A View of the cell Ch. 7 - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 39
Title:
A View of the cell Ch. 7
Description:
A View of the cell Ch. 7 – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:83
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: A View of the cell Ch. 7
1
A View of the cellCh. 7
2
- Before the microscope, many believed that
diseases were caused by curses and supernatural
spirits.
3
- Microscopes enabled scientists to view and study
cells, the basic units of living organisms.
4
- The first microscope was used by van Leeuwenhoek
in the 1600s and it is considered a simple light
microscope because it had only one lens.
5
- Over the next 200 years, microscopes improved by
grinding higher quality lenses. The compound
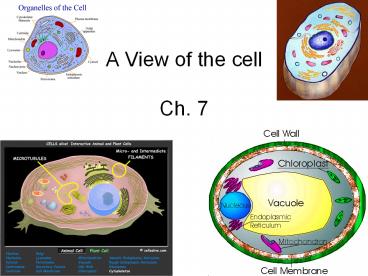
microscope was also developed, which uses a
series of lenses to magnify objects in steps.
6
- Compound light microscopes can view objects up to
about 1500 times their actual size.
7
- Robert Hooke used a compound light microscope to
study cork, the dead cells of Oak bark. - He observed small geometric shapes like boxes
which he called cells.
8
- This and other discoveries gave rise to the Cell
Theory, one of the fundamental ideas of modern
biology.
9
The Cell Theory
- 1. All organisms are composed of one or more
cells. - 2. The cell is the basic unit of structure and
organization of organisms. - 3. All cells come from preexisting cells.
10
- In the 1930s and 1940s the electron microscope
was developed . It uses a beam of electrons
instead of light and can magnify up to 500,000
times.
11
(No Transcript)
12
- With better microscopes scientists observed that
all cells contain small, specialized structures,
called organelles.
13
- Cells can be divided into two broad groups those
that contain membrane bound organelles and those
that do not. - These are called prokaryotes and eukaryotes
14
- Prokaryotes are cells that do not contain
membrane bound organelles. - Ex. Unicellular organisms such as bacteria.
15
- Eukaryotes are cells that contain membrane-bound
organelles. - Ex. Most multicellular organisms are made up of
eukaryotic cells. Also amoeba and some yeast and
algae.
16
- Eukaryotes are larger and contain a true nucleus.
- They can carry out numerous metabolic chemical
reactions at the same time.
17
- The plasma membrane maintains a state of balance
in the cell by controlling the flow of nutrients
into the cell and a flow of waste out of the
cell. It does this through a process of selective
permeability.
18
- The plasma membrane is composed of a phospholipid
bilayer which is a lipid where one of the fatty
acids has been replaced by a phosphate group.
19
- The polar phosphate group allows the cell
membrane to interact with its watery environment
because water itself is polar. - The fatty tails avoid water.
20
- When the phospholipid molecules come together to
form this sandwich, a barrier is created that
is water-soluble at its outer surfaces and water
insoluble in the middle.
21
- Water-soluble molecules will not easily move
through the membrane because they are stopped by
the water-insoluble layer.
22
- This model is called the fluid mosaic model.
- The proteins create a mosaic or pattern with the
phospholipids like boats with their decks above
water and hulls beneath it.
23
- Cholesterol is found in the cell membrane where
it helps stabilize the phospholipids by keeping
them from sticking together.
24
- Transport proteins move needed substances or
waste materials through the plasma membrane. - Other proteins play a role in attaching the cells
inner structure to the membrane and help the cell
identify chemical signals.
25
- All plant cells have a cell wall which gives
support and protection to the cell. It is a
cellulose mesh which is highly permeable. - Fungi, bacteria, and some protists also have a
cell wall.
26
- The master set of directions for making proteins
is found in chromatin, which are strands of DNA
found in the nucleus.
27
- The nucleolus is found inside the cell nucleus
and makes ribosomes. - Ribosomes are the sites where the cell produces
proteins according to the directions of DNA.
28
- Cytoplasm is the clear, gelatinous fluid within a
cell which holds all the organelles as well as
nutrients and waste waiting for export.
29
- The endoplasmic reticulum is the site of cellular
chemical reactions. It is folded up like an
accordion and thus fits into a small space.
30
- The golgi apparatus is a flattened stack of
tubular membranes that modify proteins made by
the ribosomes, which sort and package proteins
like mail at the post office.
31
- Vacuoles are temporary storage compartments used
to store food, enzymes, and other materials. - Most animal cells dont contain vacuoles.
32
- Lysosomes are organelles that contain digestive
enzymes. They digest excess or worn out
organelles, food particles and engulfed viruses
or bacteria.
33
- The cell requires a large amount of energy to
perform all its vital functions. - Two organelles chloroplasts and mitochondria
provide this energy.
34
- Chloroplasts are organelles in plant cells that
contain chlorphyll and capture light energy and
convert it to chemical energy. - They contain a double membrane which contains the
stroma and grana which help trap the suns energy.
35
- Mitochondria are organelles in plant and animal
cells that transform energy for the cell and
store it in the bonds of other molecules.
36
- Mitochondria can occur in varying numbers
depending on the cells function. - Liver cells can hold up to 2000 mitochondria.
37
- The cytoskeleton forms a framework for the cell
like the skeleton. Microtubules and
microfilaments, that can be dismantled and
reassembled elsewhere, make up the cytoskeleton.
38
- Centrioles are organelles found in animal cells
and aid in cell division. - Cilia and flagella are organelles on the surface
of the cell that are made of microtubules and aid
in locomotion and feeding
39
- Cilia are short numerous and look like hairs.
They move like oars in a rowboat. - Flagella are longer and move in a whip-like
motion. Cells have only one or two flagella.