AKS 44: Industrialization, Nationalism, and Imperialism - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 37
Title:
AKS 44: Industrialization, Nationalism, and Imperialism
Description:
Policy of Realpolitik: Tough power politics - no idealism. Issues not decided by resolutions, but by 'blood and iron' ... Seven Weeks' War (1866) Bismarck ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:179
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: AKS 44: Industrialization, Nationalism, and Imperialism
1
(No Transcript)
2
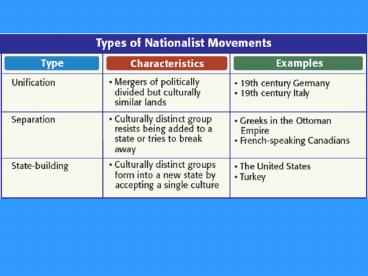
NationalismUnification of Germany
- Led by Prussia
- Otto von Bismarck Prime Minister under Wilhelm
I - Policy of Realpolitik
- Tough power politics - no idealism
- Issues not decided by resolutions, but by blood
and iron - Allowed him to expand Prussia achieve dominance
3
GermanySeven Weeks War (1866)
- Bismarck provoked Austria to declare war on
Prussia - Prussia (superior training equipment)
humiliated Austria - Austrians lost Venetia given to Italy
- Had to accept Prussian annexation of more German
territory - Prussia took control of N. Germany for 1st
time, E W Prussia joined
4
GermanyFranco-Prussian War (1870-1871)
- Bismarck manufactured incident that caused
France to declare war on Prussia - Final stage in German unification
- S. Germans (Catholic) accepted Prussian
(Protestant) leadership - King Wilhelm I crowned Kaiser emperor
- Called empire Second Reich (HRE was the 1st)
- Bismarck achieved Prussian dominance by blood
and iron
5
NationalismUnification of Italy
- Led by Sardinia
- Camillo di Cavour Prime Minister under Victor
Emmanuel II - Worked to expand Sardinian Empire
- Succeeded through war, alliances, help of
nationalist rebels - Unified Italy in process
6
Germany Italy - Similarities
- Leaders were aristocrats
- Nations united by nationalism
- One state led unification
7
JapanModernization Pays Off for Japan
- By 1890, Japan had
- Several dozen warships
- 500,000 well-trained, well-armed soldiers
- Became strongest military power in Asia
8
JapanJapan Gains Western Favor as a Nation-State
- Constitution legal codes similar to European
nations - Wanted to eliminate extraterritorial rights of
foreigners - 1894 foreign powers accepted it
- Strength feeling of equality rose
- Became more imperialistic
9
Reaction to Foreign DominationRusso-Japanese War
(1904-1905)
- Causes
- Russia refused to stay out of Korea
- Japanese led surprise attack on Russian navy
anchored off coast of Manchuria
10
Reaction to Foreign DominationRusso-Japanese War
(1904-1905)
- Results
- Destruction of Russian navy
- Territorial gains for Japan
- Withdrawal of Russia from Manchuria Korea
11
Reaction to Foreign DominationYoung Turks
- Progressive group that believed in liberalism,
constitutionalism, materialism, centralized
government, and nationalism - Opposed imperialism
- Impact
- Tradition of dissent shaped political and
intellectual life in late Ottoman period - State was instrument for social/political change
- Ideals helped form early modern Turkish state
12
Forces of ImperialismMotives
- Economic competition for markets raw materials
- National pride
- Racism
- Missionaries' desire to Christianize civilize
non-European peoples
13
Forces of ImperialismTechnological Advantages
over Africa
- Superior weapons
- Railroads, cables, steamships
- Quinine (drug) to protect from malaria
14
Forces of ImperialismFactors Making Africa
Vulnerable
- Africans great diversity of languages and
cultures - Ethnic rivalries
- Lower level of technology, including weapons
15
Division of AfricaBerlin Conference of 1884
1885
- Agreement among 14 European nations about how to
divide Africa among European countries - Outcomes
- Random distribution of African ethnic
linguistic groups among European nations - Transformation of the way of life of Africans
16
(No Transcript)
17
From Cairo to Cape Town
18
Division of AfricaClash in South Africa
- Zulus
- Shaka created large centralized state
- Successors unable to keep together against
British superior arms British invaded 1879 - Fell to British control in 1887
- Boers (Dutch) a.k.a. Afrikaners
- 1st Europeans to settle in S. Africa
- British
- Took over Cape Colony in early 1800s clashed
with Boers over British policy regarding land
slaves
19
Division of AfricaBoer War (1899-1910)
- Diamonds/gold discovered in 1860s 1880s
- Boers launched commando raids used guerilla
tactics - British burned farms imprisoned women
children - Britain finally won
- Outcome
- Creation of self-governing Union of South Africa
controlled by British
20
French Control of IndochinaHow Brought Under
Control
- Missionaries were killed
- French army invaded Vietnam
- Combined it with Laos and Cambodia
21
French Control of IndochinaMethod of Control
- Direct control
- French themselves filled all important positions
in govt
22
French Control of IndochinaEconomic Policies
- Discouraged local industry
- Rice became major export crop
23
French Control of IndochinaColonial Impact
- Imposed French culture
- All schools, courts, businesses followed French
models - ? of local industries
- Less food for peasants
24
Japanese in AsiaWar with China (Sino-Japanese
War) (1894-1895)
- How it started
- Rebellion broke out against Koreas king, who
asked China for military help - Chinese troops marched into Korea
- Japan protested violation of agreement sent its
troops to fight the Chinese - Consequences
- Destruction of Chinese navy
- Beginning of Japanese colonial empire
- Change to worlds balance of power
- Emergence of Russia Japan as major powers (
enemies) in Asia
25
Japanese in AsiaOccupation of Korea
- Annexed Korea brought under control
- Ruled Korea harshly
- Established very repressive govt that denied
rights to Korea - Inspired Korean nationalist movement
26
Interaction with WesternersOpium War (China)
- Setting the Stage
- China self-sufficient, little trade w/ west ?
favorable balance of trade - Europeans wanted to find product Chinese would
buy in large quantities ? found it in opium - Many Chinese became addicted
27
Interaction with WesternersOpium War (China)
- Causes
- Chinese emperor wanted trade stopped ? Britain
refused to stop
28
Interaction with WesternersOpium War (China)
- Results Effects
- Chinese defeat humiliation
- Cession of Hong Kong to Britain
- Continuation of opium trade
- Extraterritorial rights for foreign citizens
- Chinese resentment against foreigners
29
Interaction with WesternersTaiping Rebellion
(China)
- Setting the Stage
- Population provided major challenge growing 30
in only 60 years
30
Interaction with WesternersTaiping Rebellion
(China)
- Causes
- Hunger/starvation caused by inability to feed
enormous population - Increasing opium addiction
- Poverty
31
Interaction with WesternersTaiping Rebellion
(China)
- Results Effects
- Rebellion put down
- Restoration of Qing to power (with help of
British and French forces) - 20 million people died
32
Interaction with WesternersCommodore Matthew
Perry (Japan)
- Perry Arrives in Tokyo
- Arrives with letter from U.S. President Fillmore
- Letter politely asked shogun to allow free trade
- Perry gave threat that he would return with
larger fleet in one year to get Japanese reply - Purpose shock frighten Japanese into accepting
trade with U.S.
33
Interaction with WesternersCommodore Matthew
Perry (Japan)
- Treaty of Kanagawa (1854)
- Japan opened two ports where ships could take
supplies
34
Interaction with WesternersCommodore Matthew
Perry (Japan)
- Benefits to U.S.A.
- Gained rights to trade at those two ports
- Opened door for other W powers
35
Effects of ImperialismColonization
- Europeans control land and people in areas of
Africa, Asia, and Latin America
36
Effects of ImperialismColonial Economics
- Europeans control trade in the colonies and set
up dependent cash-crop economies
37
Effects of ImperialismChristianization
- Christianity is spread to Africa, India, and Asia