LE 01-10b - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 30
Title:
LE 01-10b
Description:
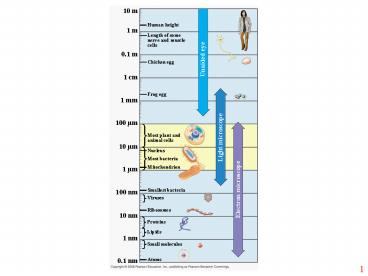
10 m Human height Unaided eye 1 m Length of some nerve and muscle cells 0.1 m Chicken egg 1 cm Frog egg 1 mm Light microscope 100 m Most plant and animal cells – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:84
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: LE 01-10b
1
10 m
Human height
1 m
Length of some nerve and muscle cells
0.1 m
Unaided eye
Chicken egg
1 cm
Frog egg
1 mm
100 µm
Most plant and animal cells
Light microscope
10 µm
Nucleus
Most bacteria
Mitochondrion
1 µm
Electron microscope
Smallest bacteria
100 nm
Viruses
Ribosomes
10 nm
Proteins
Lipids
1 nm
Small molecules
0.1 nm
Atoms
2
Fimbriae
Nucleoid
Ribosomes
Plasma membrane
Cell wall
Bacterial chromosome
Capsule
0.5 µm
Flagella
(a)
A typical rod-shaped bacterium
(b)
A thin section through the bacterium Bacillus
coagulans (TEM)
3
TEM of a plasma membrane
(a)
Outside of cell
Inside of cell
0.1 µm
Carbohydrate side chain
Hydrophilic region
Hydrophobic region
Hydrophilic region
Phospholipid
Proteins
(b) Structure of the plasma membrane
4
Surface area increases while total volume remains
constant
5
1
1
Total surface area Sum of the surface
areas (height ? width) of all boxes sides ?
number of boxes
150
750
6
Total volume height ? width ? length ? number of
boxes
125
125
1
Surface-to-volume (S-to-V) ratio surface area
volume
6
6
1.2
5
Nuclear envelope
ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM (ER)
NUCLEUS
Nucleolus
Smooth ER
Rough ER
Flagellum
Chromatin
Centrosome
Plasma membrane
CYTOSKELETON
Microfilaments
Intermediate filaments
Microtubules
Ribosomes
Microvilli
Golgi apparatus
Peroxisome
Mitochondrion
Lysosome
6
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Nuclear envelope
Nucleolus
NUCLEUS
Chromatin
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Ribosomes
Central vacuole
Golgi apparatus
Microfilaments
Intermediate filaments
CYTO- SKELETON
Microtubules
Mitochondrion
Peroxisome
Chloroplast
Plasma membrane
Cell wall
Plasmodesmata
Wall of adjacent cell
7
Nucleus
1 µm
Nucleolus
Chromatin
Nuclear envelope
Inner membrane
Outer membrane
Nuclear pore
Pore complex
Rough ER
Surface of nuclear envelope
Ribosome
1 µm
0.25 µm
Close-up of nuclear envelope
Pore complexes (TEM)
Nuclear lamina (TEM)
8
Cytosol
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
Free ribosomes
Bound ribosomes
Large subunit
Small subunit
0.5 µm
Diagram of a ribosome
TEM showing ER and ribosomes
9
Smooth ER
Nuclear envelope
Rough ER
ER lumen
Cisternae
Transitional ER
Ribosomes
Transport vesicle
200 nm
Rough ER
Smooth ER
10
cis face (receiving side of Golgi apparatus)
0.1 µm
Cisternae
trans face (shipping side of Golgi apparatus)
TEM of Golgi apparatus
11
1 µm
Nucleus
Vesicle containing two damaged organelles
1 µm
Mitochondrion fragment
Peroxisome fragment
Lysosome
Digestive enzymes
Lysosome
Lysosome
Plasma membrane
Peroxisome
Digestion
Food vacuole
Digestion
Mitochondrion
Vesicle
(a) Phagocytosis
(b) Autophagy
12
Central vacuole
Cytosol
Central vacuole
Nucleus
Cell wall
Chloroplast
5 µm
13
Nucleus
Rough ER
Smooth ER
cis Golgi
Plasma membrane
trans Golgi
14
Intermembrane space
Outer membrane
Free ribosomes in the mitochondrial matrix
Inner membrane
Cristae
Matrix
0.1 µm
15
Ribosomes
Stroma
Inner and outer membranes
Granum
1 µm
Thylakoid
16
Chloroplast
Peroxisome
Mitochondrion
1 µm
17
Microtubule
Microfilaments
0.25 µm
18
Vesicle
ATP
Receptor for motor protein
Microtubule of cytoskeleton
Motor protein (ATP powered)
(a)
Microtubule
Vesicles
0.25 µm
(b)
19
10 µm
10 µm
10 µm
Column of tubulin dimers
Keratin proteins
Actin subunit
Fibrous subunit (keratins coiled together)
25 nm
7 nm
812 nm
Tubulin dimer
?
?
20
Centrosome
Microtubule
Centrioles
0.25 µm
Microtubules
Longitudinal section of one centriole
Cross section of the other centriole
21
Direction of swimming
(a) Motion of flagella
5 µm
Direction of organisms movement
Power stroke
Recovery stroke
(b) Motion of cilia
15 µm
22
Outer microtubule doublet
Plasma membrane
0.1 µm
Dynein proteins
Central microtubule
Radial spoke
Protein cross-linking outer doublets
Microtubules
(b)
Cross section of cilium
Plasma membrane
Basal body
0.5 µm
0.1 µm
(a)
Longitudinal section of cilium
Triplet
(c) Cross section of basal body
23
Microtubule doublets
ATP
Dynein protein
(a) Effect of unrestrained dynein movement
ATP
Cross-linking proteins inside outer doublets
Anchorage in cell
(b) Effect of cross-linking proteins
1
3
2
(c) Wavelike motion
24
Microvillus
Plasma membrane
Microfilaments (actin filaments)
Intermediate filaments
0.25 µm
25
Muscle cell
Actin filament
Myosin filament
Myosin arm
(a) Myosin motors in muscle cell contraction
Cortex (outer cytoplasm)
gel with actin network
Inner cytoplasm sol with actin subunits
Extending pseudopodium
(b) Amoeboid movement
Nonmoving cortical cytoplasm (gel)
Chloroplast
Streaming cytoplasm (sol)
Vacuole
Parallel actin filaments
Cell wall
(c) Cytoplasmic streaming in plant cells
26
Secondary cell wall
Primary cell wall
Middle lamella
1 µm
Central vacuole
Cytosol
Plasma membrane
Plant cell walls
Plasmodesmata
27
Polysaccharide molecule
Proteoglycan complex
Collagen
EXTRACELLULAR FLUID
Carbo- hydrates
Fibronectin
Core protein
Integrins
Proteoglycan molecule
Plasma membrane
Proteoglycan complex
CYTOPLASM
Micro- filaments
28
Cell walls
Interior of cell
Interior of cell
Plasmodesmata
Plasma membranes
0.5 µm
29
Tight junction
Tight junctions prevent fluid from moving across
a layer of cells
0.5 µm
Tight junction
Intermediate filaments
Desmosome
Desmosome
Gap junctions
1 µm
Extracellular matrix
Space between cells
Gap junction
Plasma membranes of adjacent cells
0.1 µm
30
Cell Component
Structure
Function
Houses chromosomes, made of chromatin (DNA, the
genetic material, and proteins)
contains nucleoli, where ribosomal subunits are
made. Pores regulate entry and exit of materials.
Nucleus
Concept 6.3
Surrounded by nuclear envelope (double
membrane) perforated by nuclear pores. The
nuclear envelope is continuous with
the endoplasmic reticulum (ER).
The eukaryotic cells genetic instructions are
housed in the nucleus and carried out by the
ribosomes
(ER)
Ribosome
Two subunits made of ribo- somal RNA and
proteins can be free in cytosol or bound to ER
Protein synthesis
Extensive network of membrane-bound tubules
and sacs membrane separates lumen from
cytosol continuous with the nuclear envelope.
Concept 6.4
Endoplasmic reticulum
Smooth ER synthesis of lipids, metabolism of
carbohy- drates, Ca2 storage, detoxifica-tion of
drugs and poisons
The endomembrane system regulates protein traffic
and performs metabolic functions in the cell
(Nuclear envelope)
Rough ER Aids in synthesis of secretory and
other proteins from bound ribosomes
adds carbohydrates to glycoproteins produces new
membrane
Modification of proteins, carbo- hydrates on
proteins, and phos- pholipids synthesis of
many polysaccharides sorting of Golgi products,
which are then released in vesicles.
Golgi apparatus
Stacks of flattened membranous sacs has
polarity (cis and trans faces)
Breakdown of ingested substances, cell
macromolecules, and damaged organelles for
recycling
Lysosome
Membranous sac of hydrolytic enzymes (in animal
cells)
Digestion, storage, waste disposal, water
balance, cell growth, and protection
Vacuole
Large membrane-bounded vesicle in plants
Concept 6.5
Mitochondrion
Bounded by double membrane inner membrane
has infoldings (cristae)
Cellular respiration
Mitochondria and chloro- plasts change energy
from one form to another
Chloroplast
Typically two membranes around fluid stroma,
which contains membranous thylakoids stacked into
grana (in plants)
Photosynthesis
Contains enzymes that transfer hydrogen to water,
producing hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) as
a by-product, which is converted to water by
other enzymes in the peroxisome
Peroxisome
Specialized metabolic compartment bounded by
a single membrane


















![10b Computational Complexity: P and NP [14.2, 14.3, 14.4] PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/P1246211285GsHjr.th0.jpg?_=20110627057)











