ACDC - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 20
Title:
ACDC
Description:
Schematic Diagram- a graphical representation of a circuit that uses lines to ... Fuse- an electrical device that contains a metal strip that melts when current ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:1648
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: ACDC
1
(No Transcript)
2
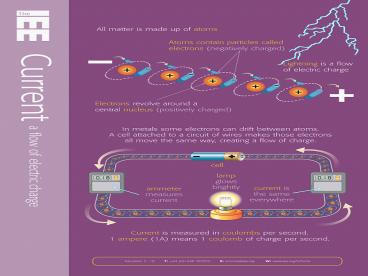
ELECTRIC CURRENT
- Electric current is the flow of electric charge.
- Natural examples include lightning and the solar
wind, the source of the polar aurora. - The most familiar artificial form of electric
current is the flow of conduction electrons in
metal wires, such as the overhead power lines
that deliver electrical energy across long
distances and the smaller wires within electrical
and electronic equipment. - In electronics, other forms of electric current
include the flow of electrons through resistors
and the flow of ions inside a battery,
3
OHMs LAW
V
R
I
4
VOLTAGE
- Voltage is an electric potential difference
between two points on a conducting wire. Voltage
is measured in volts. Voltage comes from various
sources. Two examples of these sources are
batteries and electrical outlets.
5
CURRENT
- Current is measured in amps. Current is charged
particles which flow from the voltage source
through conductive material to some form of
resistance or a ground. Flows between opposite
charges.
6
RESISTANCE
- Resistance is the opposition that a material
offers to the passage of an electric current.
Resistance is measured in ohms. Examples of items
with resistance are light bulbs, hair dryers,
toasters.
7
BATTERIES
- In very simple terms, there are two chemicals in
a battery - one chemical wants more electrons and
the other chemical wants to get rid of electrons.
- When a path (i.e. circuit) is completed between
the two opposite ends of the battery the
electrons are free to move from one post to
another. - The movement of electrons is current. Different
chemicals and/or configurations determine how
badly the electrons want to get from one chemical
to another. - That drive to get from one to another is called
voltage potential, and is expressed in volts. - How fast the electrons travel between the two
chemicals is the flow, or current, and is
expressed in Amperes or Amps...
8
(No Transcript)
9
Conductors have low resistance.Insulators have
high resistance.
- SUPER CONDUCTORS- certain metals and compounds
have zero resistance when their temperature falls
to a certain temperature. - Ex. Niobium, Tin, Mercury
- SEMICONDUCTORS- in between conductors and
insulators. Pure state is an insulator when
other materials are added they can often conduct
electricity.
10
Electric Circuit
- A set of electrical components connected such
that they provide one or more complete paths for
the movement of charges.
11
Switches interrupt the flow of charges in a
circuitOpen Off Closed On
12
Schematic Diagram- a graphical representation of
a circuit that uses lines to represent wires and
different symbols to represent components
13
Series circuits have a single path for current.
Parallel circuits have multiple paths for current.
14
(No Transcript)
15
FUSES CIRCUIT BREAKERS
- Fuse- an electrical device that contains a metal
strip that melts when current in circuit becomes
too great. - Circuit Breaker- a switch that
- opens a circuit automatically when
- the current exceeds a certain value.
16
(No Transcript)
17
(No Transcript)
18
(No Transcript)
19
(No Transcript)
20
(No Transcript)