Biochemistry - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 38
Title:
Biochemistry
Description:
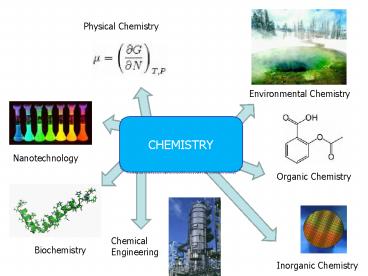
Physical Chemistry Environmental Chemistry CHEMISTRY Nanotechnology Organic Chemistry Chemical Engineering Biochemistry Inorganic Chemistry Temperature Measure of how ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:109
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Biochemistry
1
Physical Chemistry
Environmental Chemistry
CHEMISTRY
Nanotechnology
Organic Chemistry
Chemical Engineering
Biochemistry
Inorganic Chemistry
2
(No Transcript)
3
Measurement
- Metric system (National Assembly of France, 1790)
- International System of Units (SI, 1960)
Derived units combinations of fundamental
units Ex. Speed (m/s)
4
Equipment for Measurement
5
Scientific Notation
Width of a human hair 0.000008 m
Coefficient
Power of Ten 10x
Coefficient?
8
Power?
10-6
8 x 10-6 m
6
Scientific Notation
- How many atoms of water are in a Lake Washington?
- 97,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,
000,000,000,000,000 atoms - -or-
- 9.7 x 1037 atoms
7
Scientific Notation on Calculators
- Your calculator should work with scientific
notation! Look for
EE
EXP
Note 9.64 x 105 9.65 E5
Coefficient
Power of Ten
2. x 10-8 2.E-8
8
Scientific Notation
- Conversion to a standard number
- 3.252 x 106
If power of ten is positive, move decimal point
to the RIGHT (add zeros if necessary)
3252000
If power of ten is negative, move decimal point
to the LEFT (add zeros if necessary)
4.56 x 10-3
0.00456
9
Measured Numbers
- Numbers obtained when you measure a quantity
- Estimate the final digit
4.8 in
Read greater than 4 and less than 5 estimate
last digit
4.84 in
Read greater than 4.8 and less than 4.9 estimate
last digit
10
Significant Figures
- All measured digits, including the estimated
digit - 4.84 cm
- 2045 g
- 2.333 x 10-5 L
- 50. s
- Zeros not significant in 2 situations
- At the beginning of a decimal number
- At the end of a number without decimal point
- 4500 cm
- 0.0063 kg
- 0.05202 L
11
Exact Numbers
- A counted number (not measured!)
- Ex. of students in this classroom
- A definition comparing two units in same
measurement system - Ex. 1 ft 12 in
- Ex. 1 kg 1000 g
- NOT considered as significant figures!
12
Significant Figures in Calculations
- In lab, at work, we measure things. Then what?
- The number of sig figs in measured numbers limits
the number of sig figs in a calculated answer. - You cant have more detail in your answer than
- you have in your measurements
- Number of sig figs in answer depends on what
type of calculations you performed
13
Sig Figs in Calculations
- Multiplication and Division
- Final answer has the same number of sig figs as
the measurement with the fewest significant
figures - Addition and Subtraction
- Final answer has the same number of decimal
places as the measurement with the fewest decimal
places
24.64 x 3.2 78.848
79.
3.525 - 5.2 -1.675
-1.7
3.525 6.475 10
10.000
14
Rounding Rules
- How do we limit the number of sig figs? Rounding!
- Look at first non-significant number (to be
dropped) - Is this number 4 or less?
- Is this number 5 or more?
Round down
Round up
2390.321 to 4 sig figs
2390.
0.0056194 to 2 sig fig
0.0056
688511 to 3 sig figs
689000
15
Prefixes
- Is it easier to write
- 590000 g or 590 kg?
- 0.0004 g or 0.4 mg?
- Prefixes can be attached to units to increase or
decrease size by a factor of 10 - (multiply by 10 or divide by 10)
Multiply by 10x
Multiply by 10-x
16
Common Prefixes with SI Units
17
Equalities used in Measurements
- Equality
- A relationship between two units that measure
the same quantity - Length
- 1 m 100 cm 1000 mm
- Volume
- 1 L 10 dL 1000 mL
- 1 dL 100 mL
Cubic centimeter cc
1 cm x 1 cm x 1 cm 1 cm3
1 cc 1 cm3 1 mL
18
Volume Conversions
- If 1 cubic centimeter equals 1 mL,
- how many milliliters does 1 cubic meter equal?
1 m 100 cm
100 cm x 100 cm x 100 cm 1000000 cm3
1000000 cm3 1000000 mL
1 x 106 mL
1 m3 1000 L
1 x 103 L
19
Conversion Factors Changing Between Units
- 1 hr 60 min
Conversion Factor
Metric Conversion Factor
20
More Conversion Factors
Metric Conversion Factors
Metric- U.S. System Conversion Factors
1 kg 2.20 lb
1 km 0.621 mi
21
More Conversion Factors
- Standard equalities can be looked up in a table
(Table 1.9 in your book, for example) - Other equalities may be stated in a problem
- Examples
- The average speed of cars driving on I-5 during
rush hour is 11 mph.
Equality 11 miles 1 hour
- One five pound bag of sugar costs 4.00.
Equality 1 bag 5 lb 4.00
22
Percents as Conversion Factors
- Percent means 1 per 100
- Example
- If a person is 20 body fat by mass, then
20 kg fat 100 kg body total
23
End of class Practice Questions
- How many sig figs are in each the following?
- 0.00500 L
- 53,069 s
- 0.00004715 m
- 0.509 kg
- Write the numbers above in scientific notation.
- How many sig figs does each have now?
- Write a conversion factor relating micrograms to
grams
24
Practice Questions
What is the temperature on each (C) thermometer
shown? (sig figs!)
4.9 C
61.5 C
- Is each of the following an exact or measured
number? - The number of chair legs in this room
- The length of your benchtop in inches
- The length of your benchtop in cm
- The area of the projector screen
Exact
Measured
Measured
Measured
25
Using Conversion Factors
Your patient tells you that she recently lost 15
kg. How many pounds has she lost?
- Whats given? What do we want to
know? - What conversion factors do I need?
- Set up problem
weight lost (kg) 15 kg
weight lost (lb) ? lb
kg ? lb
2.20 lb 1 kg
26
Using Conversion Factors
kg ? lb
- 3. Set up problem
15 kg
x
?
Check sig figs!
27
Using Conversion Factors
The recommended daily value of vitamin C is 60
mg. If an average orange contains 45 mg of
vitamin C, how many oranges should you eat in a
week?
- Whats given? What do we want to
know? - What conversion factors do I need?
1 week
of oranges
week ? oranges
? days
? mg vitamin C
28
Physical Properties of Materials
- Physical Property
- can be measured or perceived without changing the
materials identity - Intensive
- Independent of amount of substance
- Ex. Boiling point
- Extensive
- Depends on amount of substance
- Ex. Mass, volume
29
Density
- Relationship between mass and volume
- Density is a physical property
- Density is an intensive property
4 times more mass 4 times more volume
30
Density
- Units
- SI kg/m3
- often use g/L
- g/mL
- g/cm3
- g/cc
- Density of water (at 20C and typical room
pressure) - 1 g/cc 1 g/mL
31
Density of Solids
- How can we determine the density of a solid?
- Need to know mass
- Need to know volume
Measure displacement of water
Does this method work for all solid materials?
32
Density Table
- Density can be used as a conversion factor!
- (relates mass to volume)
33
Specific Gravity (sp gr)
- Ratio between density of substance density of
water
Measure sp gr with a hydrometer
Units for sp gr?
Unitless!
34
Temperature
- Measure of how hot or cold a substance is
relative to another substance - Scales and Units
Scale Boiling Point H2O Freezing Point H2O
Celsius C
Fahrenheit F
Kelvin K
100C
0C
212F
32F
373.15 K
273.15 K
Note the unit is not K
35
Temperature Conversions
- How many units are between boiling point and
freezing point of water?
Scale
Celsius C
Fahrenheit F
Kelvin K
100C 0C
100 units
212F 32F
180 units
373 K 273 K
100 units
the unit 1 Kelvin equals the unit 1 degree
Celsius
36
Converting Units Fahrenheit to Units Celsius
180 Fahrenheit degrees 100 Celsius degrees
37
Things to Remember about the Temperature Scales
- 0 K is absolute zero
- You can never (ever ever ever) have a temperature
of negative K - The unit for the Celsius scale is the degree C
(C) - The unit for the Fahrenheit scale is the degree F
(F) - The units for the Kelvin scale is the Kelvin (K)
- A change of x Kelvin a change of x C
Start value and end values are different Both
changed the same amount (50 K units 50 C units)
38
Precision and Accuracy
- Precision reproducibility
- Accuracy how close to actual value
Temp (C)




![DOWNLOAD [PDF] Medical Biochemistry PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10133538.th0.jpg?_=20240918087)

![[PDF] Principles of Biochemistry (Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry) Kindle PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10087811.th0.jpg?_=202407290611)























