Community Structure - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 10
Title: Community Structure
1
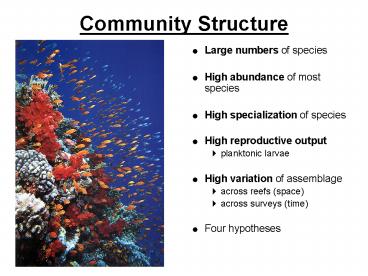
Community Structure
Dover sole (Microstomus pacificus)
- Large numbers of species
- High abundance of most species
- High specialization of species
- High reproductive output
- planktonic larvae
- High variation of assemblage
- across reefs (space)
- across surveys (time)
- Four hypotheses
Pacific hake (Merluccius productus) unknown
Sebastes or Sebastomus
eelpout (Lycodes cortezianus)
2
Competition Hypothesis
Dover sole (Microstomus pacificus)
- Competition determines community structure
- Adults are adundant
- Food and space are limiting
- Resources are finely partitioned
- Community is stable and predictable
- But assemblage varies across space and time
Pacific hake (Merluccius productus) unknown
Sebastes or Sebastomus
eelpout (Lycodes cortezianus)
3
Lottery Hypothesis
Dover sole (Microstomus pacificus)
- Random events create vacant space on reef
- Unlimited larvae available as recruits (assumed)
- Random recruitment of larval individuals
- lottery winner
- Assemblage varies over space and time
- Biological interactions are not considered
Pacific hake (Merluccius productus) unknown
Sebastes or Sebastomus
eelpout (Lycodes cortezianus)
4
Recruitment Limitation Hypothesis
Dover sole (Microstomus pacificus)
- Larval recruits are limited
- Adult population never reaches carrying capacity
- Adult density determines larval density
- more adults more larvae
- Assemblage changes over space and time
- Biological interactions are not considered
Pacific hake (Merluccius productus) unknown
Sebastes or Sebastomus
eelpout (Lycodes cortezianus)
5
Predation Hypothesis
Dover sole (Microstomus pacificus)
- Predation maintains low population size
- space not limiting for recruits
- resources not limiting for adults
- Predators account for up to 50 of reef species
- Most species have defenses against predators
- Assemblage varies across space and time
- Resource partitioning not explained
eelpout (Lycodes cortezianus)
6
So, which hypothesis is it?
Dover sole (Microstomus pacificus)
7
Epipelagic Region
Dover sole (Microstomus pacificus)
- Euphotic zone 1-200m
- Fewer than 2 of all species
- few permanent residents
- Structure is scarce
- Nutrients are scarce
- Why?
- Environmental factors
- structure
- upwellings
- temperature and light
Pacific hake (Merluccius productus) unknown
Sebastes or Sebastomus
eelpout (Lycodes cortezianus)
8
Structure
Dover sole (Microstomus pacificus)
- Oceanic islands, seamounts, and shallow banks
- Sargassum and other weeds
- ca. 50 species in community
- Cnidarians
- Anthropogenic
- trash
- old fishing nets
Pacific hake (Merluccius productus) unknown
Sebastes or Sebastomus
eelpout (Lycodes cortezianus)
9
Upwellings and Currents
Dover sole (Microstomus pacificus)
- Upwellings bring nutrient-rich waters to surface
- coastal
- equatorial
- Currents form boundaries between oceanic regions
- Warm-core rings transport fishes long distances
Pacific hake (Merluccius productus) unknown
Sebastes or Sebastomus
eelpout (Lycodes cortezianus)
10
Temperature and Light
Dover sole (Microstomus pacificus)
- Species prefer specific temperature ranges
- salmon lt 8-10C
- tuna gt 8-10C
- Visual predators in nutrient-poor waters
- Filter-feeders in nutrient-rich waters
Pacific hake (Merluccius productus) unknown
Sebastes or Sebastomus
eelpout (Lycodes cortezianus)