BIOCHEMISTRY Chapter 2 - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 53
Title:
BIOCHEMISTRY Chapter 2
Description:
CARBOHYDRATES Sugars and Starches. Carbohydrates are organic compounds that make up 1% of the cell's ... Disaccharides second group of Carbohydrates ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:112
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: BIOCHEMISTRY Chapter 2
1
BIOCHEMISTRY Chapter 2
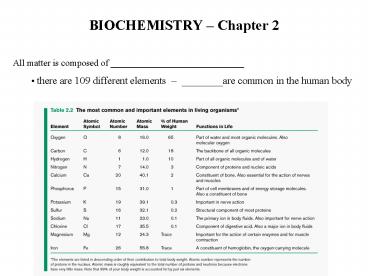
- All matter is composed of ________________________
_____ - there are 109 different elements ________are
common in the human body
2
What are Atoms/Elements made of?
Atoms are made of 3 subatomic particles
________________________ charge in atomic
nucleus ________________________no charge in
atomic nucleus ________________________ charge
in shells around nucleus
3
How do atoms differ from one another?
Atoms or elements differ by the ________________
_____________________ The number of protons is
the ___________________ 1 in hydrogen 8 in
oxygen 11 in sodium
4
Exceptions to normal atom
- An __________________ results when an atom gains
or loses electrons resulting in an electrical
charge - i.e. Na, Cl, Ca
- these are commonly found in humans when
compounds are digested - NaCl ? Na Cl
5
Molecules
- Atoms are joined together by chemical bonds to
form _________________________________________. - interactions between atoms lead to chemical
reactions in which the atoms are joined - we will observe several types of chemical bonds
as we study the many biochemicals of the living
organisms. - Most of the compounds of a living organism
contain lots of carbon and hydrogen - called
___________________________________________.
6
3 Types of Chemical Bonds
1. __________________________________ -
attraction between a positively charged ion and a
negatively charged ion i.e. Na
Cl NaCl
7
3 Types of Chemical Bonds
2. Covalent bond - different atoms
_______________________ with no change in
electrical charge i.e. Hydrogen
H2 Oxygen O2 Water H2O
8
3 Types of Chemical Bonds
- ______________________________ - bonds that form
between many hydrogen-containing molecules such
as water molecules joined together - _______________________________ may strengthen or
weaken hydrogen bonds
9
Chemical Reactions
A chemical reaction is a change in the atomic
composition and properties of molecules. reactan
ts products 2 types
of reactions a. ________________________________
____- water reacts with a large molecule to break
it into smaller units often releasing energy
chemical alteration
10
Chemical Reactions
- b. ________________________________________ -
small molecules are joined together releasing
water - dehydration often requires energy
- dehydration is the opposite of hydrolysis
11
Cell Energy
- The energy of the cell is ________________________
______________ - It is composed of _______________________________
_____________________________________________ - Energy is captured in ATP when ADP and a
phosphate group (P) are joined in a dehydration
reaction. - Energy is captured in the chemical bond between
the 2nd and 3rd phosphate groups
12
Cell Energy
Energy for cellular activities is due to release
of energy when the _______________________ group
is removed from ____________________________
13
Biomolecules of the Cell
The general chemical composition of a typical
cell is as follows
70 of the cell is _____________________. Water
is very important in many of the chemical
reactions that occur within a cell and many of
the other chemicals are in solution within
water. All other molecules (except minerals) are
____________ _______________________ chemicals
from living organisms with lots of carbon and
hydrogen elements.
lt1 nucleic acids lt1 carbohydrates 4
minerals 10 lipids 15 proteins 70 water
14
CARBOHYDRATES Sugars and Starches
- Carbohydrates are organic compounds that make up
lt1 of the cells chemicals. - Importance
- __________________________________________________
They are quickly metabolized to produce
cellular energy. - 2. ______________________________________________
____ - in form of grains (rice, wheat, corn,
oats), potatoes, and beans. - Composition C, H, O arranged in the ratio of C
H2 O (up to 10)
15
1st Group of Carbohydrates are the Monosaccharides
- 5-carbon monosaccharides
- ______________________________________________
form the 5-carbon monosaccharides - These molecules are important in the
composition of the nucleic acids - DNA and RNA
and in ATP. - We will examine them in more detail later when
we discuss the nucleic acids.
16
- 6-carbon monosaccharides simple sugars
- There are three 6-C monosaccharides - all with
the same chemical composition - C6 H12 O6 - but
different structural organization. - Chemicals having the same chemical composition
but different structural organization are called
structural _____________________________________ - The three 6-C monosaccharides are
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
17
Three 6-C Monosaccharides
Different structures of these isomers produce
significant changes in properties. i.e. fructose
is sweeter than glucose which is sweeter than
galactose.
18
Properties of Monosaccharides
- Monosaccharides are ______________________________
________________________________________________ - They are of ______________________________________
that they can easily pass through a cell
membrane to enter a cell. - They initially enter the cell by diffusion
- When the concentrations change, they enter cells
by active transport.
19
Glucose is most important monosaccharide
Glucose is the most common monosaccharide and the
most important nutrient molecule in animals. Why?
1. _____________________________________________
_ 2. ____________________________________________
________ C6 H12 O6 6 O2 ? 6 CO2 6
H2O ATP (cell
energy) This process is called
_________________________________ and will be
discussed in detail after we examine the
digestive system. Problem Glucose and the other
monosaccharides are not available in free form.
So where do they come from? _____________________
_________
20
Disaccharides second group of Carbohydrates
Disaccharides or double sugars contain two 6-C
monosaccharide units bonded together by
___________________________ (C12 H22 O11)
21
Three Disaccharides
(1) Maltose -____________________________________
_____ (2) Lactose - _____________________________
____________ (3) Sucrose - ______________________
___________________
22
Properties of Disaccharides
- Common sugars found ____________________________
- Molecular size of disaccharides is too large to
enter cell so? __________________________________
_______________ - 3. Disaccharides are broken down in the presence
of water - remember this is a ____________________
___________. This type of reaction is common in
the digestion of our food.
maltose water
glucose glucose
23
Polysaccharides third group of Carbohydrates
- These are large, insoluble carbohydrates composed
of ______________________________________ groups
joined together in a long chain. - Three important forms
- ______________________________
- (2) ______________________________
- (3)__________________________
24
Plant Starch
Plant starch consists of _________________________
________ _________________________________________
___________
25
Plant Starch
Plant starch is easily broken down by
______________________________ to produce many
_____________________________to be used by cells.
What is the glucose used for?
26
(2) Glycogen
Glycogen consists of _____________________________
__ _______________________________________________
_ Glycogen is stored in animal cells.
glucose
27
Properties of Glycogen
Glycogen is an important _________________________
__________________________ When
__________________________is taken into a cell,
it is condensed to form glycogen as an important
food reserve. glucose glucose glucose ..
glycogen H2O When glucose is
needed, glycogen is broken down by
__________________________________ to release
glucose for energy production. glycogen H2O
glucose glucose glucose
..
28
Use of glycogen as a glucose source
Glycogen is not only stored in skeletal muscles
and the liver of humans. It is also present in
the skeletal muscles and liver of
_________________________________ So if you eat a
piece of beef steak, you will ingest glycogen in
the skeletal muscle of the cow. glycogen H2O
glucose glucose glucose
.. So glycogen is another source of glucose
molecules for the cell.
hydrolysis reaction
29
(3) Cellulose
Cellulose consists of ____________________________
________ _________________________________________
____________ Glucose molecules are arranged as
Glu - - Glu - What results from this
arrangement? ________________________
__________________________________________________
___
Glu
Glu
Glu
Glu
30
Importance of Cellulose
Although cellulose cannot be used
as a source of
the glucose, it does form ________________________
_______. Why is this important in our
diet?________________________ ____________________
_______________________________ It is important
in helping us keep regular and may help prevent
__________________________________.
31
LIPIDS FATS AND STEROIDS
Lipids make up about 10 of the cell
components. Importance (1) part of
__________________________________ (2) some are
________________________________ (3) serve as
insulators against heat loss _________________ (4)
can be metabolized to make ____________
32
LIPIDS FATS AND STEROIDS
Three major groups of lipids 1. 2. 3.
33
Structure of a Triglyceride
Two components 1. __________________________-
C3 H8 03 2. __________________________ - long
chains of C and H with a carboxyl end
(-COOH) These components are joined together by
________________ _____________________________in
which water is released.
34
Triglyceride Structure
The bonds between glycerol and the 3 fatty acids
are called ______________ ________________________
_.
35
Two types of Triglycerides
- Saturated fat is ________________
- Common in ______________________________
- All carbon bonds of 3 fatty acids are filled
with hydrogens.
- Unsaturated fat is _______________
- Common in _______________________________
- Fewer H due to double bonds between some
carbons of the the 3 fatty acids.
36
Trans fat is another type of saturated fat
- A trans fat is made when manufacturers add
_______________________to vegetable oil - a
process called ____________________________ - This process changes the unsaturated fat to a
saturated fat. - This is done as hydrogenation increases the shelf
life and flavor stability of foods containing
these fats. - common in _____________________________
- ________________________________________
- no longer used by Wendys, Kraft foods, and
some local restaurants
37
Which one is good for the diet and
which one is bad for the
diet? ____________________________________________
_______ __________________________________________
_________ A diet rich in saturated fats commonly
leads to the synthesis of a steroid called
_____________________________________. Cholestero
l can form deposits in arteries and block blood
flow this is ___________________________________
. This greatly increases the possibility of a
__________________ _______________________________
_____.
38
Steroids
- Steroids form another type of lipid.
- They differ greatly from triglycerides
- interlocking rings of carbon molecules
- side groups of carbons filled with hydrogens.
- An important steroid is _________________________
___
We need some of this in our diets to form the
____________ __________________________ Problem?
39
PROTEINS
Proteins are organic compounds that form the
structural material of the cell make up about
15 of the cell 2 types of proteins (1)
_______________________________________ i.e.
hemoglobin - protein in red blood cells that
carries oxygen keratin - nails and hair
actin and myosin - muscle structure collagen
- connective tissue (2) _________________________
40
Protein Structure
The fundamental building block is an
______________________ Each amino acid is
composed of an amino group ____________ at one
end, a carboxyl group __________________at the
other end, and an R group. R groups are side
chains consisting of carbons and hydrogens.
Carboxyl group
Amino group
41
Amino Acids
There are _________________ different amino
acids that occur in nature. How do they differ?
______________________________________________
42
Formation of a Protein
A protein is composed of many amino acids joined
by _____________________________________. The
bonds between the amino groups are called
________________________.
4 amino acids
43
Formation of a Protein
- A chain of 2 to 100 amino acids is called a
_____________________ - A chain of over 100 amino acids is called a
____________________ - Primary structure consists of the sequence of
different amino acids bonded to each other in a
straight chain.
44
Formation of a Protein
A protein has a highly coiled structure
stabilized by ________________________ Coiling
produces a secondary structure, a tertiary
structure, and a quaternary structure. Hydrogen
bonds keep the ___________________ intact.
45
Denaturation of a Protein
____________________________will cause the
protein to ____________________________by
breaking these hydrogen bonds and exposing the
__________________________ of the protein (a long
chain of amino acids). The protein is no longer
functional, and if ingested, is easier to digest
into individual amino acids.
46
Protein Digestion
Proteins can be digested by hydrolysis reactions
Protein water ? __________________
water ? ________________ What are the amino
acids used for?
47
Enzymes second type of protein
Enzymes are specialized proteins that serve as
catalysts to _____________________________________
_________________ Each enzyme has an active site
with fits certain molecules called the
_______________________ These molecules bind to
the enzyme to form the ___________________________
___________________________
48
Enzymes second type of protein
The formation of the enzyme-substrate complex
lowers the ____________________ needed for a
chemical reaction to occur, and the reaction can
then occur rapidly to form a new product. Each
enzyme reverts to its original form after the
product is released. Thus, each enzyme can be
used many times.
49
Where do the enzymes come from?
All enzymes are made by the cell from
______________________ that enter after protein
digestion. We will discuss important digestive
enzymes when we discuss the digestive system
shortly.
50
Nucleic Acids
The nucleic acids are ____________________________
___ ______________________________________________
__ They make up less than 1 of cell
components DNA and RNA record ____________________
________ and pass it on to offspring in the form
of a chemical __________________________________.
We will discuss this in detail when we discuss
genetics later in the course.
51
Minerals Inorganic Ions (p. 340)
- The final group of biochemicals are the minerals.
- make up about 4 of cell components
- how do we get them? ____________________________
_ - broken down into _________________ that enter
cells. - necessary for many body functions.
52
Some Common Minerals
_______________________- bone structure, muscle
contraction, and blood clotting _________________
______- strong teeth _______________________ -
for thyroid hormone production __________________
_____- for hemoglobin formation _________________
______ enzyme function muscle nerve cell
function _______________________- bone
structure component of energy molecules
nucleic acids ___________________________________
__________- for nerve impulses __________________
_____ components of proteins
53
We should now have some idea of the many
biochemicals that occur in the human body.
- How we get these molecules into our bodies?
- What do we use these molecules for?
- We will now move to the Digestive System to
answer these questions. - THIS ENDS THE MATERIAL COVERED ON LECTURE EXAM I
ON MONDAY.