Connective Tissue Components - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 23
Title:
Connective Tissue Components
Description:
Connective Tissue Forms metabolic and structural connections between tissues Found everywhere in the body and represents most abundant tissue by weight. – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:175
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Connective Tissue Components
1
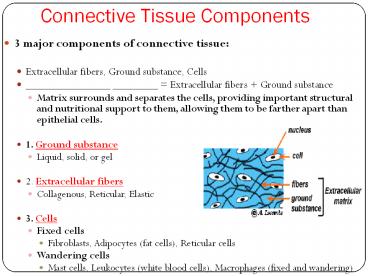
Connective Tissue Components
- 3 major components of connective tissue
- Extracellular fibers, Ground substance, Cells
- _______________ ________ Extracellular fibers
Ground substance - Matrix surrounds and separates the cells,
providing important structural and nutritional
support to them, allowing them to be farther
apart than epithelial cells. - 1. Ground substance
- Liquid, solid, or gel
- 2. Extracellular fibers
- Collagenous, Reticular, Elastic
- 3. Cells
- Fixed cells
- Fibroblasts, Adipocytes (fat cells), Reticular
cells - Wandering cells
- Mast cells, Leukocytes (white blood cells),
Macrophages (fixed and wandering)
2
(No Transcript)
3
Connective Tissue Components Ground Substance
- Composed of glycoproteins called
- __________________ (GAGs)
- hyaluronic acid
- Help to orient fiber formation in connective
tissue. - Is medium through which cells exchange nutrients
and waste with the __________ ___________. - Acts as shock absorbing cushion and helps to
protect the delicate cells that it surrounds.
4
Fibers of Connective Tissue
- Collagenous
- Most common fiber found in the body
- Strong, thick bands organized into bundles,
composed of ____________ (structural protein). - Resist ___________ forces, so they are found in
tendons and ligaments that are continuously being
pulled and stretched. - wavy appearance when not stretched
5
Fibers of Connective Tissue
- Reticular
- Composed of collagen
- Thin, delicate, ____________ into complicated
networks. - Form support around highly ____________ organs
- endocrine glands, lymph nodes, spleen, bone
marrow, liver - Elastic
- Composed primarily of protein ________.
- Are branched and form networks
- Can stretch and contract.
- Found in tissues that stretch vocal cords,
lungs, skin, blood vessel walls.
6
Major Cell Types of Connective Tissue
- Fixed Cells
- Remain in the connective tissue
- Produce and maintain the __________
- Fibroblast
- secrete fibers and ground substance of the matrix
- Can reproduce and are metabolically active.
- Name is based on _________.
- Chondroblast (cartilage), osteoblast (bone), etc.
- As the cells mature and the matrix is formed,
cells become less active and suffix is changed to
_______. - Chondrocyte, osteocyte, fibrocyte
- Can revert back to blast if more matrix is
needed.
7
Major Cell Types of Connective Tissue
- Fixed cells continued.
- Adipose cells/Adipocytes
- Found throughout connective tissue
- Resemble fibroblasts early on, but as they age
they become filled with lipid and swell. - __________ gets pushed to the side
- Adipocytes clustered together form _________
tissue. - found all over, but is prominent under the skin
and in the abdomen - Reticular Cells
- Flat, star-shaped cells that form net-like
connections with other cells - Manufacture reticular fibers.
- Found in tissues of the immune system lymph
nodes, spleen, bone marrow
8
Major Cell Types of Connective Tissue
- Wandering Cells
- Move in and out of connective tissue as needed.
- Help _______ and _________ the tissue
- Leukoctyes (white blood cells)
- Found in blood, move into connective tissue
during periods of infection/inflammation. - Squeeze through the simple squamous epithelium of
blood vessels (diapedesis) - Important in immune function- engulf and digest
invaders or produce antibodies against them - Mast cells
- Carry histamine and heparin granules which
initiate inflammatory response when released into
tissue - Usually found near blood vessels
9
Major Cell Types of Connective Tissue
- Wandering cells continued..
- Macrophages
- ___________ scavengers that may be either fixed
or transient in connective tissue. - Engulf microbes, dead cells and debris that are
digested by the macrophages lysosomes - drawn to sites of infection where they engulf
invaders
10
Types of Connective Tissue
- Connective Tissue Proper
- Loose Connective Tissue- supports structures that
it surrounds - Areolar, Adipose, Reticular
- Dense Connective Tissue- highly fibrous
(collagen) little vascularization, ground
substance, or cells reinforces and binds
structures - Dense regular, Dense irregular, Elastic
- Specialized Connective Tissue
- Cartilage
- Hyaline, Elastic, Fibrocartilage
- Bone
- Compact, Cancellous
- Blood
11
(No Transcript)
12
(No Transcript)
13
Loose Connective Tissue Areolar
- Most common type of connective tissue
- Surrounds every organ
- Acts to support and cushion organs and other
delicate structures. - Predominant cell is ____________.
- Has _______ spaces that are filled with fluid
and viscous ground substance - Filling of open spaces during trauma is called
__________
14
Loose Connective Tissue Adipose
- Commonly known as ________
- Found beneath skin, in bone marrow, in abdomen
- Energy storage, insulator, shock absorber
- Highly vascularized areolar tissue in which
adipocytes predominate - Cells __________/__________ based on amount of
lipid being stored in them. - May be classified as
- White
- Found throughout body
- Adipocytes change from resembling fibroblasts
- to filling with lipid
- Brown
- Found in _________ and ____________ animals
- Site of heat production, temperature regulation
15
Loose Connective Tissue Reticular
- Framework for spleen, liver, lymph nodes, bone
marrow - Called _________
- Contains only one type of fiber ___________
- Many fibroblasts
16
Dense Connective Tissue Regular
- Makes up tendons and ligaments, fascia
- Tightly packed,__________ collagen fibers
- Little vascularization, slow to heal
- Little ground substance
- Fibroblasts line the collagen bundles
- Resists strong pulling forces in _____ direction.
17
Dense Connective Tissue Irregular
- Found in dermis, organ capsules
- Forms tough capsule of joints.
- Collagen fibers in thicker bundles than those in
dense regular connective tissue. - Sheets of collagen in ___________ directions.
- Single sheet that can withstand pulling force
from _______ different directions.
18
Dense Connective Tissue Elastic
- Found in areas of the body that require
___________ - Stomach, artery walls, bladder
- Beneath transitional epithelium in urinary tract
- High concentration of elastic fibers (more than
collagen) that are extremely flexible.
19
Specialized Connective Tissue Cartilage
- More rigid than dense connective tissue, more
flexible than bone. - Prevents bones from rubbing against each other.
- Does not contain nerves or blood vessels.
- Receives nutrition from ________________.
- Chondrocytes live in pockets called _______
- 3 types of cartilage
- Hyaline cartilage, Elastic Cartilage,
Fibrocartilage
20
Specialized Connective Tissue Types of Cartilage
- Hyaline Cartilage
- Most common type of cartilage found in body.
- Found as ____________ cartilage at end of long
bones and joints and connects ribs to the
sternum. - Most rigid type of cartilage.
- Closely packed collagen fibers that make it tough
but more flexible than bone. - Elastic Cartilage
- Similar to hyaline cartilage but contains
_________ fibers - Give it flexibility, ability to bend
- Found in pinnae, epiglottis
21
Specialized Connective Tissue Types of Cartilage
- Fibrocartilage
- Found between vertebrae, in pelvis, and in knee
joint - Able to handle compression, absorbs ______
- Thick bundles of collagen, but few chondrocytes
22
Specialized Connective Tissue Bone
- Also called osseous connective tissue
- Hardest and most rigid type of connective tissue
- Structure
- Matrix collagen fibers and calcium salts
- ____________- tiny channels through matrix that
allows osteocytes to communicate - _________- chambers where osteocytes reside
- Blood Supply- __________ canals (channels in bone
that carry blood supply and nerves) - Cells- Osteoclasts and osteoblasts
- Remodel bone as needed
23
Specialized Connective Tissue Blood
- Most atypical type of connective tissue.
- Carries nutrients and gases through the body
- Matrix _______ (plasma)
- Fibers few and only visible in a _____
- Cells
- Erythrocytes (______ blood cells)
- Leukocytes (________ blood cells)
- Thrombocytes (________)