Endoparasites PowerPoint PPT Presentations
All Time
Recommended
... Indirect life cycle Cat = definitive host oocysts shed in cat feces Ruminants = intermediate host tissue cysts ... epithelial cells ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
... dichlorvos Ascarops strongylina stomach worm PPP: 6 weeks Dung beetle: intermediate host CS: nonpathogenic Dx: fecal sedimentation; Adults stomach Tx ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Numerous plant-parasitic nematode forms have evolved toward a more ... Heavy infection of roots reduces growth of all plant parts. Like most cyst nematodes, ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
2. Class Trematoda & 3. Class Monogenea: Both are parasitic flukes Leaf-shaped flatworms Endoparasites: Live in blood, intestines, lungs, liver, etc.
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Phylum : Platyhelminthes General Characteristics Free-living or parasitic Bilaterally symetrical, and dorso-ventrally flattened Epidermis has cilia or cuticle Coelom ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Community Ecology: Structure, Species Interactions, Succession and Sustainability Chapter 8 What is this balance of nature that ecologists talk about?
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Parasite Control. Parasite. Is an organism that makes its ... More important as carriers (vectors) of disease. Pink eye, Lyme disease, blue tongue, anaplasmosis ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Nematodes need to change plant metabolism in the infected cells! 2-Metabolic Pathway Enzymes Chorismate Mutase Functions of Nematode Effectors Chorismate Mutase ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Title: Ground Rules, exams, etc. (no make up exams) Text: read chapters 1, 6, 7, then 3, 4, 5, 8, etc. Profess -Knowledge - Study (rewire your brain!)
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Predation Species Interaction Predator Prey Predation When an individual captures, kills and consumes another individual prey. Prey The individual eaten by the ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Taxonomy Class Turbellaria (planarians) Class Trematoda (flukes) Class Cestoda (tapeworms) ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Kingdom Protista the protists Protista Characteristics Kingdom Protista Kingdom Protista Kingdom Protista Kingdom Protista Kingdom Protista Kingdom Protista ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Title: SPECIES INTERACTIONS Author: abrooks Last modified by: Aarti Brooks Created Date: 9/14/2006 2:38:35 PM Document presentation format
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Platyhelminthes pt 2 Digene trematodes and tapeworms Di(2)-Gene(birth) Schistosoma mansoni Swimmer s itch Schistosoma sp. that infect ducks, muskrat Blackspot ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Les Vers Emmanuel Bernier Les vers : situation phylog n tique Les vers Caract ristiques g n rales Classification des triploblastiques Les diff rents ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Foliar Nematode Symptoms on Hibiscus Leaves Note restriction by leaf veins ... Most important and damaging nematode in southeast US and tropics ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Ecology Community Interactions Objectives Compare and Contrast interspecific and intraspecific competition. Describe three types of symbiosis. Standard The following ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Ecological Principles Interactions among animals and the environment What is Ecology? A combination of biotic and abiotic factors Key Ecology Terms Species: natural ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Flatworms Phylum Platyhelminth Endoparasite Exoparasite / Ectoparasite Life cycles Most parasitic worms have more than one organism in their life cycle: An ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Advocate is a highly effective treatment for controlling external and internal parasites as claimed by its manufacturer Bayer. It solves the most common problem pets have to deal with i.e. fleas and with so many products already in demand for parasite control, Advocate has created its own niche in the market. Here are some common questions asked about this product by the customers that will help others to clear their doubts as well.
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Title: PowerPoint Presentation Author: Lacombe Junior High School Last modified by: grattonp Created Date: 8/21/2003 7:05:30 PM Document presentation format
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Unit 4 - Phylums Platyhelminthes and Nematoda Flatworms and Roundworms * * Phylum Platyhelminthes Largest group of acoelomate (no body cavity) worms Flatworms with ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Protozoa (Each one is unicellular=composed of one cell). 2. ... Classification of Protozoa Intestinal parasites: 1. Entamoeba histolytica. 2. Blantidium coli. 3.
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Parasitism. Parasite. An organism that lives in or on another organism (host) and ... Most virulent strains not successful. Coevolution host-parasite. Parasitoids ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
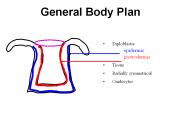
General Body Plan Diploblastic epidermis gastrodermis Tissue Radially symmetrical Cnidocytes
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
ZOO 115 Invertebrate Zoology Subphylum Crustacea Part II
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Chapter 24 Porcine Management and Surgical Procedures The true measure of an individual is how he treats a person who can do him absolutely no good.
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
General Body Plan Diploblastic epidermis gastrodermis Tissue Radially symmetrical Cnidocytes
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Acoelomate Bilateral Animals Acoelomate Bilateral Animals Consist of phyla: Phylum Platyhelminthes Phylum Nemertea And others Acoelomate Bilateral Animals Simplest ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Parasitism Parasites are organisms that live in or on another organism i.e. the host . What do parasites gain? Parasites gain: - Nutrition - absorbed from the ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Special Relationships Unit 1 Animal Geography Habitat vs- Niche Habitat The location in which the organism lives (grasslands, freshwater, tree tops, inside a ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
The Protozoans Ciliates Amoeboid Protozoans Flagellated Protozoans * Kingdom Protozoa * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Kingdom Protozoa * Protists Defining ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Antiparasitics Chapter 15-1 Dr. Dipa Brahmbhatt VMD MpH dbrahmbhatt@vettechinstitute.edu Pyrethrins and Pyrethroids May have limited residual effects Do not use near ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Embrapa Southeast Cattle. S o Carlos - SP. Pecu ria Sudeste. Embrapa Southeast Cattle. Stablished in 1975. 2,668 ha farm. Forest and reserves: 30 ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Root-lesion nematode damage to wheat. Cortical rot and pruning of lateral roots ... Root Lesion Nematode Biology. Why didn't we look before? ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Introduction to Parisitology Laboratory Procedures Parasite A smaller organism that lives on or in and at the expense of a large organism called the host.
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Introduction to Parisitology Laboratory Procedures Parasite A smaller organism that lives on or in and at the expense of a large organism called the host.
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Type III Secretion System Complex protein secretion system employed by many Gram-negative pathogenic bacteria Transport bacterial effector proteins across three ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Species Interactions Section 4-2 Pages 92-93 Species Interactions Species within a community develop close interactions, known as symbiosis. Sym means together ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
... but the two species which infect man are T. saginata and T. solium External Features: Tatnia saginata has four large muscular suckers; no mouth or hooks exist.
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Nematodes as Pathogens Characteristics Brief History Nematodes as Parasites Importance Form and Function General Disease Cycle of Plant Parasitic Nematode
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
nematode feeds on 4-6 giant cells' Which plants are infected with root knot nematode? ... susceptible cultivar on left / resistant on right ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
mites (arachnida: acari) collection, preparation, mounting, labeling, storage and packing specimens sri hartini and a. saim zoology division, research center for biology
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
... Poision ivy and poison oak Parasitism Parasitism ... food, or space) Competition may cause the development of different niches or physical characteristics.
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
2)Has no organs or tissues. 3)Body contains no internal cavity. ... 8)Reproduction quite complex involving both sexual and asexual aspects. ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
... Nematoda. Most abundant animal on earth. Diverse. Important ... Agriculture (animal and plant) Science. Ajdfj kdjf kdj fkaj d. Nematodes that live in soil are: ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
... 1413. Saturday, September 4, 2004. Chapter 2. Animal Ecology. Vocabulary. Ecology. Organism. Populations. Endotherm. Ecototherm. Communities. Species Diversity ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Chapter 4 H.1.4.11 Ecological Relationships
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Animal Diversity: The invertebrates
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Community Ecology CHAPTER 5 Structure Species Interaction Succession & Sustainability
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Interactions within Communities
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Batesian a non-dangerous organism resembles a dangerous one ... Local example Trout. Brook native. Brown and Rainbow - introduced ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Chapter 53 Community Ecology Community Ecology A community is an assemblage of species (populations) living close enough together for potential interaction in a ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Nema = thread oid = like = 'threadlike worms' Nematodes are animals therefore they are in : ... 1. Amphimixis - union of sperm and egg ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Department of Plant Pathology, Physiology, and Weed Science ... Nematodes grow a new cuticle and stylet with every molt. Life cycle differences...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view