Uracil PowerPoint PPT Presentations
All Time
Recommended
Uridine monophosphate UMP Uridine, U Uracil, U Uridine monophosphate UMP Uridine, U Uracil, U ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
RNA & Protein Synthesis Ribose RNA Hydrogen bonds Mrs. Stewart Biology I Uracil Adenine
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
... uracil Adenine bonds to uracil Guanine bonds to cytosine RNA gets its code from the DNA code 3 types of RNA Messenger (mRNA) carries protein building ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
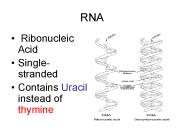
RNA Stands for Ribose Nucleic Acid Single stranded Contains a ribose sugar Uracil instead of thymine, so adenine bases with uracil RNA s Purpose To take ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Chemistry of Life Levels of Chemical ... avocados, barley, brazil nuts, blackstrap molasses, carrots, buckwheat ... thymine, or uracil, guanine, cytosine) DNA ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
From Genes to Proteins DNA and RNA differ in 3 ways RNA Single-stranded Ribose (sugar) Uracil (base) bonds to Adenine DNA Double-stranded Deoxiribose (sugar ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
RNA Ribonucleic Acid Single-stranded Contains Uracil instead of thymine RNA RNA like DNA is composed of Nucleotides 5 carbon sugar (ribose) phosphate group ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
RNA and Protein Synthesis I. RNA Formed from nucleotides Single stranded Uracil instead of thymine Sugar Ribose Copies the DNA info for protein synthesis 3 Types of ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
The Chemical Basis for Life Chapter 2 RNA Consists of only one strand of nucleotides. Does not have thymine, but instead has uracil. Pairings are: Guanine and ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
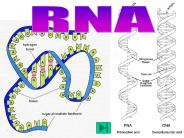
RNA (Ribonucleic acid) Structure: Similar to that of DNA except: 1- it is single stranded polyunucleotide chain. 2- Sugar is ribose 3- Uracil is instead of thymine
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Single nucleotide strand Sugar: Ribose 4 Bases: A: Adenine G: Guanine C: Cytosine U: Uracil U replaces T Three Types of RNA mRNA Function: Copies the DNA code and ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
RNA and Protein Synthesis RNA RNA Ribonucleic Acid Single stranded nucleotide chain DNA s Thymine is REPLACED by Uracil A & T break up because of the new ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Agenda * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Vocabulary Words RNA Codon Anticodon Amino Acid Intron Polypeptide Exon Uracil Gene Ribosome Enzyme Transcription ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
* * * * * * * * * * BS-seq: genomic DNA is treated with sodium bisulphite (BS) to convert cytosine, but not methylcytosine, to uracil, and subsequent high-throughput ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Introduction to Biocomputing: Structure (DNA & RNA) DNA the double helix DNA direction RNA: Thymine (T) replaced by Uracil (U) and deoxyribose ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
DNA Structure. When forming the double helix these nucleotides only bond with the opposite type. ... The bas thymine in DNA is replaced by uracil in RNA. RNA Structure ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
There are many different types ... U stands for Uracil . a different nitrogen base RNA Nitrogen Bases: A bonds with U C bonds with G THYMINE in RNA!!
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
RNA Ribonucleic Acid Structure of RNA Single stranded Ribose Sugar 5 carbon sugar Phosphate group Adenine, Uracil, Cytosine, Guanine Types of RNA Three main types ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Meischer, 1869 - isolated white powder he called nuclein from nucleus of cells ... Ribose sugar. Phosphate. Uracil instead of Thymine, Uracil complementary to Adenine ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Excessive amounts of dUTP cause the incorporation of uracil ... Non-primate Lentiviruses. HIV. RSV. HTLV-like viruses. pol gene. Herpesviruses: Poxviruses: ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Commiphora mukul Guggulsterone. Sap from the guggul tree, a species native to ... Nucleosides reported in Cordyceps include adenosine, uracil, uridine, guanine, ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
DNA self replicates before cell division. The DNA strand opens and will add ... How is RNA different than DNA? Ribose Sugar. Uracil for Thymine. Single strand ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Role of nucleic acids in cells There are 5 different bases: adenine, cytosine, guanine, thymine and uracil There are three main types of RNA mRNA messenger RNA formed ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Attach uracil-ribose-P. Activates the glucose-phosphate. 4. PPi 2 ... Start with glucose. Produces ribose and other pentoses. NADPH reduction in biosynthesis ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Which of the following influence protein folding into functional molecules? ... C. RNA contains uracil while DNA contains thymine ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
In Vitro Mutagenesis dut ung ... or phage grown in a dut ung mutant of E. coli. ... The ung gene encodes uracil N-glycosylase which normally removes U from DNA. ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
... important and difficult part in bioinformatics. Central Dogma ... In bioinformatics the sequence format does NOT make a difference between Uracil and Thymine. ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
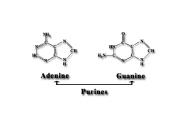
Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, Thymine, and Uracil (A,G,C,T,U) ... A Punnet Square 2. X. Y. X. X. XX. XX. XY. XY. Decoding... Best to read handout...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Three consecutive bases comprise one base triplet that becomes a codon when transcribed to RNA ... Codon Letters: A = Adenine, U = Uracil, G = Guanine, C = Cytosine ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Several nucleotide bases undergo spontaneous ... Deamination of cytosine to uracil in DNA occurs approximately 100 times per day ... Ligation. Direct repair ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
PhD in Physics and Applied Math from Russian Academy of Sciences. ... Eel. Guanin-uracil bp with H-bonds. Processes Involved in Cell-Env Interaction ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Adenine. Cytosine. Guanine. Thymine. Uracil. Alanine (Ala) Arginine (Arg) ... REMARK Alanine Structure. ATOM 1 C 1 -0.134 -0.047 -0.101. ATOM 2 C 1 -1.379 0.806 0.122 ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Ribose. Ribose. Ribose. Ribose. Uracil. Adenine. Cytosine ... Transcription, capping of 5' end. Stop codon. Start codon. 5' end (continue to next ) ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
CHM 109 Assignment 5-1 Boyle’s Law- Pressure and Volume
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
From DNA to Protein: Transcription and Translation Each gene is the information to build one protein (or polypeptide chain) that the organism needs.
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
DNA Structure and Function DNA is an example of a(n) Amino acid Nucleic acid Carbohydrate Lipid 1 DNA is made up of monomers called Triglycerides Amino acids ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
What does DNA. stand for? Deoxyribonuleic acid. 4. How are ... What is the main purpose of DNA? To make proteins within a cell. 13. What does RNA. stand for? ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Protein Synthesis DNA RNA Protein Transcription Translation
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
... formyl glycinamidine ribonucl otide Aspartate 1) ribose posphate pyrophosphokinase 2) amidophosphoribosyl transf rase 3) GAR synthase 4) ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
In messenger RNA, a codon consists of. A) 2 bases. B) ... In mRNA, each codon specifies a specific. A) nucleotide. B) purine. C) amino acid. D) pyrimadine ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Merriam Webster's Collegiate Dictionary. Helix (n) a. 'Something spiral in form. ... 10.5 bp/helix repeat. Helix diameter ~ 20 . 36 bp ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
RNA and Protein Synthesis Write ... then starts bonding nucleotides to make the RNA strand There is a gene on DNA that codes for RNA polymerase to stop TRANSCRIPTION ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Genetic control of protein structure and function The structure of DNA and RNA Genetic material of living organisms is either DNA or RNA. DNA Deoxyribonucleic ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Ninth Edition Marieb w Hoehn Chapter 3 Cells: The Living Units DNA & RNA Lecture 7, Part 2 * DNA Replication The precise ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Molecular biology basic- DNA, RNA structure, chargaff rule, nucleic acids, ATP, watson and crick model, types of DNA- A DNA, B DNA. Z DNA, types og rna
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
DNA and Protein Synthesis DNA Does 2 Important Things in a Cell: 1)DNA is capable of replicating itself. Every time a cell divides, each DNA strand makes an exact ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
DNA Deoxyribonucleic Acid The Blueprint of Life I. DNA Structure & Function
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
... Reliance on pedigrees Possible to determine sex linkage, ... Mutation rate depends on species and on gene Generally, mutations are random Hot spot: ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
RNA Protein Synthesis Mutations * Substitution Insertion Deletion Chromosomal mutations involve changes in the number or structure of chromosomes.
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Saccharomyces cerevisiae : Saccharomyces cerevisiae is commonly known as
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
4 3 2 1 1 = initiator proteins 2 = single strand binding proteins 3 = helicase 4 = topoisomerase (gyrase) Review: Proteins and their function in the early stages of ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download