Prsentation PowerPoint - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 1
Title:
Prsentation PowerPoint
Description:
The Sub-Millimetre Radiometer (SMR) on board the Odin satellite, launched in ... Measurements are performed in a time sharing mode with astronomical observations. ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:73
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Prsentation PowerPoint
1
- Potential of the Odin Sub-Millimetre Radiometer
for the Study of - Stratospheric Water Vapour and its Isotopes
- J. Urban (1), N. Lautié (2), D. Murtagh (2), Y.
Kasai (3), J. de La Noë (1), E. Dupuy (1), L. El
Amraoui (1), - P. Eriksson (2), U. Frisk (4), C. Jimenez (1), E.
Le Flochmoën (1), M. Olberg (5), and P. Ricaud
(1) - (1) Observatoire Aquitain des Sciences de
lUnivers / L3AB, Floirac, France (2) Chalmers
University of Technology, Göteborg, Sweden - (3) Communications Research Laboratory, Tokyo,
Japan (4) Swedish Space Corporation, Solna,
Sweden - Contact urban_at_obs.u-bordeaux1.fr
(5) Onsala Space Observatory, Onsala,
Sweden.
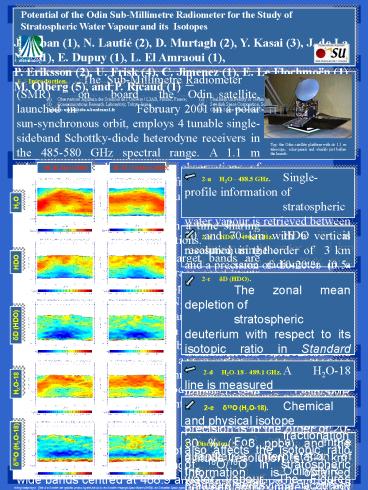
1 Introduction. The Sub-Millimetre
Radiometer (SMR) on board the Odin
satellite, launched in February 2001 in
a polar sun-synchronous orbit, employs 4 tunable
single-sideband Schottky-diode heterodyne
receivers in the 485-580 GHz spectral range. A
1.1 m telescope is used for passive observations
of thermal emissions originating from the
Earths limb. Spectra are recorded using two high
resolution auto-correlator spectrometers.
Measurements are performed in a time sharing mode
with astronomical observations. In aeronomy
mode, various target bands are dedicated to
observations of trace constituents relevant to
stratospheric / mesospheric chemistry and
dynamics such as O3, ClO, N2O, HNO3, H2O, CO, and
isotopes of H2O and O3. Profile information is
retrieved from the spectral measurements of a
limb scan by inverting the radiative transfer
equation for a non-scattering atmosphere. A
retrieval algorithm based on the Optimal
Estimation Method has beenadopted for the
ground segments of Odin-SMR in Sweden and in
France. The water isotope mode is specifically
designed for observations of stratospheric H2O,
H2O-18, and HDO using two 800MHz wide bands
centred at 488.9 and 490.4 GHz. Achieved
observation capabilities of the SMR radiometer
for these target species are presented and
examples for the global water vapour data set
are given.
Top the Odin satellite platform with its 1.1 m
telescope, solar-panels and -shields just before
the launch.
29-30 April 2002
26-27 October 2002
2-a H2O - 488.5 GHz. Single-profile
information of stratospheric water vapour is
retrieved between 20 and 70 km with a vertical
resolution in the order of 3 km and a precision
of 10-20 (0.5-1 ppmv). Measurement noise
might be reduced by data averaging. The Figures
show for example zonally averaged water vapour
fields as observed by Odin/SMR on April 29-30 and
Octobre 26-27, 2002. Odin/SMR water isotope mode
measurements are performed in about weekly
intervals.
H2O
2-b HDO - 490.6 GHz. HDO is
measured using the same radiometer in a time
shared mode during roughly half of the 15 orbits
per measurement day, each orbit corresponding to
about 60 individual limb-scans. The measurement
precision for HDO is about 20-30 (?5 ppbv), and
single-profile information is obtained between
18-55 km with an altitude resolution in the order
of 3-4 km.
HDO
2-c dD (HDO). The zonal mean
depletion of stratospheric deuterium with
respect to its isotopic ratio in Standard Mean
Ocean Water (SMOW) of 1.557610-4 can be derived
from the Odin/SMR measurements of H2O and HDO.
This variation is usually expressed using
d-notation dD (2HDO/H2O - R0) / R0 100
, where R0 is a standard isotope ratio (e.g.
SMOW). The Figures show preliminary results
obtained for April 29-30 and October 26-27,
2002. A maximum depletion in the order of 60 is
observed in the lower stratosphere of the tropics
and dD increases with altitude above. Results
are in qualitative agreement with 1-d and 2-d
model calculations e.g. Ridal, JGR, 2001
Bechtel Zahn, ACPD, 2003 simulating dD as
function of the relative contributions of the
different sources of stratospheric water vapour
such as methane oxidation and transport through
the tropical tropopause.
dD (HDO)
2-d H2O-18 - 489.1 GHz. A H2O-18
line is measured simultaneously with H2O. The
single-profile precision is in the order of 20-30
(? 3 ppbv) and the altitude resolution is 3-4
km. Information is obtained between approximately
20 and 60 km.
H2O-18
2-e d18O (H2O-18). Chemical and
physical isotope fractionation also affects
the isotopic ratio of 18O/16O in stratospheric
water vapour. The Figures show observed zonal
mean variations of d18O (H2O-18/H2O-16 -
R0) / R0 100 .
- Discussion. For a more quantitative
interpretation of the Odin/SMR measurements,
the accuracy of the H2O, HDO, and H2O-18 data
has to be determined, which is a function of
various instrumental (calibration accuracy,
antenna and sideband suppression knowledge) and
spectroscopic uncertainties. Most critical
spectroscopic errors are for example the pressure
broadening parameters of the target lines, which
will have to be determined by laboratory
experiments.
d18O (H2O-18)
Acknowledgements Odin is a Swedish-led satellite
project funded jointly by the Swedish National
Space Board (SNSB), the Canadian Space Agency
(CSA), the National Technology Agency of Finland
(Tekes) and the French Centre National dÉtudes
Spatiales (CNES).