Attitude Behavior Review - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 17
Title:
Attitude Behavior Review
Description:
racial attitudes/interracial behavior. social movements. Behavior. Attitudes ... Justify behavior to reduce internal tension. Infer own attitudes from ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:99
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Attitude Behavior Review
1
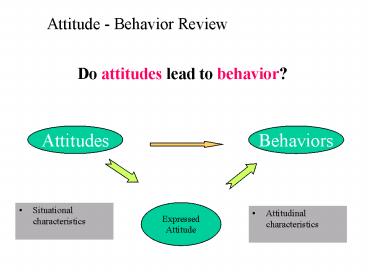
Attitude - Behavior Review
Do attitudes lead to behavior?
Attitudes
Behaviors
Expressed Attitude
- Situational characteristics
- Attitudinal characteristics
2
Does behavior lead to attitudes?
Behavior
Attitudes
- role playing
- saying becomes believing
- foot-in-the-door phenomenon
- evil acts/attitudes
- racial attitudes/interracial behavior
- social movements
3
Why do actions/behavior influence attitudes?
Behavior
Attitudes
- self presentation
- self-justification
4
Insufficient Justification Effect
Behavior
Attitudes
5
Cognitive Dissonance
Behavior
Negative Consequences
Little/No Dissonance
Self Responsible?
Little/No Dissonance
Dissonance Arousal
Attributed to own behavior
No Attitude Change
Self-justifying attitude change
6
Why do actions/behavior influence attitudes?
Behavior
Attitudes
- self-revealing
7
Self-Perception
Behavior
No external Reward
External Reward
.because I am rewarded
.because I like it
Intrinsic motivation
Extrinsic motivation
8
- cognitive dissonance versus self-perception
Cognitive Dissonance
Self-perception
Assumption
Justify behavior to reduce internal tension
Infer own attitudes from observing our behavior
Predictions
Same
Same
Applicability
Flexible enough to fit most research findings
Flexible enough to fit most research findings
Outcome?
Applies in dissonance arousing situations when
we contradict clearly defined attitudes
Applies in non-arousing situations when our
attitudes are ambiguous or unclear
Explains
Attitude change
Attitude formation
9
Why you change your mind
10
General Topic Area
- Social Influence
- change in overt behavior caused by real/imagined
pressure from others - conformity
- compliance
- obedience
- Persuasion
- change in private attitudes and belief as a
result of having received a message
11
Persuasion - changing others attitudes...
- self-perception and cognitive dissonance apply to
others - Can persuade others to change attitudes via
- action (B)
- argument (C)
- appearance (A)
- Persuasion change in private attitude/belief as
a result of receiving a message - Compliance behavior change as the result of a
direct request
12
In general, Greater external pressure leads to
greater compliance with ones wishes
- Raw physical force
- Milgram---Obedience to authority
- There are times when it is difficult to apply
this pressure for ethical, moral or practical
reasons - Factors other than external pressure are critical
in determining degree of compliance
13
Foot in the Door Phenomenon
- Tendency for people who have first agreed to a
small request to comply later with a larger
request - if you give them an inch theyll take a mile
- Once a person has agreed to any action, no matter
how small or trivial, he/she tends to feel more
involved
- Attitude of a person may shift regarding
situation or saying Yes - Dissonance between attitude action
- See yourself as the kind of person who does that
sort of thing
14
Factors leading to foot in the door phenomenon
- Low Ball Technique -
- tactic used to get people to agree with something
by offering a low initial request and then
raising it before the deal is done, - i.e.
- Role playing -
- Person tries to comply with a set of norms that
define how people should behave in a situation, - i.e.
15
Door in the Face
- Opposite of Foot-in-the-Door technique.
- After turning down a large request, one is more
likely to comply with a lesser counter-offer when
presented - Mutual concession critical-in order to proceed,
perceived compromise - i.e..
16
Advantages/Disadvantages
- Advantages
- Easy to induce compliance
- Not limited to receipt of small favors (first
request just has to be smaller/larger) - Works because of existing social norms.
Requester need not know or have power over
target, work within normal social rules - Can produce positive outcomes for both
17
Advantages/Disadvantages
- Disadvantages
- only had been tested under limited conditions
- requests have only been pro-social
- may have been other factors leading to compliance