Agenda, 92903 - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 29
Title: Agenda, 92903
1
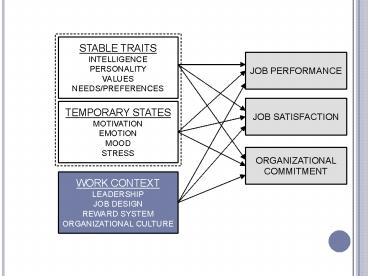
STABLE TRAITS INTELLIGENCE PERSONALITY VALUES NEED
S/PREFERENCES
JOB PERFORMANCE
JOB SATISFACTION
TEMPORARY STATES MOTIVATION EMOTION MOOD STRESS
ORGANIZATIONAL COMMITMENT
WORK CONTEXT LEADERSHIP JOB DESIGN REWARD
SYSTEM ORGANIZATIONAL CULTURE
2
True/False - Motivation
- Money is the best motivator.
- Highly motivated individuals will always
outperform low motivated individuals. - Managers do not need to focus on motivation until
they sense it is lost. - Motivating high performers is harder than
motivating low performers.
3
Motivation and Performance
- Weve observed lots of cases in which motivation
has affected performance - It is assumed
- High Motivation ? High Performance
- Performance ? (Ability x Motivation)
4
Motivation
- Reflects an employees choice regarding
- Whether to expend effort directed towards tasks
that affect performance - The level of effort to expend
- Whether to persist with the level of effort that
is chosen
5
Job Characteristics
- Five characteristics shape motivation
satisfaction - Skill variety extent to which job requires use
of a variety of skills and abilities - Task identity extent to which a person is
responsible for a job from beginning to end - Task significance extent to which work has
meaning for employee or society - Autonomy freedom a person has in his or her job
- Feedback timing and clarity of information
regarding performance
6
Job Characteristics
7
Job Characteristics
- How can a manager enhance a jobs
- Skill variety
- Task identity
- Task significance
- Feedback
- Autonomy
8
Promote Satisfaction through Mental Challenge
- One clear aspect of the work environment
consistently influences job satisfaction the
intrinsic challenge present in the work itself - Mentally challenging work is critical to
judgments of job satisfaction and expressions of
motivated behavior - When employees rate different facets of their
jobs, the nature of the work generally emerges as
the most important job facet - Of the other facets pay, promotions, etc.
satisfaction with the work itself best predicts
overall job satisfaction
9
How to increase mental challenge in jobs
- Job rotation
- Allow employees to perform different jobs
- Job enlargement
- Expand the number of tasks
- Job enrichment
- Increase the responsibilities
10
Exceptions to the Principle
- Growth Need Strength plays an important factor
- Mentally challenging jobs are important for those
with High Growth Need Strength (not for those
with Low GNS) - All else being equal, high GNS employees prefer
jobs that are challenging and interesting - Job Characteristics ? Job Satisfaction
- High GNS, r JC-JS .58
- Low GNS, r JC-JS .32
- Employees value other job attributes
- e.g., Job values, individual needs (affiliation,
power)
11
Summary
- Performance f (Ability x Motivation)
- In general, theories of motivation fall into 2
categories - Need theories emphasize satisfaction of basic
individual needs (preferences) - Maslows Hierarchy, McClelland (nACH, nPOW, nAFF)
- Job Design Theories emphasize work conditions
- Hertzberg, Job Characteristics
12
Why does this matter?
- One of the managers primary responsibilities is
to motivate employees - Employees are motivated for different reasons so
its important to know all motivational options - Effectiveness of motivational techniques changes
with the situation - What works when performance is high may not work
when performance is low - What works in a crisis situation may not work
when work environment is stable
13
The FCAT and teacher behavior
- How good is the FCAT as a measure of student
performance? Teacher performance? - Is itReliable? Valid? Strategically congruent?
- How does FCAT testing influence teacher behavior?
- To what extent does the reward system play a role
in shaping behavior/policy? - Motivating teachers for FCAT performance
14
Reinforcement TheoryThe theory of Punishments
Rewards
Suggests that Behavior is a function of its
consequences and the schedule of reinforcements
- Positive Reinforcement
- Praising an employee using incentives
- Negative Reinforcement
- Stopping at a red light to avoid a traffic fine
- Punishment
- Negative consequences (work on the weekend) are
applied - Extinction
- Extinguishing a reinforcement that maintains a
specific behavior
15
The Folly of Rewarding A, while Hoping for B
- Steven Kerr (1975)
- Whether dealing with monkeys, rats, or human
beings, it is hardly controversial to state that
most organisms seek information concerning what
activities are rewarded, and then seek to do (or
at least pretend to do) those things, often to
the exclusion of activities not rewarded (p.
769). - Academy of Management Journal 18 (1975), pp.
769-783
16
Rewarding A, Hoping for B
- Politics
- Official goals are purposely vague and general
(i.e., build better schools, lower taxes) - These goals are designed to offend no one and
are considered low quality, high acceptance. - Higher quality goals (i.e., those which specify
where the money will come from) suffer lower
acceptance. - The voting public wants public officials to be
perfectly clear, but describing clear goals is
not accepted or rewarded.
Are voters hoping for goal clarity but rewarding
vagueness?
17
Rewarding A, Hoping for B
- War
- An inherent conflict in battle
- The primary goal of the military organization?
to win - The primary goal of individuals on the front
line? - to get home alive
- Perfectly rational behavior by those on the front
lines would endanger goal attainment
18
Rewarding A, Hoping for B
- War
- World War II
- What did the GI want? To go home
- When did he get to go home? When the war was won
- Soldiers obey orders to facilitate the end of war
- Vietnam
- What did the GI want? To go home
- When did he get to go home? When his tour of duty
was over - Soldiers disobey (or avoid) orders that
jeopardize personal interests
Was the military implementing a system that
rewarded disobedience, while hoping that soldiers
would obey orders?
19
Rewarding A, Hoping for B
- Conclusion
- Managers who complain that their workers are not
motivated might do well to consider the
possibility that they have installed reward
systems which are paying for other behaviors that
those they are seeking
20
Goal-Setting Theory
- A person with higher goals will do better than
someone with lower goals - Difficult goals, when accepted, result in higher
performance than easy goals - In general, specific goals increase performance
(rather than Do your best) - People do better when they get feedback on how
well they are progressing towards their goals
21
Goal-Setting Theory
- Has been validated across all job categories
- (postal workers, loggers, engineers, sales reps)
- Presupposes that the goal is attainable
- (unattainable goals may reduce effort)
- Suggests that goal commitment increases when
employees participate in goal-setting process - When is goal setting ineffective?
- Goal setting does not necessarily generalize
across cultures - Performance vs. Learning Goals?
22
Why introduce all these approaches to motivation?
- Each makes a contribution to our understanding of
motivated behavior (i.e., each helps to explain
behavior) - As managers, we need to have lots of motivational
knowledge in our toolboxes (i.e., the same
motivational techniques do not work for everyone
all the time) - Practical value of this discussion?
- Recognition that motivation is both internal
(need) and external (job characteristics,
rewards, goals)
23
Another Explanation of Motivated Behavior
- Job Design
- Job Characteristics
- Goals
- Rewards/Consequences
- Individual Needs
- Self Efficacy
- An individuals belief about his or her own
capability to produce designated levels of
performance
24
Self Efficacy
- People with high self efficacy
- Approach difficult tasks as challenges to be
mastered rather than as threats to be avoided - Set challenging goals and maintain strong
commitment to those goals - Quickly recover their sense of self efficacy
after failure or setback - Attribute failure to insufficient effort or
deficient skills (which can be developed)
25
Self Efficacy
- People with low self efficacy
- Doubt their capabilities and shy away from
difficult assignments - Exhibit weak commitment to goals
- When faced with difficult situations, dwell on
personal deficiencies and on the obstacles that
will be encountered along the way - Are slow to recover from failure or setback
- Fall victim to stress
26
Sources of Self Efficacy
- Mastery Experiences
- Gaining relevant experience with the task or job
- Vicarious Experience
- Becoming more confident because you see someone
else doing the task VE is most effective when
you see yourself as similar to the person you are
observing - Social Persuasion
- Motivational speech convinces you that you have
the skills necessary to be successful - Physiological and Affective States
- Emotional arousal leads to an energized state
the person gets psyched up and improves
performance
27
Self Efficacy in the Workplace
- Smart managers and coaches
- Create situations that ensure small, progressive
wins - Utilize training programs encourage enactive
mastery - Find and utilize good role models
- Show how effort is related to outcomes
- In the early part of learning
- Stay close to those with low self efficacy
- Distinguish between process and performance goals
- Consider the consequences of failure for those
with high and low self efficacy
28
Self Efficacy in the Workplace
- Managers can use verbal persuasion through the
- Pygmalian Effect
- A form of self-fulfilling prophecy where
believing in something to be true can make it
true. - Teachers who were told that their students had
very IQ scores expected more of the students and
gave them more challenging assignments ? high
student self efficacy - Galatea Effect
- Occurs when high performance expectations are
communicated to directly to the employee.
29
STABLE TRAITS VALUES NEEDS PREFERENCES
MOTIVATION
A Summary of our discussion on Motivation








![get⚡[PDF]❤ Pocket Planner 2024-2025: Small 2-Year Monthly Agenda for Purse | 24 Months PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10081698.th0.jpg?_=20240719098)
![[PDF] DOWNLOAD Agenda 2021: Poker, crâne | Janvier à Décembre 2021 | A PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10095955.th0.jpg?_=20240811046)




















