Adipocytes PowerPoint PPT Presentations
All Time
Recommended
Title: Food, Digestion and Nutrition Author: Diane Last modified by: Tiangco, Jefferson Created Date: 9/24/2005 1:13:05 AM Document presentation format
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
PNS: Autonomic nervous system Autonomic NS regulates smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, gland tissue and adipocytes Anatomy of efferent pathways
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Adipocytes Welcome to basic histology of the skin * We will begin with an overview of the skin.
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Adipose Tissue FWS EDDIE SMITH LEAH WAGNER LEAH SANDERS JONATHAN GRIMWOOD What is adipose tissue? Groups of adipocytes (lipid filled cells) that are loosely held ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Fat mobilization in adipocytes bR Note: insulin inhibits TAG mobilization PKA PKA P Hormone-sensitive lipase Hormone-sensitive lipase glycerol MAG DAG TAG FFA
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
General Pathology Concepts, Case 11. 40 year-old female with subcutaneous nodule in outer thigh. Thin fibrous capsule. adipocytes ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Do white adipose adipocytes express receptors for gut hormones? Suha S Al-Naimi Characteristics of GIP and GLP-1 Did you ever wonder why you can tell it s meal ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Fibroblasts Adipocytes, Mast cells, Macrophages, Plasma cells, ... Hyaline cartilage. Connective/Supportive. Chondrocytes. Collagen fibers (not usu visable) ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are multipotent stem cells that can differentiate into a variety of cell types, including osteoblasts, chondrocytes, myocytes, adipocytes, beta-pancreatic islets cells, and potentially, neuronal cells. To know more : https://www.bharatbook.com/biotechnology-market-research-reports-90794/mesenchymal-stem-cells-advances-and-applications.html
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
... the heart and heart failure, aneurysm, renal failure, vision impairment, and atherosclerosis. ... the body (eg, brain, liver, pancreas, adipocytes, GI ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
... fatty acids. phosphate. triglycerides. glucose. adipocytes. liver. a ... fatty acids. liver. Amino acids. Absorptive state: amino acids. muscle and other cells ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
I am currently majoring in Cardiovascular, Respiratory and Renal Physiology and minoring in Neuroscience, so have a strong grasp of a broad range of biological topics. I have previously studied aspects of Psychology, developmental biology and Cellular Physiology. For my dissertation I worked in a lab in Oxford on bone marrow adipocytes and the differentiation of stem cells, and will be starting a DPhil on dietary constituents and their effect on bone health.
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are multipotent stem cells that can differentiate into a variety of cell types, including osteoblasts, chondrocytes, myocytes, adipocytes, beta-pancreatic islets cells, and potentially, other cell types. MSCs are of intense therapeutic interest, because they represent a population of cells with the potential to treat a range of acute and degenerative diseases.
Synthesis and catabolism of triglycerides
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Resistance Adiponectin Liver, Endothelium, Deficiency Muscle(?), Brain ... (adipokines): Specific Major target(s) alterations hormone in obesity Leptin ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
LIPOPROTEIN LIPASE LIPOPROTEIN LIPASE lipase = lipid hydrolyzing enzyme lipoprotein = lipid and protein non-stoichiometric non-covalent aggregate in blood, in lymph ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
INCREASED HEPATIC GLUCOSE OUTPUT FROM GLYCOGEN STORES ... METABOLIC ACIDOSIS AND INCREASED VENTILATION AS A RESULT. DEPRESSIVE EFFECT ON BRAIN FROM ACIDOSIS ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Large vacuoles, small lipid droplets, numerous mitochondria ... Poorly developed mitochondria. White Adipose Cell. White Adipose in the Bovine ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Title: Diapositive 1 Author: Jean Pierre Last modified by: H pital TENON Created Date: 2/7/2005 1:33:52 PM Document presentation format: Affichage l' cran
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
CENTRE UNIVERSITAIRE D EL TARF DEPARTEMENT DE BIOLOGIE 1 re Ann e LMD TP d Histologie n 2: LE TISSU CONJONCTIF Pr par par Dr TAIBI F. Nom: Pr nom: Groupe ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Obesity Dr. Sumbul Fatma
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Title: In situ hybridization of a human TYR RNA probe on sections of visceral adipose tissues from morbidly obese and non-obese subjects demonstrated cytoplasmic and ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
in blood, in lymph = chyle (and bile) decreasing protein content (causing less density) ... Cholic abdominal pain (even after 1st suckling) ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Title: mod le dias pp4 Author: sl Last modified by: Administrateur Created Date: 1/13/2000 8:50:52 AM Document presentation format: Diapositives 35 mm
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Lipogenesis : processes involved in absorption of nutrients from blood and ... (pate du fis gois = fatty goose liver) Blood : absorption of fatty acids (FA) ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Since obesity is a side effect of some anti-diabetic drugs, we first evaluated the effects of the compounds on 3T3-L1 adipogenesis.
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Pr sentation PowerPoint ... L ob sit
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
... Specialization and Differentiation. A comparison of eukaryote cells. 2005-2006. Squamous epithelial cells- Buccal cells. Haversian System - Bone. Peripheral Blood ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Mathematical Modeling of Fatty Acid Oxidation in Skeletal Muscle Cells Sheds New ... Understanding biochemistry may lead to new ways of controlling obesity ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Connective Tissue (CT) Compact Bone Compact Bone Spongy Bone Also known as trabecular and cancellous bone the collagen is contained within the irregularly shaped ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
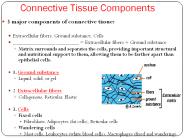
Connective Tissue Forms metabolic and structural connections between tissues Found everywhere in the body and represents most abundant tissue by weight.
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Title: PowerPoint Presentation Last modified by: Ashraf Created Date: 1/1/1601 12:00:00 AM Document presentation format: On-screen Show (4:3) Other titles
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Connective Tissue Image Gallery Loose Connective Tissue - Areolar note the collagen fiber at the pointer and the black elastic fibers. Also note the nuclei of cells.
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Connective Tissue Consists of two basic elements: Cells and Extra-cellular matrix BODY MEMBRANES Epithelial Membranes = epithelial layer of cells plus the underlying ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Tissues Chapter 5 Tissues A tissue is a group of similar cells that usually have a similar embryological origin and are specialized for a particular function.
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Tissues Chapter 5 * Hyaline cartilage - (gristle) most abundant cartilage, and weakest. It has very fine collagen fibers and a resiliant gel as its ground substance.
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Title: Thiazolidinedione and bone turnover Author: Dell Last modified by: Administrator Document presentation format: On-screen Show Other titles
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Glandular Epithelium Main Function: Secretion Location: Lie in clusters deep to the covering and lining epithelium Two Types Endocrine Exocrine Endocrine Secrete ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
OBESITY - Wikispaces ... obesity
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Title: Histolo ija Author: karlo Last modified by: Viesis Created Date: 9/10/2002 5:50:47 AM Document presentation format: On-screen Show Company
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Obesity and Weight Control. Exercise Physiology. McArdle, ... Weight Control. Selective fat reduction at specific body areas by spot reduction does NOT work. ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Title: PowerPoint Presentation Author: Stephanie Shore Last modified by: sshore Created Date: 10/4/2002 7:36:29 PM Document presentation format: On-screen Show
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
in blood, in lymph = chyle (and bile) decreasing protein ... The monomer is unfunctional as hydrolase. N. C. phospho active site GAG-binding to other monomer ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Ketones and aldehydes have double bonds that may fluoresce and glycine binds and ... Terminally differentiated cell. Stem cells used where turnover occurs rapidly ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Neuroendocrine regulation of food intake: physiology and pathophysiology
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Cryolipolysis is the new fashion treatment because it defines the figure without surgery and the results are visible in two weeks
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Metabolism Chapter 25 - pages 962-987
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Patching the Puzzle of Genetic Network Grace S. Shieh Institute of Statistical Science, Academia Sinica gshieh@stat.sinica.edu.tw
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Metabolism of lipids Vladim ra Kvasnicov Lipids = group of biological molecules that are insoluble in aqueous solutions and soluble in organic solvents structural ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Histology May also be classified by types of secretions from exocrine glands Serous mostly water but also contains some enzymes Ex. parotid glands, pancreas Mucous ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Tissues Function and Location For Epithelial, Connective, Muscular and Nervous
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Title: L-410198: Go/No-Go to Phase III and Dose Selection (I) Subject: L-410198 Author: Merck Last modified by: Eva Maria Gramatt Created Date: 4/1/2002 8:17:10 PM
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
GI hormones and digestive process
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
The islets are endocrine tissue containing 4 types of cells. ... the different cell types within an ... also WEAKLY promote insulin secretion. Our understanding of ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Obesity and Weight Control. Exercise Physiology. McArdle, Katch, & Katch. Chapter 16 ... McArdle, William D., Frank I. Katch, and Victor L. Katch. 2000. ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view