Pinocytosis PowerPoint PPT Presentations
All Time
Recommended
phagocytosis = Ingesting large molecules pinocytosis = Ingesting large amounts of a fluid Draw endocytosis: Exocytosis- Active Transport The opposite of endocytosis.
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
* The Pathway of Protein Synthesis Figure 3.10 * Lysosomes Vesicles within the cytoplasm which contain ... pinocytosis or autophagy. Autophagy (self-eating) ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
These are the storage sacs of the cell membrane. Vesicles are smaller and are formed by pinocytosis (cell drinking) usually made by Golgi body or from infoldings ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Chapter 29: Heredity I Clicker Question The process by which liquid-containing vesicles are expelled out of a cell is called A) pinocytosis. B) phagocytosis.
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
active and passive transport. What is the difference between active and passive transport? ... Pinocytosis- moves fluid into the cell. ( cell drinking) ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Transport of Golgi, lysosomes. Endo/exo/pinocytosis. Polarization. Gastrulation. Cell motility ... Myosin V An Atypical Myosin Motor ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Phenomena Created Due to Osmosis. Turgor Pressure ... reverse pinocytosis = reverse phagocytosis. Endocytosis in animal cells. VII. ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Chapter 7 Membrane Structure & Function Movement of LARGE molecules Animation-05-03.swf Phagocytosis & Pinocytosis Phagocytosis cell membrane wraps around and ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Cell structure, genetic control, and life cycle Movement of molecules into cells Through membrane Phagocytosis Endocytosis/pinocytosis Exocytosis/secretion Receptor ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
3 types of proteins found associated with cell membrane... Channel Proteins form physical pathway through ... pinocytosis (cell drinker)- brings in liquids ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
The ability of an organism or cell to maintain internal balance and stability by ... Pinches off into a vacuole. Pinocytosis- Cell drinking. Phagocytosis- Cell eating ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to ... Pinocytosis: take in solutes or fluids. Phagocytosis: take in large particles or whole cells. ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Forms vacuoles 'cell eating' Pinocytosis. The engulfed material is ... In plant cells, the central vacuole loses water and the cells shrink, causing wilting. ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Substance moves across a membrane by binding to ... Phagocytosis: solid particles ingested into cell by vesicles. Endocytosis. Phagocytosis. Pinocytosis ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
5-2 Active Transport The movement of materials against a concentration gradient. (requires energy) Carrier Proteins are involved in passive transport and Active ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Passive Transport From high to low concenration Does not require energy from the cell Diffusion Osmosis Facilitated diffusion Active transport is an energy-requiring ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Microcirculation: control of exchange with tissues
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
... hydrophobic molecules move through. Ions, hydrophilic molecules larger than water, and large molecules such as proteins do not move through the membrane on their ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
SC.912.L.14.2 How does something as thin as a cell wall or membrane protect a cell? Among the most important parts of a cell are its borders, which separate the cell ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
... OR large quantities need to pass through the cell These situations use vesicle transport Two kinds Endocytosis Exocytosis Endocytosis Cells ingest external ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Occurs continuously and in almost all cells EXOCYTOSIS Many cells also release large amounts of material from the cell.
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Passive and Active Transport Passive Transport Cell membranes help organisms maintain Homeostasis by controlling what substances may enter or leave cells Doing this ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Title: Plasma Membrane Author: Biology Computer User Last modified by: Teacher Created Date: 1/21/2001 11:07:55 PM Document presentation format: On-screen Show (4:3)
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Title: LE 01-10b Author: System_70 Created Date: 12/12/2005 9:42:59 PM Document presentation format: On-screen Show (4:3) Company: PIT Other titles
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Cell Membrane & Cell Transport
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
PASSIVE VS ACTIVE TRANSPORT PASSIVE TRANSPORT Requires no energy input from the cell Goes WITH the concentration gradient Usually small, uncharged particles ACTIVE ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
its an important topic of transporting required necessory substances through cell membrane for cell survival , a little lfe but complex and important when combine to form tissue organ ans complex human being
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Movement of Materials Through the Cell Membrane all cells are found in a liquid environment because it makes it easier for materials such as food , oxygen, and ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Cell Transport: The Plasma Membrane The Gateway to the Cell Photograph of a Cell Membrane Cell Membrane The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Passive transport~ diffusion of a substance across a biological membrane ... Turgid (very firm) Flaccid (limp) Plasmolysis~ plasma membrane pulls away from cell wall ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Homeostasis and Cell Transport Chapter 5 Homeostasis The steady-state physiological condition of the cell or body. Cellular Transport Passive Transport Diffusion The ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Membrane Chapter 7
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
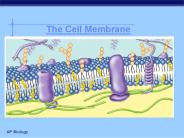
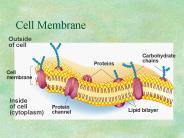
Cell Membrane Outside of cell Carbohydrate chains Proteins Cell membrane Inside of cell (cytoplasm) Protein channel Lipid bilayer
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Cell Membrane Outside of cell Carbohydrate chains Proteins Cell membrane Inside of cell (cytoplasm) Protein channel Lipid bilayer
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
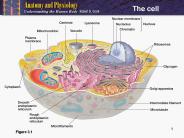
Cellular Transport Chapter 8 The detailed structure of an animal cell s plasma membrane The fluidity of membranes Some functions of membrane proteins Cells move ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
bio. 1300/1400/2393/3393 the cell cell membrane fluid mosaic model semipermeable contains phospholipids contains numerous proteins transport proteins enzymes channel ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Title: 1 Author: wit Last modified by: for Home Used Only Created Date: 9/4/2006 12:02:46 AM Document presentation format ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Pharmokinetics CHAPTER 3 - 2 Dr. Dipa Brahmbhatt VMD MpH dbrahmbhatt@vettechinstitute.edu
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Trilaminar structure thought to correspond to staining of phospholipid bilayer (See 2.2b) ... Barrier nonpolar tails - hydrophobic. Receptors glycoproteins ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Pharmacokinetics CHAPTER 4 L. VanValkenburg, RVT, BAS
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Pharmacokinetics CHAPTER 4 L. VanValkenburg, RVT, BAS Drug Elimination Terminology Drug residue: amount of drug that can be detected in tissues after administration ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
SV40 binding) in a cholesterol- and dynamin-dependent fashion ... Emerging theme: involves detergent-resistant membranes/ lipid rafts. Lipid rafts ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Endocytosis: Process in which the plasma membrane takes in substances (2 types) ... Amoeba and endocytosis. Endocytosis & the lysosome. Exocytosis ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Membrane Structure and Function Facilitated diffusion Transport proteins ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
moving upstream against the concentration gradient. B) Moving the ... Requires energy or ATP. Moves solutes from LOW to ... UPHILL. Called Na -K Pump. 6 ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Concentration gradient. Passive transport~ diffusion of a substance across a biological membrane ... proteins across a membrane down the concentration gradient ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Chapter 7 and 11 Membrane Strunction Fluid Mosaic Model Fluidity: P.Membrane (PM) held together by weak hydrophobic interactions Lateral drifting ability Lipids ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Title: PowerPoint Presentation Author: PYLUSD Last modified by: custom Created Date: 10/14/2004 4:29:11 AM Document presentation format: On-screen Show
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Transport Flip n Go
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Integral Membrane Proteins penetrate the core of the lipid bilayer ... Turgid (normal) H2O. H2O. H2O. H2O. Normal. Isotonic solution. Flaccid. H2O. H2O. Shriveled ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Movement of materials against the concentration gradient. Requires a cell to ... http://www.rpi.edu/dept/bcbp/molbiochem/MBWeb/mb1/part2/images/carrier.gif ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Homeostasis and cell transport Biology class Pg 96-111 A macrophage consuming a fungal spore shows off modo's subsurface Biology Chapter 7.3 * Biology- chapter 5 ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Title: Endocytosis - Exocytosis Author: Genetikai Int zet Last modified by: K hidai L szl Created Date: 10/5/2001 10:28:52 AM Document presentation format
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
IX. Plasma Membrane A. Fluid Mosaic Model B. Cell Transport 1. Singer & Nicolson, 1972 2. Plasma membrane is a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view