Cell Membranes - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 12
Title:
Cell Membranes
Description:
Cell Membranes Cell membrane Also known as the PLASMA MEMBRANE Cell membrane functions Surrounds the cell and controls what enters and leaves the cell. – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:191
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Cell Membranes
1
Cell Membranes
2
Cell membrane
- Also known as the PLASMA MEMBRANE
3
Cell membrane functions
- Surrounds the cell and controls what enters and
leaves the cell. - Provides protection and support.
4
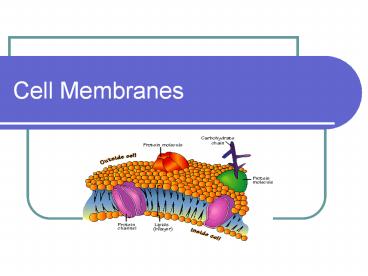
Cell membrane structure
- The fluid-mosaic model states that membranes are
phospholipid bilayers with other molecules
embedded in the bilayer.
5
Phospholipids
- Most of the lipids in a membrane are
phospholipids.
6
Phospholipids
- Phospholipids contain glycerol, two fatty acids,
and a phosphate group. - The phosphate group is polar (hydrophilic),
enabling it to interact with water. The fatty
acid tails are nonpolar (hydrophobic) and do not
interact with water.
7
Phospholipid bilayer
- Phospholipids automatically form a bilayer ( a
double layer) in a watery environment. - They arrange themselves so that the heads face
toward the water and the fatty acid tails face
toward the inside of the bilayer.
8
Flexibility
- The fatty acid tails are flexible, causing the
lipid bilayer to be fluid. This makes the cells
flexible. - At body temperature, membranes are a liquid with
a consistency that is similar to cooking oil.
9
Cholesterol
- In animals, cholesterol is a major membrane
lipid. It may be equal in amount to phospholipids.
10
Cholesterol
- It is similar to phospholipids in that it one end
is hydrophilic, the other end is hydrophobic. - Cholesterol makes the membrane less permeable to
most biological molecules.
11
Proteins embedded in the membrane
- Proteins are scattered throughout the membrane.
- They may be attached to inner surface, embedded
in the bilayer, or attached to the outer surface. - Proteins in the membrane help move large
molecules into or out of the cell.
12
Cell Identification markers
- Lipids and proteins within the membrane may have
a carbohydrate chain attached. - These molecules often function as cell
identification markers, allowing cells to
identify other cells. - This is particularly important in the immune
system where cells patrolling the body's tissues
identify and destroy foreign invaders such as
bacteria or viruses.