- http//www.riversideonline.com/health_reference/Di
sease-Conditions/DS00691.cfm - http//www.netdoctor.co.uk/diseases/facts/ttp.htm
11
Your not out of the woods yet. SUDDENLY!!! Your
patient is having an allergic reaction to your
primary treatment.
- What would be your next step into curing this
disease ? - Hint
- It is a commonly used on patients with this
dangerously 20th century disease. About 1.2
million people get diagnosed with this disease a
year.
12
Circulatory and Respiratory System Activity 2
Respiration
Now, Its time to work on the Respiratory System
13
- As you know, the lungs of the human respiratory
system takes in oxygen from the area surrounding
us and takes out carbon dioxide from our bodies.
This process is something called gas exchange. - People mostly think our lungs only work in air,
but it doesnt seem to be the case!
14
- In an anime called Neon Genesis Evangelion, mech
pilots have to breathe in liquid in the cockpit. - This is similar to some process called
- Liquid breathing.
15
- Your mission is, by these three links Ive given
you, found out all about what the process is in
real life! - Liquid Beathing Page from Bristol University's
School of Chemistry - Liquid Breathing page from BSAC
- Article at Skyaid.org
16
Cardiovascular Respiratory Activity 3
Circulation Respiration
Now, Let put all your detective work
together!!!!!!
17
Situation-
You are a doctor at a free clinic. A man is
brought in late at night With a bullet wound in
his chest, Below the right nipple and above the
diaphragm. There is no exit wound. You suspect
that the bullet punctured the lung and is still
in the body.
Tasks -
What steps do you take?
- Using these links to help your complete your
tasks good luck - http//www.steinergraphics.com/surgical/006_18.9.h
tml - http//www.med.umich.edu/1libr/aha/aha_irthor_crs.
htm - http//www.chestjournal.org/cgi/content/full/115/4
/1210
18
References
- Anatomy of the Human Circulatory System.
Circulatory System. April 30, 2008 from
http//users.rcn.com/jkimball.ma.ultranet/BiologyP
ages/C/Circulation.html - Blood Circulation. Circulator System. April 30,
2008 from http//www.marymount.k12.ny.us/marynet/s
twbwk03/03bio/Circulatory/CHpage.html - Body Systems. The Human Heart. April 30, 2008
from http//fi.edu/learn/heart/systems/respiration
.html - Circulation System. Hillendale Health Curriculum.
April 30, 2008 from http//hes.ucfsd.org/gclaypo/c
irculatorysys.html - Homeostasis. Animal Organ Systems. April 30, 2008
from http//www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/B
IOBK/BioBookANIMORGSYS.html - Review 2. Biology 112. April 30, 2008 from
http//www.bio.davidson.edu/courses/bio112/112cp/r
ev2prack.html