Sequential Circuit Analysis - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 13
Title:
Sequential Circuit Analysis
Description:
State tables show the inputs, outputs, and flip-flop state changes for sequential circuits. ... Design a two's complementer using J-K flip-flops ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:47
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Sequential Circuit Analysis
1
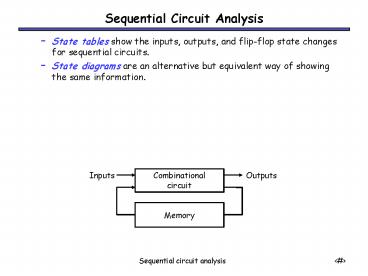
Sequential Circuit Analysis
- State tables show the inputs, outputs, and
flip-flop state changes for sequential circuits. - State diagrams are an alternative but equivalent
way of showing the same information.
2
How do you analyze a sequential circuit?
- For a combinational circuit we could find a truth
table, which shows how the outputs are related to
the inputs. - A state table is the sequential analog of a truth
table. It shows inputs and current states on the
left, and outputs and next states on the right. - For a sequential circuit, the outputs are
dependent upon not only the inputs, but also the
current state of the flip-flops. - In addition to finding outputs, we also need to
find the state of the flip-flops on the next
clock cycle.
3
Flip-flop input equations
- Finding the next states is harder. To do this, we
have to figure out how the flip-flops are
changing. - Step 1
- Find Boolean expressions for the flip-flop
inputs. - I.e. How do the inputs (say, J K) to the
flip-flops - depend on the current state and input
- Step 2
- Use these expressions to find the actual
flip-flop input values for each possible
combination of present states and inputs. - I.e. Fill in the state table (with new
intermediate columns) - Step 3
- Use flip-flop characteristic tables or
equations to find the next states, based on the
flip-flop input values and the present states.
4
Derive the state table and state diagram.
5
Derive the state diagram
6
Step 3 Find the next states
- Finally, use the JK flip-flop characteristic
tables or equations to find the next state of
each flip-flop, based on its present state and
inputs. - The general JK flip-flop characteristic equation
is - Q(t1) KQ(t) JQ(t)
- In our example circuit, we have two JK
flip-flops, so we have to apply this equation to
each of them - Q1(t1) K1Q1(t) J1Q1(t)
- Q0(t1) K0Q0(t) J0Q0(t)
- We can also determine the next state for
- each input/current state combination
- directly from the characteristic table.
7
Sequential circuit design procedure
- Step 1
- Make a state table based on the problem
statement. The table should show the present
states, inputs, next states and outputs. (It may
be easier to find a state diagram first, and then
convert that to a table.) - Step 2
- Assign binary codes to the states in the state
table, if you havent already. If you have n
states, your binary codes will have at least - ?log2 n? digits, and your circuit will have at
least ?log2 n? flip-flops. - Step 3
- For each flip-flop and each row of your state
table, find the flip-flop input values that are
needed to generate the next state from the
present state. You can use flip-flop excitation
tables here. - Step 4
- Find simplified equations for the flip-flop
inputs and the outputs. - Step 5
- Build the circuit!
8
Class example revisited
- 1) Find non overlapping sequence 1001. Design
using D-flipflops.
9
Blank Sheet
10
Design a twos complementer using J-K flip-flops
- InputX,Y. Input Sequence a binary number of
arbitrary length. Sequence represented by
sequential values of X. Output Z, the
corresponding bit in the twos complement. When
y1 gt the sequence is complete, Y0 gt
Sequence ongoing. - Solution The trick is in identifying that
whenever we compute a 2's complement, we
complement each bit and add a 1. So as long as we
keep receiving 0's, we complement them to convert
to 1's and then we add a 1. So until we hit our
first 1, we stay on the same state outputting
0's. As soon as we hit a 1, the complement for
that is a 0 to which we add a 1 getting a 1. And
then we have no carry so we move onto a state
where we just complement each bit we receive.
11
Blank Sheet
12
Excitation tables for all flip-flops
13
Summary
- The basic sequential circuit design procedure
- Make a state table and, if desired, a state
diagram. This step is usually the hardest. - Assign binary codes to the states if you didnt
already. - Use the present states, next states, and
flip-flop excitation tables to find the flip-flop
input values. - Write simplified equations for the flip-flop
inputs and outputs and build the circuit. - Next, well look at common examples of sequential
circuits, including different types of counters.