Ingen lysbildetittel - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 47
Title:
Ingen lysbildetittel
Description:
MHC molekyler og sykdomsassosiasjon. Nettundervisning i ... Cataplexy. Sleep paralysis. Hypnagogic hallucinations. Very strong HLA association with DR2-DQ6 ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:122
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Ingen lysbildetittel
1
MHC molekyler og sykdomsassosiasjon Nettundervisni
ng i immunologi og transfusjonsmedisin
Ludvig M. Sollid 28. februar, 2008
2
DISORDERS ASSOCIATED WITH HLA
Immune related
- Diseases with autoimmune features
- Adverse reactions to drugs
- Infections
- Malignancies
Not related to immunity
- Hemachromatosis HFE (HLA-A3)
- Congenital adrenal hyperplasia CYP21 (HLA-B47)
From M. Ráki
3
DISEASES WITH AUTOIMMUNE FEATURES
Ank. spondylitis (Bechterews disease) Narcolepsy
Myasthenia gravis Graves disease Rheumatoid
arthritis Celiac disease Multiple
sclerosis Diabetes (type I) Pemphigus vulgaris
4
INFECTIONS AND MALIGNANCIES
- Adverse drug reactions
- Stevens-Johnson syndrome - Carbamazepine, B1502
(Chinese) - Hypersensitivity syndrome - Abacavir, B5701
(Caucasians) - Sev cutaneus hypersens reactions, Allopurionol,
B5801 (Chinese) - Infections
- Lower rate progression to AIDS in HIV infected
individuals carrying B27 or B57 - Self-limiting HCV in DR11, DQ7 positive
individuals - HLA-B53 protects against severe malaria
- Malignancies
- Decreased frequency of B35 in gastric MALT
lymphomas
5
SOME HLA ASSOCIATED DISEASES
HLA
Frequencies ()
Patients
Healthy
Ank. spondylitis
B27
gt95
9
(Bechterews disease)
Narcolepsy
gt95
33
DQ6 (DQA10102, DQB10602)
Myasthenia gravis
50
27
DR3
Graves disease
65
27
DR3
Rheumatoid arthritis
80
33
DR4 (DRB10401/0404)
Celiac disease
95
26
DQ2 (DQA105,DQB102)
Multiple sclerosis
86
33
DQ6
Diabetes (type I)
DQ8
81
23
(DQA103,DQB10302)
DQ2 (DQA105,DQB102)
62
26
DQ6 (DQA10102, DQB10602)
lt0.1
33
Pemphigus vulgaris
DR4 (DRB10402)
Stevens-Johnson synd. (carbamazepine induced)
B1502
100
9
6
CLASSICAL HLA MOLECULES
a
b
b2m
a
HLA class II
HLA class I
7
CLASSICAL HLA MOLECULES
a
b
b2m
a
HLA class II
HLA class I
DP
DQ
DR
B
C
A
Series
Loci
B5
B3
B4
A
B
A
B
A
B1
A
A
A
8
CLASSICAL HLA MOLECULES
a
b
b2m
a
HLA class II
HLA class I
DP
DQ
DR
B
C
A
Series
Loci
B5
B3
B4
A
B
A
B
A
B1
A
A
A
190
2
400
42
45
19
Alleles
372
661
93
21
13
18
9
Figure 5-16
10
HLA MOLECULES PRESENT PEPTIDE ANTIGENS TO T CELLS
CD8
CD4
TCR
HLA class II
HLA class I
11
Reinherz et al, Science 1999
12
Stern et al, Nature 1994
13
Stern et al, Nature 1994
14
POCKET PROFILES OF SOME DR MOLECULES
Sturniolo et al, Nat. Biotech. 1999
15
HLA NOMENCLATURE -BY SEROLOGY AND GENOMIC TYPING
DQ2
DR3
16
HLA NOMENCLATURE -BY SEROLOGY AND GENOMIC TYPING
DQ2
DR3
DQA1 0501
DQB1 0201
DRB3 0101
DRB1 0301
DRA1
17
HLA NOMENCLATURE -BY SEROLOGY AND GENOMIC TYPING
DQ2
DR3
DQA1 0501
DQB1 0201
DRB3 0101
DRB1 0301
DRA1
18
HLA ALLELES ASSOCIATED WITH DISEASE PROBLEM OF
LINKAGE DISEQUILIBRIUM
DP1
DQ2
B8
A1
C7
DR3
C3
DQ8
B62
A2
DR4
DP
DQ
DR
B
C
A
Class II
Class I
HLA gene complex
19
MHC gene families
Chromosome 6
Thorsby Lie Transplant Immunol 2005
20
- The extended MHC (xMHC)
- 7.6 Mb
- 421 gene loci
- 252 predicted to be expressed
- Several gene clusters (12)
- Histone
- HLA class I
- tRNA
- Butyrophilin
- Olfactory receptor
- Tumour necrosis factor
- HLA class II
Horton et al, Nat Rev Genet 2004
21
Horton et al, Nat Rev Genet 2004
22
MECHANISMS OF ASSOCIATION VIA
- CLASSICAL HLA MOLECULES
- related to binding of specific peptide
- not related to specificity of peptide binding
NOT CLASSICAL HLA MOLECULES
23
CLASSICAL HLA MOLECULES
- Related to binding of specific peptides
- peptide binding preferences
- thymic selection
- Not related to binding of specific peptides
- drug adverse reactions
- HLA acting via NK cells
- unusual biology
24
LOCALIZATION OF PEPTIDE-BINDING
- In the periphery presenting peptide antigens to T
cells (peptide binding preferences and epitope
mimicry) - In the thymus presenting self peptide antigens to
T cells under education - positive selection - - negative selection
25
T CELL SELECTION
26
DIRECT MECHANISMS OF ASSOCIATION
- Related to binding of specific peptides
- peptide binding preferences
- thymic selection
- Not related to binding of specific peptides
- drug adverse reactions
- HLA acting via NK cells
- unusual biology
From M. Ráki
27
DRUG ADVERSE REACTIONS
Non-hapten
Hapten
Direct modification of proteins and/or
MHC-peptide complexes
Labile binding of drugs to TCR stabilzed by
MHC-peptide interaction
Posadas et al Clin Exp Allergy 2007
28
ANKYLOSING SPONDILYTIS (AS) AND HLA-B27
- Chronic inflammation sacroiliac joints (prev
1800) - AS not associated with all variants (n24) of B27
(not B2706 and B2709) - No good explanation why some B27 subtypes
predispose to AS others do not - Mechanism for HLA association
- Preferential peptide binding? Which peptide?
- Could it be a gene in linkage disequilibrium with
HLA-B27? - Could it be some other feature of HLA-B27?
29
UNUSUAL BIOLOGY OF HLA B27 I.
Could inefficient folding of HLA B27 heavy chain
lead to unfolded-protein response leading to an
inflammatory response?
Gaston Nat Clin Pract Rheum 2006
30
UNUSUAL BIOLOGY OF HLA B27 II.
Relative independence of HLA from tapasin ? HLA
B27 molecules that loaded with suboptimal
antigenic peptides ? dissociation on the cell
surface ? free HLA B27 heavy chains, which may
form disulphide-linked multimers, especially
dimers.
Gaston Nat Clin Pract Rheum 2006
31
NARCOLEPSY A NEUROLOGICAL DISORDER
- ? Sleep disturbances (prev 12000)
- Excessive daytime sleepness
- Cataplexy
- Sleep paralysis
- Hypnagogic hallucinations
- ? Very strong HLA association with DR2-DQ6
32
NARCOLEPSY PRIMARY HLA ASSOCIATION TO
DQA10102-DQB10602
Caucacians Japanese
DQB1 0602
DRB1 15
DQA1 0102
DRA1
90 -100
DRA1
African Americans
DQB1 0602
DQA1 0102
DRB1 15
DRA1
60
DRA1
DQB1 0602
DQA1 0102
DRA1
Non-DRB115
30
DRB1 15
DRA1
33
NARCOLEPSY PRIMARY HLA ASSOCIATION TO
DQA10102-DQB10602
Caucacians Japanese
DQB1 0602
DRB1 15
DQA1 0102
DRA1
90 -100
DRA1
African Americans
DQB1 0602
DQA1 0102
DRB1 15
DRA1
60
DRA1
DQB1 0602
DQA1 0102
DRA1
Non-DRB115
30
DRB1 15
DRA1
34
ABSENCE OF HYPCRETIN TRANSCRIPT IN LATERAL
HYPOTHALAMUS IN NACROLEPSY
NARCOLEPSY
CONTROL
34
Chabas et al Ann Rev Genomics Hum Genet 2004
35
NARCOLEPSY - HLA
SOME QUESTIONS WHY DISTURBANCES IN HYPOCRETIN
BALANCE? AUTOIMMUNE ATTACK TOWARDS HYPOCRETIN
PRODUCING CELLS? WHICH ANTIGEN DRIVES THE
IMMUNE RESPONSE?
36
CELIAC DISEASE
Genes
Environment
HLA
Gluten
37
CELIAC DISEASE
- Gluten (wheat) intolerance. (Prev. 1100)
- Inflammation small intesinal mucosa.
- Loss of intestinal villi.
- Malabsorption diarrhea. More often
extraintestinal symptoms (fatigue, osteoporosis,
anemia, infertility, depression, neurological
diseases). - ? Autoantiboides to transglutaminase 2 (TG2)
- Very strong HLA association (DQ2 and DQ8).
38
HLA ALLELES ASSOCIATED WITH CELIAC DISEASE THE
PROBLEM OF LINKAGE DISEQUILIBRIUM
DQ2
DR3
B8
A1
DP1
DP
DQ
DR
B
C
A
Class II
Class I
HLA gene complex
39
HLA-DR PHENOTYPES OF CELIAC PATIENTS
Norway
Italy-Sardinia
Italy-Bologna
England
Spain
Czechoslovakia
Argentina
Italy-Rome
DR3
DR5/DR7
Non DR3 and non DR5/DR7 -most are DR4(DQ8)
40
HLA ASSOCIATION CELIAC DISEASE
Those few CD pts who are DQ2 neg, are DR4DQ8 pos.
41
In DR4DQ8 pts, DQ8 restricted gluten reactive T
cells are found
42
GENERATION OF T CELL EPITOPES IN THE GUT
a2-gliadin 1 MVRVPVPQLQ PQNPSQQQPQ EQVPLVQQQQ
FPGQQQPFPP QQPYPQPQPF PSQQPYLQLQ 61 PFPQPQLPYP
QPQLPYPQPQ LPYPQPQPFR PQQPYPQSQP QYSQPQQPIS
QQQQQQQQQQ 121 QQKQQQQQQQ QILQQILQQQ LIPCRDVVLQ
QHSIAYGSSQ VLQQSTYQLV QQLCCQQLWQ 181 IPEQSRCQAI
HNVVHAIILH QQQQQQQQQQ QQPLSQVSFQ QPQQQYPSGQ
GSFQPSQQNP 241 QAQGSVQPQQ LPQFEEIRNL ALETLPAMCN
VYIPPYCTIA PVGIFGTNYR
LQLQ 61 PFPQPQLPYP QPQLPYPQPQ
LPYPQPQPF
Transglutaminase (QXPY)
43
THE CELIAC LESION
T-NK
T
TG2
TH1
IFN-?
APC
APC
TCR
TH1
CD4
T
T
HLA-DQ2 (or DQ8)
APC
T
44
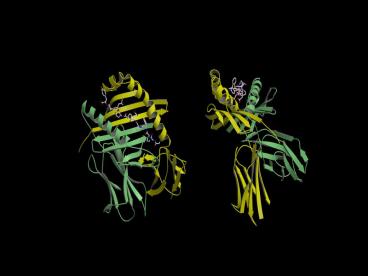
DEAMIDATED GLUTEN PEPTIDE CAUGHT IN THE ACT
X-ray crystal structure (2.2 Å resolution)
Kim et al PNAS 2004
45
HLA DISEASE
- For most diseases the involved HLA genes have not
been unequivocally identified - Classical, peptide-presenting, HLA molecules are
likely to be involved - For most diseases the antigens involved are
unknown - HLA molecules can both predispose to or protect
against disease development - HLA molecules can predispose/protect
- at the level of thymic selection of TCR
repertoire or - by presentation of antigens in the periphery
46
(No Transcript)
47
HLA typing and diagnosis of celiac disease
Sensitivity the fraction of celiac disease
patients with a positive test result.
Specificity the fraction of non-celiac
individuals with a negative result. PPV,
positive predictive value the probability that
the patient has the disease, given a positive
test NPV, negative predictive value the
probability that the patient does not have the
disease, given a negative test.