Cladistics PowerPoint PPT Presentations
All Time
Recommended
Human- 46 chromosomes Chimpanzee- 48 chromosomes Chimpanzees have 2 smaller chromosome pairs we don t have Humans have 1 larger chromosome pair (#2 ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Taxonomy and Cladistics How are organisms grouped and organized? Identifying, naming, and classifying species Why does everything need a scientific name?
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
In the 1600's, biology was changed forever by the discovery and refining of ... In the United States, we call both black vultures and turkey vultures buzzards. ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
IB Biology HL Why Classify? Identify connections between _____ and _____ organisms Identifying unknown organisms Understanding evolutionary relationships and the ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Cladistics and Molecular Systematics. Depicting evolutionary changes. Homology. Homoplasy ... Characters for Cladistics. Qualitative presence / absence ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Check out this cladogram! Quick Lab p 453 ... help estimate the length of time two species have been evolving independently. ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
DIVERSITY OF EARTH'S ORGANISMS (AND CLADISTICS) NEW MATRIX Characters Clam Shark Bluegill Salamander Iguana Alligator Crow Racoon Human Allosaurus Backbone 0 1 1 1 1 ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Parents pass information on to offspring; higher fitness strings are more likely ... to pass on 'useful' information. A simple example: Evolve a string that ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Cladistics - distinguishes ancestral from shared characters ... Cladistics ... Systematic phylogenetics is based on evolutionary relationships using cladistics. ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Phylogeny Systematics Hypothesis Cladistics Derived character Cladogram Dichotomous Key Order Family Genus Species Common name Scientific name Binomial
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
17.2 The Six Kingdoms Classification models Phylogeny evolutionary history Phylogenetic classification reflects evolutionary relationships Two models Cladistics ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Cladistics Pattern of systematics in which ... Cladistics. A true clade is a group with a single common ancestor. ... Cladistics. Other Cladistic Factors ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Phylogeny and Systematics Cladistics Analysis of phylogenetic relationships based on shared characters Characters may be primitive or derived Clade = Group of species ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Why is teaching taxonomy & cladistics so difficult? -the problems -the old way ... Linnean Hierarchy vs cladistics -Venn Diagrams ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
KEY CONCEPT Modern classification is based on evolutionary relationships. Cladistics is classification based on common ancestry. Phylogeny is the evolutionary history ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Phylogeny, the evolutionary history of an organism, ... There are three basic assumptions in cladistics: Organisms within a group are descended from a common ancestor.
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Evolutionary processes reflected in organismal phylogeny ... Cladistics. Analysis of phylogenetic relationships based on shared characters ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
The two major schools of classification are evolutionary systematics and cladistics. ... Cladistics is concerned with ancestral and derived characters. ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Chrysophyta (yellow), Rhodophyta (red), Phaeophyta (brown) ... cladistics described in the previous pages concludes that the eukaryotic algae ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
cladistics: study of evolutionary relationships based on an organism and. its descendents ... cladistics looks over time; phylogenetic tree looks at current organisms ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Phylogenetic systematics (Cladistics) Hennig (1960s-1970s) DNA sequences (1970s) ... THE SIMPLIFIED HISTORY OF SYSTEMATICS -Hillis, et al, 1996 ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
'A Likelihood Approach to Estimating Phylogeny from Discrete Morphological ... Based on cladistics, a method of hypothesizing relationships based on shared, ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Systematics Classifying organisms into groups Why classify? To create the fundamental database of the science Analogy - classification systems for rocks Big ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Chapter 25: Phylogeny and Systematics Fossils are preserved remnants of organisms that lived in the past Fossils form in sedimentary rock, the oldest fossils in the ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Dichotomous Key. A dichotomous key is a method for determining the identity of something by going through a series of choices that leads the user to the correct name ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Evolution and Systematics Chapter 18
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Taxonomy & Phylogeny Introduction Classification Phylogeny Cladograms Quiz Which of the following cladograms incorrectly illustrates sister groups? Question 12 Sorry!
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Classification Chapter 18(M) Classification/Taxonomy Classification the grouping of objects for practical purposes. Ex: Taxonomy the identification, naming and ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Taxonomy Reflects Evolutionary History Section 15.4 Classification/Taxonomy Classification the grouping of objects for practical purposes. Ex: Taxonomy the ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Some scientists may think one character is important, ... Scientists must look carefully at similar traits, ... Inferring Evolutionary Relatedness, ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Title: PowerPoint Presentation Author: McDougal Littell Last modified by: Jennifer McQuade Created Date: 9/14/2006 4:17:10 PM Document presentation format
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Title: Classification and Diversity Author: Preferred Customer Last modified by: Bashab Banerjee Created Date: 11/27/2006 12:44:38 AM Document presentation format
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Warm-Up 3/24 What is a derived characteristic? What is a clade? Circle a clade on the cladogram below. 18.2 Modern Evolutionary Classification 18.2 Modern ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
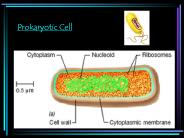
Prokaryotic Cell
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Towards a theoretical model for the evolution of manuscript ... Too many bifurcating trees (bifid stemmata) = unrealistic. Cerquiglini, 'Eloge de la variante' ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
It is an attempt by humans to organize living things into ... Cars, SUVs, Pick-ups. Taxonomy - Biological. Kingdom. Phylum. Class. Order. Family. Genus ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
CLASSIFICATION Why do you think scientists like to put organisms into groups, like mammals or insects? WHAT IS CLASSIFICATION? Classification is the arrangement of ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Organize knowledge of groups (filing system) 2. ... Grouping by unique characters and similar adaptation. Homology ... POLYPHYLETIC group(s) ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Chapter 18: The Tree Of Life
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
... Genus & species Leopard = Panthera pardus African Lion = Panthera leo Hierarchical classification system Taxon = a group at any level (plural,taxa ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Modern Taxonomy Reflects Evolutionary History Section 15.4 Taxonomy Identification, naming, & classification of species Common names don t always work well, because ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Biology EOC Review Evolution Evolution Explain biological evolution as the consequence of the interaction of population growth, inherited variability of offspring, a ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Evolution Geology 103 ... 1859) publishes his theory of organic evolution based on observations he had made on the voyage of the Beagle and other work.
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
What are the 6 Kingdoms of Organisms? What is a cladogram? What are the 5 ways we can determine evolutionary relationships? Archeabacteria, Eubacteria, Protists ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Tetrapoda clade 1 Amniota clade 2 Reptilia clade 3 Diapsida clade 4 Archosauria clade 5 EMBRYO PROTECTED BY AMNIOTIC FLUID OPENING IN THE SIDE OF THE SKULL SKULL ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Kingdoms and Domains Kingdoms and Domains Bacteria Archaea Eukarya Bacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Monera Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia The three ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Biological Classification Chapter 17 iRespond Question Master A.) Response A B.) Response B C.) Response C D.) Response D E.) Response E Percent Complete 100% 00:30 ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
The Diversity of Life The key thing about bacteria is their metabolic diversity. Although they didn't radiate much morphologically (spheres, rod, spirals), they DID ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Introduction to Zoology I. General Information about Zoology Zoology = study of animals Why study animals? 1. Learn about animals ( including humans) 2.
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Phylogenetic trees. Cladistic versus phenetic analyses. Model of sequence evolution ... Branch length (scaled trees only): represents the number of changes that have ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Classification Go to Section: Kingdom Eubacteria Go to Section: E. coli Streptococcus Cell Type Prokaryote Number of Cells Unicellular Nutrition Autotroph or ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
CHAPTER 18 CLASSIFICATION (Taxonomy) THE SIX KINGDOMS Animalia Eukaryotic Heterotrophic Multicellular Movement Organized into tissues and organs (most animals ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
A species is a group of interbreeding natural ... Species can arise from a single population either by spatial ... external gills in a salamander ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Classification This is Panorpa japonica. Commonly known as the scorpion fly. Developing the scientific naming system Binomial Nomenclature. Before Carolus Linnaeus ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Title: Phylogeny and Systematics Author: Nancy Wheat Last modified by: NANCY WHEAT Created Date: 2/11/2006 3:37:02 AM Document presentation format
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Combination of taxonomy & phylogeny ... Amniotes animals with amniotic membrane around developing embryo. Birds, Reptiles, Mammals ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view