Electromotive PowerPoint PPT Presentations
All Time
Recommended
s for (long) solenoid, c for (short) coil s for (long) solenoid, c for (short) coil * electromotance electromotive force Stokes theorem ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
27-3. Electromotive Force (emf) Emf Devices. Charge Pump. 27-3. Electromotive Force (emf) ... 27-6. Potential Difference (R in Series) Behave like capacitors ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Electromotive Force - EMF. The potential difference when no charge flows to an external circuit is called the electromotive force or EMF. ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Title: No Slide Title Author: R. H. BERUBE Last modified by: Dell-JB Created Date: 8/11/2005 7:05:15 PM Document presentation format: On-screen Show (4:3)
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Electrical current (I) in amperes is defined as the rate of electric charge flow ... 1 ampere (A) of current is a rate of charge flow of 1 coulomb/second. (25-1) ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Electromotive drug administration (EMDA): A novel method for the treatment of ... Abdol-Mohammad Kajbafzadeh , Laleh Montaser-Kouhsari, Hamed Ahmadi, Nima ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Electric Circuits Electric potential difference Electromotive force- emf Circuits Conductors and resistors Resistivity and Resistance Circuit Diagrams
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Electromagnetic Induction Motional Electromagnetic Induction Use a magnetic field to create a current emf (electromotive force) ~ potential difference
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Electromotive force (emf) The electromotive force (emf) of a power supply is equal to the energy supplied ... What is electromotive force? ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Electromotive Force. The potential difference, or voltage, given to the charges by a battery ... EMF electromotive force in volts. B magnetic field strength ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Conductivity (G), Electric Fields and Electromotive Force (EMF) ... Electromotive force (E) or voltage (V), and. DC Circuit Analysis. ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
electromotive force ( Voltage) is present. How dose electricity flow? ... (Electromotive Force) The flow of the electrons is referred to as Current ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Electromotive force: DC voltage needed to halt the ionization of a metal in a standard electrolyte. 2 ... Electromotive force series. Reactive metals -0.13. Pb ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Oxidation loss of one or more electron(s) oxidation state will increase ... Potential difference = EMF, electromotive force. Ecell = cell potential = cell voltage ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
where is the electromotive force of an ideal voltage-point source positioned at ... The electromotive force excites the loop also and generates current in it. ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
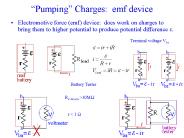
Electromotive force (emf) device: does work on charges to bring them to higher ... Generators/alternator: most influential emf device. Amplitude: Vm. Vrms=Vm ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
ELECTROMOTIVE SERIES. Weakest oxidant Strongest reductant. Zn Zn2 2e- Fe Fe2 2e ... us the position of the reaction in the electromotive series relative to SHE. ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Chelmsford Amateur Radio Society Advanced Course (3) Technical Aspects Part-2 - Resistors and Capacitors Voltage Drop Source Resistance ElectroMotive Force - EMF ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
21.4 Electromotive force (emf), potential. difference and internal resistance ... Electromotive force (emf), is defined as the energy provided by the source ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Equipotential surfaces and E fields. Equipotential = constant voltage ... Electromotive force e = DV = dW/dq =work done per unit charge. de/dx = -E = electric field ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
16.360 Lecture 23. Faraday's Law. 16.360 Lecture 23. Electromotive force. Stationary Loop in a Time-varying Magnetic field. Lenz's law ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
SOFC, a challenge SOFC, a challenge Power density delivered by SOFC in W/cm2 P = Emf x i ASR x i2 where - Emf is electromotive force, ca. 1V - i is ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
16.360 Lecture 23. Today. Dynamic Filed. Faraday's Law ... Electromotive force. Stationary Loop in a Time-varying Magnetic field. Lenz's law ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Electrochemical Reactions. DE=Eright-Eleft=Ecu/Cu2 -Ezn/Zn2 ... Electromotive force (EMF) mk=mk0 RTlnak. Snimi=DGrxn=DG0 RTln[p(niai)] Electrochemical Reactions ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
3 ??.??????. 3 ?????????. ???? 312 101 General Chemistry I. ??????????????? ... 5. Effect of concentration on cell electromotive force. 6. Applications : ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Concept of MHD power generation for hypersonic vehicle ... Hall electromotive force. Electric field. Hall parameter. Joule dissipation ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
The time response of photon detectors is. faster than that ... Generate an electromotive force when photons are detected. Photovoltaic (PV) Photoconductive (PC) ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Describe the phase relationship between current and voltage in an ... Voltage is induced in the inductor coil called a counter-electromotive force (CEMF) ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Galvanic cell - an electric cell that generates an electromotive ... A salt bridge consist of a gel made by adding agar to a concentrated aqueous KCl solution. ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Non-Fickian diffusion and Minimal Tau Approximation from numerical turbulence ... Electromotive force (astrophysics) Effects of stratification, Coriolis force, B-field ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Assignment #4 is due at 10 PM, on Wednesday. ... The term EMF (electromotive force),symbol E, is used to describe the work done ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Voltage is sometimes referred to as electromotive force (EMF) ... Voltages is represented as the letter V, and sometimes E, for electromotive force. ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
EMF and Terminal Voltage. A device such as a battery or an electric generator ... so on) into electric energy is called a source of electromotive force, or emf. ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
A technique by which molecules are separated by ... electromotive force. migration. http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/units/biotech/gel. Staining ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Biotechnology and Medicine Prof. S.K.Panda Department of Pathology All India Institute of Medical Sciences Micro Fludic Peltier Microarray Electromotive Nucleic acid ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
e electromotive force a force that creates a charge such as the chemical ... Basic power for homes comes in 110 VAC and 220 VAC. ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Circuits are usually powered by batteries or generators, which are called sources of emf. The emf (E)stands for electromotive force and is not a fundamental force. ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
When an electromotive force, called a potential difference or voltage (measured ... The 'E' stands for electromotive force. I = current in Amperes (A) ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
What is an Atom? An atom is the smallest particle on any element. Element ... Electromotive Force -Voltage. Electrical Flow Current. AC/DC Highway to Hell ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
An electromotive force (EMF) is produced in a conductor whenever it cuts across ... Question: Electromotive force (emf) is most closely related to. electric ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Electromotive Force (emf, e) Electromotive 'force', emf, is a measure of the voltage that can be ... For a given device, if a charge Q passes through that ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
ampere of current. One volt of electromotive force will cause one ampere to flow ... I=Current through resistor, amperes. R=Resistance, ohms. I=E/R R=E/I. Power ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
The fundamental factor which should be taken into consideration ... Charge electromotive force Power =Ppv PL (PPV PL) ----(1) ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
STUDENTS WILL ALSO BE ABLE TO SOLVE PROBLEMS USING OHM'S LAW TO FIND VOLTAGE, ... ELECTROMOTIVE FORCE (EMF) IT IS THE FORCE THAT PUSHES ELECTRONS THROUGH A WIRE ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Electrons are 'driven' from anode to cathode by an electromotive force or emf. ... 'distance' from 'top' half-reaction (cathode) to 'bottom' half-reaction (anode) ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
The sum of the oxidation numbers in a compound is zero. ... Activity (Electromotive) Series. Elements at top like to lose electrons ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Energy stored in B-fields. What is an electromotive force (emf)? Source of energy ie. An ordinary battery that provides a potential difference ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Why bother with Electric Potential V, Capacitance, and Electric Fields? The electric potential difference between ... Batteries and Electromotive Force (emf) ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Charge Q on plates. Charge 2Q on plates. Capacitor ... Electromotive Force. Battery. Maintains potential difference V. Not constant power ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Methods Used to Solve the Problem and Solution. Michael Faraday (1791 1867) ... a closed circuit will produce a current or an induced Electromotive Force (EMF) ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Bring a copy of your s printed two to a page ... Back-electromotive force (emf) Torque-current constant. Moment balance on load. T. eo(t) ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Euclidean m-Space & Linear Equations. Electric Circuits and Pipe Networks. Direct Current Electric Circuits ... Consists of one or more electromotive forces ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Electrochemistry. Utilizing electrons from. oxidation-reduction reactions ... Write a balanced reaction ... Eo is the electromotive force or work per ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
A moving electric charge, such as an electron, will accelerate in the presence ... The generation of an electromotive force and current by a changing magnetic ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Many of the general laws of nature are best expressed as ... Electromotive force (battery) L for inductance. Kirchoff's Law. In words: 'The sum of the voltage ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Electrochemistry. The study of the interchange of chemical and ... Cell Potential or Electromotive Force (emf): The 'pull' or driving force on the electrons. ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view