17th Century Microscopy - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 24
Title:
17th Century Microscopy
Description:
The cork cells Hooke observed may have looked similar to this. 18th Century Microscopy ... Mussel sea shell images. Fibrous texture of shell surface seen with SEM. ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:37
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: 17th Century Microscopy
1
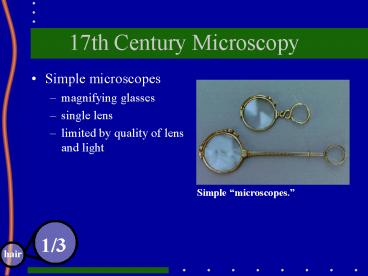
17th Century Microscopy
- Simple microscopes
- magnifying glasses
- single lens
- limited by quality of lens and light
Simple microscopes.
2
17th Century Microscopy
- Compound Microscopes
- Hans and Zacharias Janssen
- invented first compound microscope
- Robert Hooke
- looked at cork
- many common materials
3
18th Century Microscopy
- Antoni van Leeuwenhoek
- built over 500 microscopes only about 3 to 4
inches long with a single lens - viewed animalcules or beasties
- bacteria
- spermatazoa
- red blood cells
Leeuwenhoek
A beastie perhaps observed by Leeuwenhoek.
4
19th Century Microscopy
- Advances due to improved lenses
- Theodore Schwann
- cell is basic unit of life
5
19th Century Microscopy
- Advances due to improved light technology
- Solar microscope
- ultraviolet microscope
- ultraviolet fluorescence microscopy
- J.J. Thompson in 1897
- discovered the electron
6
20th Century Microscopy
- Max Rushka in 1931
- Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)
- VERY thin specimen
- Can not use living specimens
7
20th Century Microscopy
- Dennis McMullan in 1948
- Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
- metallic coated specimen that reflected back
electrons - 3-dimensional image
- can not use live specimens
SEM images provide 3-D details of the specimens
surface.
8
20th Century Microscopy
- Heinrich Rohrer and Gerd Binnig in 1982
- Scanning Probe Microscope (SPM)
- extends the sense of touch
- 1986 Nobel Prize with Max Rushka
9
Scanning Probe Microscopy
- Scanning Tunneling Microscope (STM) in 1982
- Atomic Force Microscope (AFM) in 1985
Atomic Force Microscope used at IN-VSEE lab.
10
Scanning Probe Microscopes
Use the sense of touch to create images .
11
Scanning Tunneling Microscope
- Requires an electrically conductive sample
- Small current will flow between tip and sample
surface - Current changes with the height of sample and
image is produced on this change
12
Atomic Force Microscope (AFM)
- Can be used to look at non-conductive samples
- bacteria and viruses
- computer chips and CDs
- Probe moves over sample surface and reads
repulsive force
Measures forces between atoms, between surfaces,
etc.
13
Views by different microscopes
- Mushrooms can be seen with out any magnification.
14
Views by different microscopes
- Cross-section through a mushrooms as seen with
light microscopy.
15
Views by different microscopes
- Mushrooms are composed of thread-like cells, like
this seen at a higher power with a light
microscope.
16
Views by different microscopes
- Organelles in the cell are more obvious in a TEM.
17
Views by different microscopes
- Using SPM, the 3-D surface of the spore-producing
basidium can be visualized.
18
Views by different microscopes
- The bud scars of a different kind of fungus, a
yeast cell, can be be visualized using SPM.
1/4
19
Snake images
20
Mussel sea shell images
Fibrous texture of shell surface seen with SEM.
Fibers at higher SEM magnification.
21
Mother of pearl sea shell images
Layers of plates in the shell SEM image.
22
AFM images
Horse hair.
Gold film.
23
AFM images
Bacterium from a dog dish.
Tungsten.
24
STM images
CD-ROM surface.
Video tape surface.