Disaccharides - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 25
Title:
Disaccharides
Description:
Heteropolysaccharides ?????????? monomer ??????? 2?????????? ... Ampicillin ( semisynthetic derivative ) R = aminobenzyl group. ?????: Voet and Voet, 1995 ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:390
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Disaccharides
1
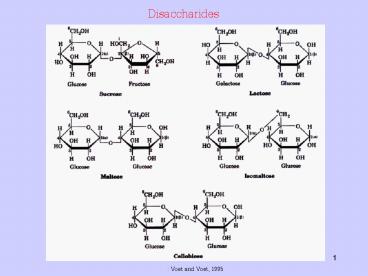
Disaccharides
????? Voet and Voet, 1995
2
Polysaccharides (Glycans)
Homopolysaccharides ?????????? monomer
?????????????? (starch, glycogen, cellulose and
chitin) Heteropolysaccharides ?????????? monomer
??????? 2?????????? (peptidoglycan)
????? Nelson and Cox, 2000
3
????? Nelson and Cox, 2000
4
Starch ??? Glycogen
a-amylose ???? linear polymer ???????? glucose
???????????????????????????? a(1 4) bonds
??????? isomer ??? cellulose
???????????? a-amylose ???? coiled helical
structure
????? Voet and Voet, 1995
5
Starch
Amylose chain ???????????????????????
glucose units ???????????????? a (1
4)glycosidic bond
????? http//ull.chemistry.uakron.edu/genobc/Chap
ter_17/
6
a (1 6) branch point
Amylopectin ??????????????? glucose
??? ????????????? a (1 4) bond
??????????????? ???? 24-30 ????? glucose ???? a
(1 6) bond
????? Voet and Voet, 1995
7
Glycogen
????? http//ull.chemistry.uakron.edu/genobc/Ch
apter_17/
8
Structural Polysaccharides Cellulose ??? Chitin
Cellulose ???? linear polymer ???????? D-glucose
??? 15,000 ????? (glucan) ?????????? b(1 4)
glycosidic bonds
????? Voet and Voet, 1995
9
b(1 4)-linked homopolymer of
N-acetyl-D-glucosamine
Chitin ?????????????????????????? exoskeletons
?????? invertebrates ???? crustaceans, insects
??? spiders ????????? ??????? cell walls ???
fungi ??? algae
????? Voet and Voet, 1995
10
Glycoconjugate carbohydrate ?????? protein ????
lipid ????
covalent bond
?????? proteoglycans, glycoproteins ???
glycolipids
Glycoproteins proteins ????????????
glycoproteins ?????? carbohydrates (1 ???? gt 1
????? oligosaccharides) ???? covalent bond
????????? carbohydrate ?????????? ??????? lt 1
??? gt 90 ?????????? ???? oligosaccharides ???
glycoproteins ???? recognition sites ?????
affinity ??????????? proteins ??????? Proteoglycan
s (Mucoproteins) ???? macromolecules ??? cell
surface ???? extracellular matrix ???
proteins(membrane proteins ???? secreted
proteins) ??? glycosaminoglycan 1 chain ???? gt
???????????? covalent ??? noncovalent bond
????????????????????????? connective tissue
???? cartilage Glycolipids ???? membrane
lipids ??? hydrophilic head groups
???? oligosaccharides ???????????????? specific
sites ?????? recognition ??? carbohydrate- binding
proteins
11
Glycosaminoglycans (Mucopolysaccharides)
Extracellular spaces ??? connective tissues ????
cartilage, tendon, skin ??? blood vessel walls
?????????? collagen ??? elastin fibers
??????gel-like matrix ??????????? ground
substance Ground substance ??????????
glycosaminoglycans ??????? unbranched
polysaccharides ???????? uronic acid ???
hexosamine
12
????? http//ull.chemistry.uakron.edu/genobc/Chap
ter_17/
13
????? Voet and Voet, 1995
14
????????? proteoglycan ??? integral membrane
protein
????? Nelson and Cox, 2000
15
Glycoprotein Structure ???????????????? sugar
??? protein
O-glycosidic bond ??? -OH group ???
Ser ??? Thr
Polypeptide chain
N-glycosidic bond ??? amide N
side chain ??? Asn
????? http//ull.chemistry.uakron.edu/genobc/Cha
pter_17/
16
????? Nelson and Cox, 2000
17
Bacterial Cell Walls
Cell walls ??? gram-positive ??? gram- negative
bacteria ?????????? peptidoglycan ???? murein
???????? polysaccharides ?????? polypeptide
chains ???? covalent bond
????? Voet and Voet, 1995
18
Peptidoglycan structural polysaccharide
Unbranched polymer ??? repeating disaccharide ???
N-acetylglucosamine ??? N-acetylmuramic acid
peptide crosslinks ?????????? polymers
????????????????????????? bacteria
????? http//ull.chemistry.uakron.edu/genobc/Cha
pter_17/
19
Cell wall peptidoglycan ??? S. aureus
Repeating unit ??? peptidoglycan
????? Voet and Voet, 1995
20
thiazolidine ring
Benzyl penicillin ( penicillin G ) R benzyl
group Ampicillin ( semisynthetic derivative )
R aminobenzyl group
b-lactam ring
????? Voet and Voet, 1995
21
Surfaces ??? gram-positive bacteria
?????????? teichoic acids ??????????????????????
50 ??? ?????????????? cell walls Teichoic acids
???? polymers ??? glycerol ????
ribitol ????????????? phosphodiester bonds
??????? teichoic acid glycerol phosphate
backbone ????????????? D-Ala ??? NAG
????? Voet and Voet, 1995
22
Almost all the secreted and membrane-bound
proteins of eukaryotic cells are glycosylated.
Protein Glycosylation 1. post-translational
modification.
2. oligosaccharides form 2 types
of direct
attachment to these proteins
2.1
N-linked oligosaccharides (N-glycosidic)
2.2
O-linked oligosaccharides(O-glycosidic)
23
N-linked oligosaccharides
N-glycosidic protein attachments occur through a
b-N-acetylglucosamino -Asn bond in which the Asn
occurs in the sequence Asn - X - Ser/Thr, X
any amino acid(except Pro or Asp)
N-linked oligosaccharides usually have the
branched (mannose)3(NAG)2 core.
????? Voet and Voet, 1995
24
N-linked oligosaccharides
????? Voet and Voet, 1995
25
O-glycosidic attachments of oligosaccharides to
glycoproteins
Disaccharide core b-galactosyl- (1 3)-a-
N-acetylgalactosamine a linked to the OH group of
Ser or Thr
(less common)
galactose or xylose
????? Voet and Voet, 1995