Liquid membranes - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 9
Title:
Liquid membranes
Description:
Feed/eluent. Flow-through/eluate. Membrane stack. Membrane geometry ... eluent. Flow-through/eluate. Spiral wound membrane. Membrane adsorber calculations ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:1089
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Liquid membranes
1
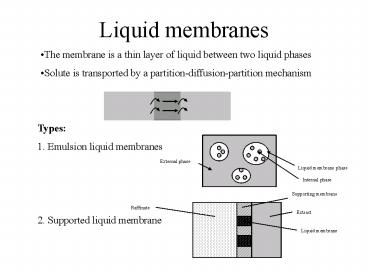
Liquid membranes
- The membrane is a thin layer of liquid between
two liquid phases - Solute is transported by a partition-diffusion-par
tition mechanism
Types 1. Emulsion liquid membranes 2.
Supported liquid membrane
External phase
Liquid membrane phase
Internal phase
Supporting membrane
Raffinate
Extract
Liquid membrane
2
Liquid membrane process
Membrane phase
Feed
Emulsion phase
Applications 1. Antibiotics 2. Metallurgy 3.
Petroleum 4. Effluent treatment
Membrane phase recycle
Primary emulsifier
Extracting phase
Emulsion breaker 2
Secondary emulsifier
Emulsion breaker 1
Raffinate
Extract
3
Supported liquid membrane process
Supported liquid membrane membrane
Feed
Raffinate
Extracting phase
Extract
Applications 1. Antibiotics 2. Metallurgy 3.
Petroleum 4. Effluent treatment
4
- Limitations of packed bed adsorbers
- High pressure drop
- Increase in pressure drop during operation
- Column blinding by proteins
- Dependence on intraparticle diffusion for the
transport of proteins to their binding sites - High process time
- High flow rates cannot be used
- High recovery liquid volume
- Radial and axial dispersion resulting from the
use of polydisperse media - Problems associated with scale-up
5
Packed bed versus membrane adsorber
Mobile phase flow
Mobile phase flow
Diffusive solute transport
Mobile phase flow
Convective flow through membrane
Mobile phase flow
Membrane adsorber
Adsorbent particle in packed bed
6
Membrane adsorbers Merits and demerits
- Advantages
- Low process time
- Low recovery liquid volume
- Possibility of using higher flow rates
- Lower pressure drop
- Less column blinding
- Ease of scale-up
- Fewer problems associated with validation (if a
disposable membrane is used) - Disadvantage
- Relatively low solute binding capacity
7
Membrane adsorbers Chemistry and Geometry
- Separation chemistries
- Affinity binding
- Ion-exchange interaction
- Reverse phase and hydrophobic interaction
- Membrane geometry
- Flat sheet
- Radial flow
- Hollow fibre
Feed/eluent
Membrane stack
Flow-through/eluate
8
Membrane geometry
Hollow fibres
Feed/eluent
Feed/ eluent
Flow-through/eluate
Spiral wound membrane
Flow-through/eluate
9
Membrane adsorber calculations
?D should always be smaller than ?C.