The Plasma Membrane - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
The Plasma Membrane
Description:
... hydrophobic molecules move through. Ions, hydrophilic molecules larger than water, and large molecules such as proteins do not move through the membrane on their ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:142
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: The Plasma Membrane
1
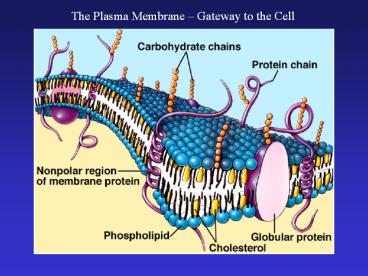
The Plasma Membrane Gateway to the Cell
2
The Plasma Membrane is Semipermeable
Small molecules and larger hydrophobic molecules
move through.
Ions, hydrophilic molecules larger than water,
and large molecules such as proteins do not move
through the membrane on their own.
3
Plasma Membrane Functions
Maintain a high concentration of materials in the
cell.
Keep harmful materials out.
Control the movement of materials into and out of
the cell.
Let the cell sense its environment.
4
Membrane Components
Phospholipids
Proteins (peripheral and integral)
Cholesterol
Carbohydrates
5
Proteins Are Critical to Membrane Function
6
Transport Processes - Diffusion
Solutes move down a concentration gradient until
they are evenly distributed. This is diffusion.
Another way of saying this is that solutes move
from a region of higher concentration to a region
of lower concentration until there is no
difference in concentration.
7
Three Forms of Transport Across the Membrane
8
Three Forms of Transport Across the Membrane
Example Oxygen or water diffusing into a cell
and carbon dioxide diffusing out.
9
Three Forms of Transport Across the Membrane
Examples Glucose or amino acids moving from
blood into a cell.
An nerve electrical impulse results from opening
protein channels for ions that move by
facilitated diffusion.
10
Three Forms of Transport Across the Membrane
Examples Pumping Na (sodium ions) out and K
(potassium ions) in against strong concentration
gradients.
11
Moving the Big Stuff
Large molecules move in via one of three forms of
endocytosis.
12
Pinocytosis
This is the most common form of endocytosis.
Pinocytosis takes up most proteins and other
large molecules.
13
Pinocytosis
mature transport vesicle
pinocytic vesicles forming
Transport into a capillary cell (blue).
14
Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis
Receptor proteins make this a highly specific
form of transport.
Cholesterol is taken-up this way.
15
Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis
16
Cholesterol Delivered to Cells is Carried to
Cells in a Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL) Particle
The LDL particle is taken-up by receptor-mediated
endocytosis.
17
Endocytosis Phagocytosis Transports Large
Particles
18
In Preparation for Phagocytosis
19
The Threshold of Phagocytosis - Capture of a
Yeast Cell (yellow) by Membrane Extensions of an
Immune System Cell (blue)
20
Moving the Big Stuff
Exocytosis moving things out.
Molecules are moved out of the cell by vesicles
that fuse with the plasma membrane.
This is how many hormones are secreted and how
nerve cells communicate with one another.
21
Exocytosis
22
Exocytosis and Nervous System Function
A nerve cell communicates to another cell by
releasing chemicals via exocytosis at the
synaptic terminal.
23
Exocytosis and Chemical Communication at the
Synapse
The synapse is the region where a nerve cell and
its target cell are closely apposed.
24
Black Widow Spider Venom and Exocytosis
Black widow spider venom causes massive
exocytosis of neurotransmitter into the synapse.
25
Botulism and Exocytosis
Botulism is caused by botulinim toxin a protein
produced by a bacterium that sometimes
contaminates foods.
Botulinim toxin blocks exocytosis at the synapse
and causes paralysis.
Mechanism of botulinum toxin web site.