Cardiovascular Anatomy - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 18
Title:
Cardiovascular Anatomy
Description:
Systemic circulation passes blood through the arteries, capillaries, ... Detecting surge of blood with fingers (palpation) Electronic recording and analysis ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:48
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Cardiovascular Anatomy
1
Cardiovascular Anatomy
2
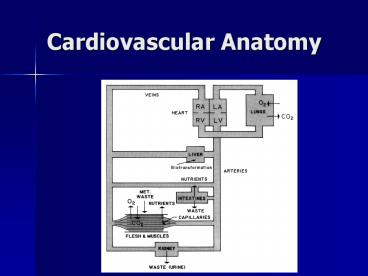
Cardiovascular Anatomy
- Pulmonary circulation passes blood through the
heart and lungs. - Systemic circulation passes blood through the
arteries, capillaries, and veins. - Blood transfers gases, compounds, and heat.
3
Cardiovascular Anatomy
- If legs are immobile, blood pools in them (venous
pooling) - Walking decreases ankle venous pressure.
- Walking aids blood circulation.
- Active standing is less uncomfortable than
standing.
4
Cardiac Output
- Output of left ventricle
- CO HR SV
- Basal cardiac output
- COBASL CI DBSA
- Activity cardiac output
- COACT CLMW TOTMET
5
Blood Pressure
- The pressure blood puts on the blood vessel
walls. - Systolic pressure diastolic pressure pulse
pressure. - To estimate
- SBP 101.3 .68 AGE
- DBP 63.7 .36 AGE
6
Metabolism
- Basal metabolism maintains body temperature,
body functions, blood circulation. - 1.28 W/kg for males
- 1.16 W/kg for females
- Activity metabolism provides energy for
activities - Very light work lt100 W/m2
- Light work 100 165 W/m2
- Moderate to heavy work 165 W/m2
- Digestion metabolism accounts for transformation
of food
7
Metabolism and Body Weight
- Basal metabolism body weight .86
- Activity metabolism hours body weight
.86 - Digestion metabolism
- Daily calorie requirement
- Eating more or less results in weight gain or
loss.
8
Body Mass Index
- BMI ( Weight in Pounds (Height
in inches) x (Height in inches)) x 703
BMI
9
Responses to Exercise
- Heart rate
- Stroke volume
- Arteryvein differential
- Blood distribution
- Going into debt
10
Measuring Heart Rate
- Shining light on artery in earlobe
- Listening to sound through stethoscope
- Detecting surge of blood with fingers (palpation)
- Electronic recording and analysis
11
Stroke Volume
- Amount of blood pumped through left ventricle
- Adjusts oxygen supply to the body
- Depends on exertion, body posture, exercise, and
physical fitness - Peaks at about 40 of maximum oxygen consumption
12
ArteryVein Differential
- Difference between oxygen content of blood in
arteries and blood in veins - Increases in emergencies to up to 13 mL
- Normal coronary blood arteryvein differential is
17 mL
13
Blood Distribution
- During exercise, capillary density and muscle
blood flow increase. - Cramps may result from reduced digestion.
14
Going into Debt
- Muscles draw on anaerobic oxygen stored in blood
- Anaerobic supply is limited and must be repaid
15
Cardiovascular Limits
- Individuals work capacity is determined from
maximum oxygen uptake (VO2max). - VO2max is product of cardiac output and AV
differential. - Determined from treadmill or ergonometer test,
step test, or walk/run test. - Testing for screening purposes is controversial.
16
Cardiovascular Limits
- What proportion of capacity is reasonable for
work? - Avoid anaerobic metabolism
- 50 for trained workers
- 33 for untrained workers
- Reduce for longer shifts.
- Mechanize high metabolic rate jobs.
- Reduce cardiovascular stress
- Engineering solutions (motors, wheels, balancers)
- Administrative solutions (job rotation, part-time
work)
17
Gender, Age, and Training Effects
- Average female VO2max 1530 lower than males.
- Industrial tasks should not require max output.
- VO2max decreases approx. 12/yr after age 25.
- Most of decline due to low physical activity and
increased body fat, not age itself. - Fitness can improve cardiovascular endurance,
muscle strength, and flexibility. - If work loads muscles dynamically, relax and
stretch them. - If work loads muscles statically, exercise should
move them.
18
Responses to Mental Work
- Mental load can be measured by heart rate
variability. - Low variability corresponds to high mental load.