Prejudice - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 24
Title:
Prejudice
Description:
Prejudice - negative attitude, feeling or action tendency that is expressed ... Affective or emotional dimension - negative feelings such as hatred or anger ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:56
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Prejudice
1
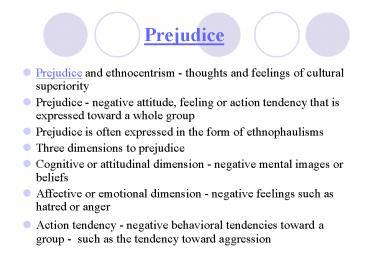
Prejudice
- Prejudice and ethnocentrism - thoughts and
feelings of cultural superiority - Prejudice - negative attitude, feeling or action
tendency that is expressed toward a whole group - Prejudice is often expressed in the form of
ethnophaulisms - Three dimensions to prejudice
- Cognitive or attitudinal dimension - negative
mental images or beliefs - Affective or emotional dimension - negative
feelings such as hatred or anger - Action tendency - negative behavioral tendencies
toward a group - such as the tendency toward
aggression
2
Hate Crimes
- Hate crimes statistics act became law in 1990
- Crime motivated in whole or part by the
offenders bias - Race
- Religion
- National origin/Ethnicity
- Sexual orientation
3
Discrimination and Prejudice
- Discrimination - behavioral pattern that excludes
a group from the same opportunities - Prejudice is an attitude - discrimination is a
behavior - The relationship between prejudice and
discrimination is complex - Richard LaPieres - 1930-1932 study and travels
with a Chinese couple across the United States - Robert Mertons study and typology of the
relationship between prejudice and discrimination
4
Figure 2-3 Prejudice and Discrimination
5
(No Transcript)
6
Theories of Prejudice and Discrimination
- Scapegoat theory - occurs when an individual
(group) projects and blames their own
inadequacies or problems onto another group - Of biblical origin
7
Criticisms of Scapegoat Theory
- Fails to explain why one group is used as a
scapegoat and not another - Fails to explain why two individuals who share
the same experience vary in tolerance - Does not explain personality differences
8
Authoritarian Personality Theory
- Adorno et al 1950 study of authoritarianism and
prejudice Authoritarian traits - Rigid adherence to conventional values
- Uncritical acceptance of authority
- Power and toughness
- Intolerance and aggressivity toward those that
dont conform to conventional values
9
Criticisms of the Theory
- Focus on right wing groups and ignored left wing
groups - Prejudice is related to other traits such as
social class - Methodology employed
- Focused on only extreme forms of prejudice and
not on other forms of prejudice
10
Exploitation Theory
- Exploitation theory - prejudice is rationally and
economically motivated on the basis of self
interests - The dominant group benefits from prejudice in
that it is rooted within the exploitation of a
group
11
Criticisms
- Not all subordinate groups are exploited equally
- Prejudice occurs for reasons other than economic
- Prejudice is not necessarily rational and may
undermine dominant group interests
12
Normative Approach
- Normative approach - prejudice is patterned into
the cultural norms and values of a group or
society - Prejudice is a function of conforming to group
norms of intolerance - All four views contributed to our understanding
of prejudice
13
Content of Prejudice Stereotypes
- Stereotypes - are generalizations that are
attributed to an entire category - Stereotypes are often exaggerated and negative
images of a group - Stereotypes come from a variety of sources
- a kernel of truth
- the media
- but power plays a role in their effect
14
Content of Prejudice Stereotypes
- Trends in Stereotypes
- Stereotypes often become a self-fulfilling
prophecy - Affect how we feel
- Affect how we relate to others
- Ignore facts that contradict ones belief system
- Inter-group patterns and stereotypes
- Stereotyping In Action Racial Profiling
- Racial Profiling any police action based on
race, national origin rather than a persons
behavior
15
Extent of Prejudice
- It is difficult to quantify the extent of
prejudice between groups - Measure the relative extent of prejudice between
groups - One measure is Emory Bogarduss Social Distance
Scale - used to measure the relative extent of
prejudice between groups
16
Example of Items on the Bogardus Scale
- To close kinship by marriage (1.00)
- To my club as personal chums (2.00)
- To my street as neighbors (3.00)
- To employment in my occupation (4.00)
- To citizenship my country (5.00)
- As only visitors to my country (6.00)
- Would exclude from my country (7.00)
17
(No Transcript)
18
Figure 2-4 What is the State of Race Relations?
19
The Mood of the Oppressed
- Prejudice and its affect on the self esteem of
the subordinate group - Prejudice affects perceptions on fairness or
equality of opportunity - Jobs
- Housing
- Justice
20
Intergroup Hostility
- Inter-group hostility - content and extent of
prejudice and stereotypes between ethnic - racial
groups - Subordinate - Subordinate patterns of prejudice
and stereotypes - Sources of intergroup hostility
21
Reducing Prejudice
- Mass media and research
- Experimentally created situations
- Influence of movies
- Television
- Advertising
- Media has had both positive and negative effects
depending on the program, situation and subjects
exposed.
22
Reducing Prejudice continued
- Education and research
- Well constructed programs tend to have an impact
on reducing prejudice but to be effective they
have to address the cognitive, affective and
action tendency dimensions - Some programs only focus on the cognitive or
affective - Formal education is related to a reduction in
prejudice - Formal education may not reduce prejudice
uniformly within a group.
23
Reducing Prejudice continued
- Equal - Status Contact - intergroup contact with
people of equal status under positive situations
tends to reduce prejudice - Corporate response Diversity Training
- Diversity training in the workplace
- Aimed at eliminating barriers that groups
encounter to receive rewards - Effective diversity training is integrated
throughout the organization
24
Ways to Fight Hate
- 1. Act
- 2. Unite
- 3. Support the Victims
- 4. Do your Homework
- 5. Create an Alternative
- 6. Speak Up
- 7. Lobby Leaders
- 8. Look Long Range
- 9. Teach Tolerance
- 10. Dig Deeper















![Download [PDF] Passion and Prejudice: A Family Memoir (Appla PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10089175.th0.jpg?_=20240731011)












![Download Book [PDF] WITHOUT PREJUDICE, Refutal of Chief J.A Nsirim and Rejoinder to Chief B.E [PDF] PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10122308.th0.jpg?_=20240906119)

