Prokaryotic Cell - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title: Prokaryotic Cell
1
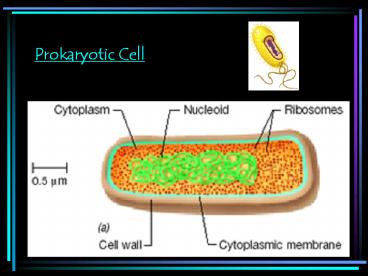
Prokaryotic Cell
2
Eukaryotic Cell
3
Autotrophs capture the light energy from
sunlight and convert it to chemical energy they
use for food.
- Heterotrophs must get energy by eating
- autotrophs or other heterotrophs.
- Decomposers, aka saprobes, are heterotrophs
- that recycle dead organisms by breaking them
- down.
4
(No Transcript)
5
- Phylogeny
- Systematics Hypothesis
- Cladistics
- Derived character
- Cladogram
- Dichotomous Key
- Order
- Family
- Genus
- Species
- Common name
- Scientific
- name
- Binomial
- nomenclature
- Classification
- Taxonomy
- Aristotle
- Linnaeus
- Kingdom
- Phylum
- Class
6
- Taxonomy is the science of grouping
- and naming organisms.
- Classification the grouping of
- information or objects based on
- similarities.
7
- We only know about a fraction of the
- organisms that exist or have existed on Earth.
- Taxonomists give a unique scientific name to
- each species they know about whether its
alive - today or extinct.
- The scientific name comes from one of two
- dead languages Latin or ancient Greek.
Why use a dead language?
8
Devil Cat
9
Ghost Cat
10
Mountain Lion
11
Screaming Cat
12
Puma
13
Florida Panther
14
Cougar
15
- There are at least 50 common names for
- the animal shown on the previous 7 slides.
- Common names vary according to region.
- Soooowhy use a scientific name?
16
Binomial Nomenclature
17
"Formal" scientific names should have a third
part, the authority. The authority is not
italicized or underlined. The authority is
written as an abbreviation of the last name of
the person responsible for naming the organism.
Since Carolus Linnaeus was the first person to
name many plants, the L. for Linnaeus is very
common in plant scientific names. An example is
Quercus alba L.
18
Phylogeny, the evolutionary history of an
organism, is the cornerstone of a branch of
biology called systematic taxonomy.
Systematics, as systematic taxonomy is commonly
called, is the study of the evolution of
biological diversity.
19
A phylogenetic tree is a family tree that shows a
hypothesis about the evolutionary relationships
thought to exist among groups of organisms. It
does not show the actual evolutionary history of
organisms. Why a hypothesis?
20
(No Transcript)
21
Phylogenetic trees are usually based on a
combination of these lines of evidence
Fossil record Morphology
Embryological patterns of development
Chromosomes and DNA
22
Fossil
23
Morphology
24
Homologous Structures
25
modifies homologous
structures
Adaptive Radiation -
Modifies homologous structures
26
(No Transcript)
27
Convergent Evolution
These animals have evolved similar adaptations
for obtaining food because they occupy similar
niches. What can you infer about their
phylogeny from their geographic locations?
28
Convergent evolution leads to.
- Analogous Structures -
- Traits that are morphologically and
- functionally similar even though there
- is no common ancestor.
29
(No Transcript)
30
(No Transcript)
31
(No Transcript)
32
Embryology
33
Cladistics - is a relatively new system of
phylogenetics classification that uses shared
derived characters to establish evolutionary
relationships. A derived character is a feature
that apparently evolved only within the group
under consideration.
34
DNA
35
- There are three basic assumptions in cladistics
- Organisms within a group are descended from a
common ancestor. - There is a bifurcating pattern of cladogenesis.
- Change in characteristics occurs in lineages over
time.
36
A phylogenetic tree based on a cladistic analysis
is called a cladogram. What derived character
is shared by all the animals on the cladogram on
the next slide?
37
(No Transcript)
38
The acacia and its ants are an example of
coevolution. Each influences the others
evolution. Can you think of any other examples
of coevolution?
39
Punctuated Equilibrium instead of a slow,
continuous movement, evolution tends to be
characterized by long periods of virtual
standstill ("equilibrium"), "punctuated" by
episodes of very fast development of new
forms The "punctuated equilibrium" theory of
Niles Eldredge and Stephen Jay Gould was proposed
as a criticism of the traditional Darwinian
theory of evolutionwhat is it called?
40
(No Transcript)
41
(No Transcript)
42
(No Transcript)
43
The Three Domains
- Domain Archaea
- Includes newly discovered cell types
- Contains 1 kingdom the Archaebacteria
- Domain Bacteria
- Includes other members of old kingdom Monera
- Has 1 kingdom the Eubacteria
- Domain Eukarya
- Includes all kingdoms composed of organisms made
- up of eukaryotic cells
- Protista
- Fungi
- Animalia
- Plantae
44
The major classification levels,from most
general to most specific (several of these have
subdivisions)
A group at any level is a taxon.
45
Kingdoms are divided into groups called
phyla Phyla are subdivided into
classes Classes are subdivided into
orders Orders are subdivided into
families Families are divided
into genera Genera contain
closely related species Species is unique
Categories within Kingdoms
46