Mon. Tues. Wed. Thurs. Fri. - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Mon. Tues. Wed. Thurs. Fri.
Description:
Title: PowerPoint Presentation Last modified by: Fairfield University Document presentation format: On-screen Show Other titles: Times New Roman Arial Default Design ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:85
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Mon. Tues. Wed. Thurs. Fri.
1
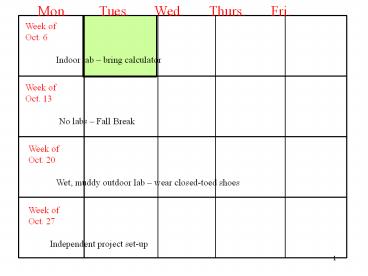
Mon. Tues. Wed. Thurs.
Fri.
Week of Oct. 6
Indoor lab bring calculator
Week of Oct. 13
No labs Fall Break
Week of Oct. 20
Wet, muddy outdoor lab wear closed-toed shoes
Week of Oct. 27
Independent project set-up
2
Structure of course
Environmental variability Organisms Ecosystems Pop
ulations Species interactions Communities
Applied Ecological Issues
3
Outline for ecosystems
Introduction How does energy move through an
ecosystem? How does matter move through an
ecosystem?
4
(No Transcript)
5
What happens to net primary production?
6
Figure 6.2
Herbivore
Carnivore
Herbivore
7
Figure 6.1
Trophic pyramid
Tertiary consumers
Secondary consumers
Primary consumers
Primary producers
8
Ecological/food chain efficiency the percentage
of energy in the biomass produced by one trophic
level that is incorporated into the biomass
produced by the next higher trophic level
9
Ecological/food chain efficiency exploitation
efficiency x gross production efficiency
10
How fast does energy move through an ecosystem?
Biomass accumulation ratio biomass / rate of
biomass production
11
Figure 6.13
standing biomass biomass production rate
lowest on land
12
Ecosystem Management
- process of sustaining ecosystems, their
processes, and the services they provide for
future generations - example of Lake Mendota
13
(No Transcript)
14
Outline for ecosystems
Introduction How does energy move through an
ecosystem? How does matter move through an
ecosystem?
15
How does matter move through an ecosystem?
Matter elements e.g., what are ways that a
carbon atom moves from one compartment of an
ecosystem to another? How fast do carbon atoms
move from one compartment to another?
16
Organisms move elements through chemical
transformations
inorganic C
organic C
17
Figure 7.1
organic
organic
inorganic
inorganic
18
Figure 7.2
19
(No Transcript)
20
How does matter move through an
ecosystem? Cycles between inorganic and organic
forms and between different compartments of
ecosystems Difference between matter and energy
movement?
21
Figure 7.3
22
Cycles of matter water carbon nitrogen phosphorus
sulfur
Focus on important pools and transfers
23
Water cycle
Figure 7.4
24
C cycle
Figure 7.5
Carbon cycle
25
Figure 7.6
Biological transformations of carbon
26
Fig. 7.11
N cycle
27
Figure 7.11b
inorganic forms used by plants
e.g., proteins
Biological transformations of nitrogen
28
P cycle
Figure 7.13
29
Figure 7.14a
S cycle
30
Figure 7.14b
Biological transformations of sulfur
31
What do I expect you to know about element cycles?
- - which forms are available to bacteria, plants,
- and animals
- which transfers are changes in form of the
- element
- which transfers are biological transfers vs.
- chemical or physical transfers