Introduction to - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 12
Title:
Introduction to
Description:
When R0 = 1, disease is in equilibrium (endemic) S = (b*L)-1 ... Endemic (t=e) Se = 1/(b*L) Proportion to immunize: PV = (S0 Se) / S0 = 1 Se/S0 = 1 1/R0 ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:52
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Introduction to
1
Introduction to Epidemology
The Population Dynamics of Disease
2
Lecture Goals
- The S.I.R. model
- background
- conceptual model
- quantitative model
- Herd Immunity
- disease dynamics
- vaccination for disease eradication
3
The S.I.R. Model
- tracks disease through host effects
- three types of host
- Susceptible (S)
- Infected (I)
- Recovered (R)
- some period of immunity after infection)
- instantaneous model
- 3 ordinary differential equations
- no lags, but many diseases have incubation
- a starting point for many current models
4
The S.I.R. Model
Infected
Susceptible
Recovered
5
Change in the Susceptible Componentof the Host
Population
dS/dt b(SIR) - dS bSI gR
b(SIR) new births (lack immunity) dS natural
mortality bSI infection (density
dependent) gR loss of immunity
S, I, and R are the numbers of each population
component (variables). b, d, b, and g are the
rate parameters for each process.
6
Change in the Infected Componentof the Host
Population
dI/dt bSI (adn) I
bSI new infections (adn) I loss from -
disease induced mortality (a)
(virulence) - natural mortality (d) -
recovery (n)
Recovered individuals are immune.
7
Change in the Recovered Componentof the Host
Population
dR/dt nI (dg) R
nI newly recovered from infection (dg)
R loss from - natural mortality (d) - loss of
immunity (g)
8
The Classic S.I.R. Model
dS/dt b(SIR) - dS bSI gR
dI/dt bSI (adn) I
dR/dt nI (dg) R
bd
bgtd
9
Population Dynamics of the Disease
R0 net reproductive rate of the disease bSL
S number of susceptible hosts b infection
rate as in SIR model L life expectancy of
infected host (adn) 1 from the SIR model
representing the lose of infected individuals
by mortality and recovery
What can we do with such a simple model?
10
When R0 gt 1, disease is increasing (epidemic)
When R0 1, disease is in equilibrium (endemic)
S (bL)-1
When R0 lt 1, disease is in decline (eradication)
S (bL)-1 is the threshold value of the
infection.
The threshold value indicates the number of
susceptible hosts required for the disease to
spread.
11
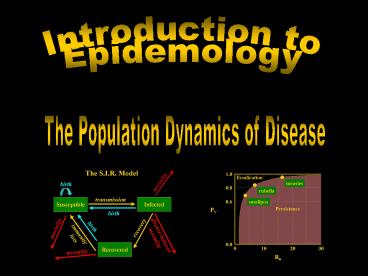
Herd Immunity
R0 bSL S R0/(bL)
Initially (t0) S0 R0/(bL) After successful
immunization R0 1 Endemic (te) Se
1/(bL) Proportion to immunize
PV (S0 Se) / S0 1 Se/S0 1 1/R0
12
1.0
Eradication
measles
0.8
rubella
0.6
smallpox
Persistence
PV
0.0
0
30
10
20
R0