Anaerobic respiration: Glycolysis - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 11
Title:
Anaerobic respiration: Glycolysis
Description:
Anaerobic respiration: Glycolysis & fermentation What is the definition of cellular respiration? Energy is obtained by breaking down food molecules. – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:324
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Anaerobic respiration: Glycolysis
1
Anaerobic respiration Glycolysis fermentation
2
What is the definition of cellular respiration?
- Energy is obtained by breaking down food
molecules. - Energy is stored in ATP.
- Covalent bond energy is converted to ATP energy.
A panda is very poor at digesting bamboo and so
must spend much of its day eating.
3
How is energy transferred during cellular
respiration?
- Most reactions involving energy transfer are
electron transferring reactions. - Oxidation an electron being taken from a
molecule - Reduction an electron being added to a molecule
Hint to remember think the molecule is reduced
in charge from to when an electron is
transferred.
4
balanced equation for cellular respiration
- Glucose Oxygen ? Carbon dioxide Water
36 ATPs - C6H12O6 O2 ? CO2 H2O
- C6H12O6 6 O2 ? 6 CO2 6 H2O
- The three processes that make up cellular
respiration and where they occur - Glycolysis - cytoplasm (anaerobic)
- Krebs cycle - mitochondria (aerobic)
- Electron transport system - mitochondria
(aerobic)
5
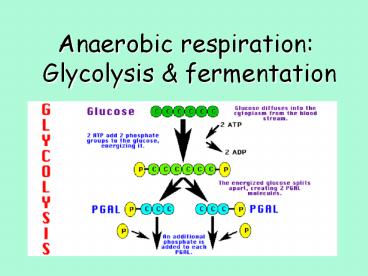
the first stage of Cellular Respiration
Glycolysis
- glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm of all cells.
- Does not use oxygen, its anaerobic
- Glycolysis is a series of 10 reactions.
- Each produces a product used by the next.
6
Glycolysis in a nutshell
- Reactant 1 Glucose molecule.
- Product 2 Pyruvic acids molecules
- 2 ATP are need to start the reaction
- 4 ATP are produced so.. 2 ATP are gained
- NAD stores 1 electron a hydrogen to be used
later.
Do you know the expression it takes money to
make money? (like a loan to start a
business.) Well, it takes energy to get energy
out of a large molecule
7
The next step in the absence of oxygen gas
fermentation
- Yeasts Pyruvic acid is converted into ethyl
alcohol and CO2 - Yeast grape juice wine
- Yeast bread dough makes it rise
Yeast cells
Dough rising
8
- What is the point of fermentation if no ATP is
produce? - To oxidize NADH into NAD to be used in Glycolysis
9
Fermentation in animal cells
- Animals Pyruvic acid is converted lactic acid
- Lactic acid can build up in muscles and cause
fatigue
Muscles produce lactic acid when short of oxygen
10
Energy Yield
- Glycolysis is about 2 efficient.
- Simple organisms such as bacteria survive on
anaerobic respiration. - More complex organisms require more energy.
11
Review
- What are the reactants and produces of
Glycolysis? - What is the net yield of ATP from glycolysis?
- What is the point of fermentation (other than all
the useful or yummy products)?