PETA KONSEP - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
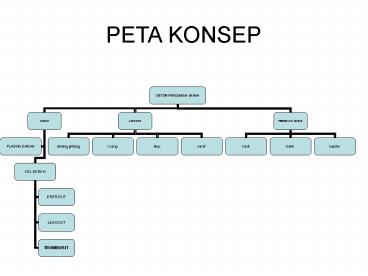
PETA KONSEP
Description:
Title: STRUKTUR, FUNGSI AN SISTEM PEREDARAN DARAH Author: user Last modified by: BPK PENABUR JAKARTA Created Date: 10/4/2005 3:04:04 AM Document presentation format – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:6910
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: PETA KONSEP
1
PETA KONSEP
2
(No Transcript)
3
Sirkulasi Hydra dan Planaria
- Dilakukan oleh sistem gastrovaskuler
- Pada planaria,rongga pencernaan berfungsi sebagai
alat peredaran sekaligus alat ekskresi
4
The Squid Hearts
- Jantung sistemik menerima darah dari insang dan
memompa darah keseluruh tubuh,sedang jantung
insang memompa darah kedalam insang. - 1 jantung sistemik,2 jantung insang
5
Peredaran darah pada mollusca
- 2 atrium,1 ventrikel
- Aorta keposterior dan anterior
- Jantung ditembus usus
6
gastropoda
- 1 atrium,1 ventrikel
- Aorta bercabang kebagian depan dan belakang
- Vena melingkar mengumpulkan darah dari rongga
darah/sinus untuk dialirkan ke paru-paru
7
Peredaran darah pada cacing tanah dan belalang
Pembuluh darah dorsal, ventral, Kapiler (td 5
ps lengkung aorta Sebagai jantung)
Peredaran darah terbuka, jantung pembuluh
aortake jaringan tubuh- Beredar dalam rongga
tubuh (homocoel)-tanpa melalui poembuluh
8
CACING TANAH
- DARAH BERWARNA MERAH
- MEMILIKI JANTUNG PEMBULUH/JANTUNG SEMU PADA
SEGMEN VII HINGGA IX,PEMBULUH DARAH DORSAL
,VENTRAL ,DAN KAPILER - PEMBULUH BESAR MAMPU BERKONTRAKSI
9
Arthropoda
- Sebuah jantung
- Pembuluh darah berupa arteri dan sel-sel darah
- Tidak terdapat kapiler dan vena
- Jantung terletak dalam bilik jantung yaitu
ruangan yang berguna untuk mengumpulkan cairan
darah - Peredaran darah terbuka
- Tidak ada haemoglobin
- Ostia lubang kecil
10
Sistem peredaran darah ikan
- Jantung 2 ruang dilindungi perikardium
- Atrium lebih tipis dari pada bilik
- Sistem peredaran darah tunggal
- Sistem vena porta hepatis dan renalis
11
VENA CORDINALIS ANTERIOR DAN POSTERIOR
AORTA DORSALIS
SINUS VENOSUS
A.AFFERENT BRANKIALIS
KONUS ARTERIOSUS
AORTA VENTRALIS
12
(No Transcript)
13
Sistem transportasi pada katak
- Jantung 3 ruang
- Waktu larva(berudu atau kecebong)sistem peredaran
sama dengan ikan - Eritrosit berinti,bulat panjang,pipih terdapat
kantung(sinus venosus)tempat bermuaranya vena - Aorta bercabang 2
- Tiap cabang aorta bercabang 2 yaitu arteri
karotis dan arteri pulmokutanea - Sistem vena ada 3 Yaitu vena cava,vena
pulmokutaneus,vena porta hepatis dan renalis - PEREDARAN DARAH GANDA
14
(No Transcript)
15
(No Transcript)
16
Sistem Peredaran darah reptilia
17
S.Peredaran darah Reptilia
- Jantung 4 ruang
- Antara serambi kanan dan kiri serta bilik kanan
kanan dan kiri telah bersekat tapi belum sempurna - Pada buaya sekat antar bilik mempunyai lubang
yang dikenal dengan Foramen panizzae - Fungsi foramen memungkinkan distribusi oksigen
yang cukup kealat pencernaan,memelihara
keseimbangan tekanan cairan di dalam jantung pada
waktu menyelam - Dari ventrikel jantung reptil terdapat 2 aorta
yang membelok kekiri dan kekanan - Sistem vena sama dengan katak
18
(No Transcript)
19
S Peredaran darah Burung
- Jantung berbentuk kerucut
- 4 ruang dengan perikardium
- Lengkung aorta menuju kekanan
- Sistem vena porta hanya hepatis saja
20
PEREDARAN DARAH VERTEBRATA
21
FUNGSI DARAH
FUNGSI DARAH
- Pembawa sari-sari makanan, hormon, oksigen
- Mencegah Infeksi
- Pengirim Oksigen dan sari-sari makanan yang
berguna untuk tubuh - Mengandung berbagai bahan sistem imunisasi yang
bertujuan mempertahankan badan dari kuman
penyakit. - Mengangkut bahan sisa metabolisme tubuh,
obat-obatan dan bahan kimia asing ke hati untuk
diuraikan dan ke ginjal untuk dibuang sebagai air
seni.
22
PLASMA DARAH
- Zat organik dan anorganik
- Zat makanan
- Ensim, antibodi, hormon
- Protein darah albumin tekanan osmotik,
fibrinogen, globulin komponen zat kebal - AIR 91,PROTEIN 8,MINERAL 0,9
- Zat sisa
- Gas
- Cara kerja zat antibodi
- Aglutinin/menggum-palkan
- Presipitin/mengendap-kan
- Lisin/ menguraikan
- Antitoksin/menetralkan
23
(No Transcript)
24
SEL DARAH
25
Sel darah merah
- Cakram,bikonkaf
- 5 juta sel/mm3
- Kuning pucat
- Pembungkus luarstroma
- Ada Hb
- Pada wanita Fe gt dikeluarkan waktu
haid,melahirkan - Dibentuk disumsum tulang,usia 115 hari
dihancurkan di limpa dan hati
26
Haemoglobin
- Tersusun atas Fe,globin dan hemin
- Hb lt 40 harus transfusi
- Hb normal 15 gr/100ml darah100
- Anemia parah 5gr/100ml lt 30,napas pendek
27
Sternal puncture testuji tusuk tulang dada
tujuan untuk mengetahui terjadinya pembentukan
sel darah merah di sumsum
28
SEL DARAH
29
SEL DARAH
30
Cell Type Blood Conc. Basic Function Major Features Lifespan
Red Cell Erythrocyte 4.2jt-6.2jt/mm3 5x106/µl, 45 of blood vol. O2 and CO2 transport biconcave, no nucleus or organelles, stain pink w. eosin, 7.5µm diam. 120 days
Platelet Thrombocyte 250000-400000/mm3 3x105/µl clotting small cell fragments, granules store mediators of clotting, 2-3µm diam. 10 days
White Cells Leukocytes 5000-9000/mm3 granulosit 75,agranulosit 25 .perbandingan dengan sel darah merah 1600
Granulocytes
Neutrophil PMN Poly 60-70 6,000/µl phagocytize bacteria, secrete inflammation mediators multilobed nucleus, azurophil granules (red/purple), pink specific granules (hardly visible) 12-15µm diam,fagosit. lt 1 day in blood, 1-2 days in tissues
Eosinophil 2-4 200/µl attack parasites bilobed nucleus, many large brick red specific granules, crystal inclusions, 12-15µm diam,fagosit lt 1 day in blood, weeks in tissues
Top Search this site? IDS100 Home Page
UCSF
31
Basophil 0,5-1 50/µl cause rapid increases in blood vessel permeability, immediate hypersensitivity,fagosit irregularly lobed nucleus, obscured by large deeply basophilic specific granules, 12-15µm diam.
Agranulocytes
Lymphocyte 20-25 2,000/µl B cells differentiate into plasma cells and secrete specifc antibodies T cells recognize cell associated antigens and lyse foreign or virus infected cells, regulate other immune cells round dark blue nucleus, thin rim of gray/blue cytoplasm, 7-9µm diam.
Monocyte 3-8 400/µl become tissue macrophages which scavenge debris, present antigen to lymphocytes,bergerak bebas oval to kidney nucleus eccentrically located, chromatin more lacy than in lymphocytes, gray-blue cytoplasm, 12-17µm diam.
32
PROSES PEMBEKUAN
33
PEMBEKUAN DARAH
FAH
TROMBOSIT PECAH
TROMBOPLASTIN
/TROMBOKI-NASE
TROMBIN
PROTROMBIN, dihasilkan di hati dgn pertolongan
vi. K
ION KALSIUM
FIBRIN
FIBRINOGEN
34
Golongan darah
ABOBlood Type
ABOBlood Type Antigen A Antigen B Antibody anti-A Antibody Anti-B
A yes no no yes
B no yes yes no
O no no yes yes
AB yes yes no no
42
8,5
46,55
3
35
Golongan rhesus
- Berdasarkan ada/tidaknya aglutinogen rhesus
- Rhesus (rhesus positif)
- Rhesus (rhesus negatif)
- Penyakit Erytroblastocyst foetalis, sel darah
merah bayi binasa oleh aglutinin ibu
rhesus_macaque
36
Fungsi golongan darah
- Transfusi darah
- Penyelidikan tindak kriminal
- Transfusi dilakukan bila
- Kecelakaan/luka parah
- Tubuh t erbakar
- Penyakit kronis
- Kehilangan banyak darah
- Kekurangan darah akut
37
Penyimpanan darah
- Hindari permukaan kasar
- Simpan pada suhu 2-4 derajat celcius
- Menambah cairan dikumarol/heparin
- Menambah Natrium sitrat 2,5
38
SKEMA TRANSFUSI DARAH
A A
O O
B B
AB AB
39
Aglutinasi
40
DONOR DARAH
- HINDARI PERMUKAAN TAJAM
- TEMPAT DINGIN
- LARUTAN NA SITRAT
- KECELAKAAN, TERBAKAR, KELUAR BANYAK DARAH-- SAAT
OPERASI - KEKURANGAN DARAH
- PENYAKIT KRONIS/MENAHUN
- 300-1000 cc darah
41
ALAT PEREDARAN DARAH JANTUNG
42
DINDINGRUANG JANTUNG
- Perikardium, berlapis dua ada cairan limfa,
fungsi menahan gesekan - Miokardium, otot tidak sadar, otot bilik lebih
tebal dari serambi, otot bilik kiri lebih tebal
dari bilik kanan - Endokardium, selaput membatasi ruang jantung
- Ruang jantung
- Dua atrium
- Dua ventrikel
- Klep Jantung
- Valvula trikuspidalis
- Valvula bikuspidalis
- Valvula semilunaris
43
(No Transcript)
44
CARDIAK
45
SISTOL DAN DIASTOL
Tek. Paling rendah pada ruang jantung
Tek. Max pada ruang jantung
46
SARAF JANTUNG
- Dikendalikan oleh saraf otonom
- Simpul saraf
- Keith-Flack/Nodus Sino aurikularis, ada pada
dinding serambi di antara vena yang masuk ke
serambi kanan
- Tawara/nodus atrioventrikularis, ada pada sekat
antara serambi-bilik - Berkas His, kelanjutan simpul tawara, ada pada
sekat antara bilik bercabang ke dinding ventrikel
47
- STEP 1. The Sinoatrial Node (SA node), the
natural pacemaker of the heart, generates an
electrical signal.
- STEP 2. The electrical signal follows natural
electrical pathways, through both atrial
chambers, the upper chambers of the heart. The
electricity flowing through those muscles, cause
the atrial chambers to contract, which pushes
blood into the ventricle chambers, the lower
chambers of the heart.
48
- STEP 3. The electrical signal reaches the AV node
(the hearts electrical regulator). There, the
signal pauses to give the ventricles time to fill
with blood
- 4. After the AV nodes delay time, the electrical
signal spreads through the ventricle chambers,
the lower chambers of the heart.
49
(No Transcript)
50
(No Transcript)
51
jantung
52
SISTOLE DAN DIASTOLE
53
SISTOLE DAN DIASTOLE
54
EKG
55
(No Transcript)
56
PEMBULUH DARAH
57
Perbedaan arteri dan vena
arteri vena
Dinding Tebal elastis Tipis kurang elastis
Arah aliran Meninggalkan jantung Menuju jantung
Tekanan Kuat memancar Lemah menetes
Darah didalamnya Banyak O2, kec. Kurang O2, kec.
Letak Lebih dalam Dekat permukaan
klep Hanya satu banyak
58
KAPILER
59
PEREDARAN DARAH
Peredar-an darah Besar Kecil Portae
60
Sistem peredaran darah
61
(No Transcript)
62
PEREDARAN DARAH FETUS
- Janin belum bernafas dengan paru-paru
- Kebutuhan oksigen dipenuhi oleh ibu melalui
pembuluh darah ari-ari/plasenta atau tali pusat - Darah dari jantung janin(serambi kanan), tidak ke
bilik kanan tetapi ke serambi kiri melalui
Foramen Ovale. Selanjutnya ke plasenta melalui
arteria umbilikalis, setelah menyerap oksige dari
plasenta kembali ke janin melalui vena
umbilikalis - Darah dari nadi paru berjalan melalui duktus
arteria
63
(No Transcript)
64
(No Transcript)
65
(No Transcript)
66
(No Transcript)
67
Diametro di vene, capillari, arterie
68
What is rhesus factor? Rhesus factor is a
substance most people have in their blood, which
makes them Rh positive. Some people are Rh
negative they do not have the Rh factor. On its
own this does not cause health problems. But when
a mother is Rh negative and the fetus is Rh
positive, there can be health risks for the
fetus.
What is rhesus factor? Rhesus factor is a
substance most people have in their blood, which
makes them Rh positive. Some people are Rh
negative they do not have the Rh factor. On its
own this does not cause health problems. But when
a mother is Rh negative and the fetus is Rh
positive, there can be health risks for the
fetus.
1. If the mother is Rh negative and the father is Rh positive, their fetus may be Rh positive or Rh negative. 2. If the fetus is Rh positive, there could be a problem if the fetal Rh-positive blood mixes with the mothers Rh-negative blood.
3. Left untreated, the mothers blood will make antibodies () that attack the Rh-positive blood of the fetus. 4. These antibodies can cause health problems for the fetus. These include blood problems or even death.
1. If the mother is Rh negative and the father is Rh positive, their fetus may be Rh positive or Rh negative. 2. If the fetus is Rh positive, there could be a problem if the fetal Rh-positive blood mixes with the mothers Rh-negative blood.
3. Left untreated, the mothers blood will make antibodies () that attack the Rh-positive blood of the fetus. 4. These antibodies can cause health problems for the fetus. These include blood problems or even death.
What are the risks? If the blood of your fetus is
Rh positive, your Rh-negative blood may form
antibodies to the Rh factor. These antibodies
will fight the Rh-positive blood. This is called
Rh disease. Rh disease can cause the fetus to
lose blood cells or have other health problems.
Medical treatment can prevent Rh disease by
stopping the antibodies from forming
What are the risks? If the blood of your fetus is
Rh positive, your Rh-negative blood may form
antibodies to the Rh factor. These antibodies
will fight the Rh-positive blood. This is called
Rh disease. Rh disease can cause the fetus to
lose blood cells or have other health problems.
Medical treatment can prevent Rh disease by
stopping the antibodies from forming
69
(No Transcript)
70
LIPATAN SIKU, KETIAK, LUTUT, PAHA, LEHER. LENDIR
USUS, PANGKAL LIDAH, TONSIL, AMANDEL, ADENOID
71
Sistem Limfatik
- suatu sistem kelenjar getah bening (KGB) yang
penting dan menyebar ke seluruh jaringan pembuluh
kelenjar tubuh - mengangkut protein dan zat zat berpartikel
- salah satu jalan untuk penyerapan nutrien
- bertanggung jawab atas absorpsi lemak
72
Cairan Limfe
- berasal dari cairan jaringan yang mengalir ke
dalam sistem limfatik - mengandung leukosit
- mengandung lemak
Pembuluh Limfatik
Hampir seluruh jaringan tubuh mempunyainya Pembulu
h limfatik di usus disebut pembuluh kil
73
- Pembuluh limfe ada 2
- Pembuluh limfe kiri
- menerima cairan limfe dari bagian kiri kepala,
leher, dada, dan lengan kiri bagian atas - Bermuara ke vena bagian bawah tulang selangka
kiri - -Pembuluh limfe kanan
- menerima cairan limfe dari bagian lain
- Bermuara ke vena bagian bawah tulang selangka
kanan
74
Kapiler Limfatik Merupakan struktur yang
khusus Kira-kira 1/10 dari cairan yang disaring
dari kapiler arteri hingga diabsorpsi kembali ke
ujung vena kapiler darah itu memasuki kapiler
limfatik dan kembali ke darah melalui sistem
limfatik
Kelenjar Limfe Kumpulan jaringan limfe yang
terbungkus dalam suatu kapsula jaringan
ikat Terdapat di sepanjang pembuluh limfe
tubuh Berfungsi sebagai tempat memproduksi dan
akumulasi limfosit
75
Organ-organ limfe Limpa Organ limfe
terbesar Merupakan saringan sistem pembuluh
darah Berfungsi dalam pembentukan leukosit dan
antibodi, menyaring zat asing dalam aliran darah,
menyediakan kembali zat besi yang terkandung
dalam hemoglobin, dan tempat cadangan eritrosit
Tonsil Terbenam dalam selaput pelapis
tenggorokan Mensekresikan kelenjar yang
mengandung limfosit, sisa-sisa buangan, dan
mikroorganisme berfungsi dalam pembentukan
limfosit Timus Tersusun atas sel-sel epitel yang
menyerupai limfosit Memproduksi hormon untuk
merangsang produksi limfosit dalam organ limfe
76
(No Transcript)
77
(No Transcript)
78
DUKTUS LIMFATIKUS DEKSTER
DUKTUS TORAKSIKUS
79
PEMBULUH
80
BAGIAN DARAH YANG KELUAR DARI PEMBULUH DARAH
GETAH BENING, AIR, GLUKOSA, LEMAK, GARAM MINERAL
81
- Peredaran limfe
- Merupakan peredaran terbuka karena ujung ujung
pembuluh limfe tidak - saling bersambungan
82
GETAH BENING
83
Organ limfe
- Limpa
- Tonsil
- Timus
- Kekebalan alami
- Kekebalan buatan
84
Penyakit Darah
- Anemia
- Thallasemia
- Polisitemia
- Hemofilia
- Thrombositopenia
- Leukemia
- Arterosklerosis-aterosklerosis
- /kapur
- Jantung koroner
- Emboli-trombus
- Hipertensi
- Hipotensi
- Varises
- Eritroblastosis foetalis
85
thalassemia
- Darah merah kecil-kecil lonjong
- Jumlah lebih banyak dari normal
- Afinitas terhadap oksigen kurang
- TH mayor anemia parah,kematian waktu bayi
- TH minor anemia tak parah
86
polycythemia
- Polycythemia vera is an abnormal increase in
blood cells (primarily red blood cells) resulting
from excess production by the bone marrow - overproduction of all three blood cell lines
white blood cells, red blood cells, and platelets
.
87
(No Transcript)
88
(No Transcript)
89
(No Transcript)
90
(No Transcript)
91
(No Transcript)
92
- 1. vena subclàvia dreta / vena subclavia derecha
2. gran vas limfàtic / gran vaso linfático 3.
vena subclàvia esquerra / vena subclavia
izquierda 4. canal limfàtic toràcic / canal
linfático torácico 5. cisterna de Pecquet /
cisterna de Pecquet 6. vas quilífer / vaso
quilífero 7. intestí / intestino 8. gangli
limfàtic / ganglio linfático
93
Thrombositopenia
94
(No Transcript)
95
(No Transcript)
96
(No Transcript)
97
(No Transcript)
98
(No Transcript)
99
(No Transcript)
100
(No Transcript)
101
Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery
102
(No Transcript)
103
(No Transcript)
104
gumpalan darah
105
atherosclerosis
106
Development of Peripheral Artery Disease