world-system theory - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
world-system theory
Description:
world-system theory colonialism fragile states – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:137
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: world-system theory
1
world-system theory colonialism fragile states
2
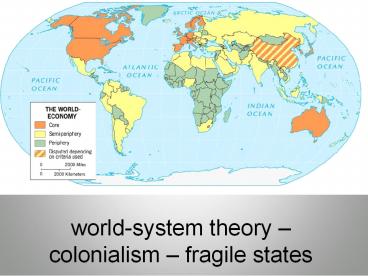
The Three-Tiered Structure of the World-Economy
- Core (Many were colonial powers)
- More commonly has core processes that generate
more wealth in the world-economy - Higher levels of education
- Higher salaries
- More technology
- Periphery (Many were colonies)
- More commonly has peripheral processes associated
with a more marginal position in the world
economy - Lower levels of education
- Lower salaries
- Less sophisticated technology
- Semiperiphery
- Places where core and periphery processes are
both occurring - Places that are exploited by the core but exploit
the periphery
3
- Explain the connection between
- Colonialism
- World-system theory
- Fragile states
4
Forces that Unite and Divide
- Do Now What keeps the 50 states united?
5
Form of Government
- Unitary vs. federal
- Unitary government
- One main governmental decision-making body for
the entire state - More common in smaller more homogeneous states
- Federal system
- Central government shares power with regional
governments - Which promotes unity more effectively?
6
Blue unitary government
7
Whee!....(barf)
8
Forces that Unite and Divide
- Centripetal forces
- Unify a states people and regions
- Examples
- Unifying symbols (flags), pledge of allegiance,
transportation/communication infrastructure,
charismatic leader, strong national identity
(based on language, religion, other cultural
traits), shared history, external threat,
disaster response - Centrifugal forces
- Divide and tear apart a states people and
regions - (fragile states)
- Balkanization
- When centrifugal forces break apart a state into
smaller pieces - Examples
- Regional separatism, cultural divisions
(religion, language), internal boundary
conflicts, multicore state, physical
geography/morphology
9
- Devolution
- Movement of power from the central government
to regional governments within the state, or
breakup of large state into several independent
ones. - What causes devolutionary movements?
- Ethno-cultural forces
- Economic forces
- Spatial forces
10
1.) Ethno-nationalism - ethnic groups see
themselves as distinct nations with the right to
control their own territory.
11
- Quebec and Parti Quebecois in Canada
- Belgium Flemish (Dutch) in north, Walloons
(French) in south - Sudan Muslim north Christian south
- Sri Lanka Tamils, a Hindu minority fight for
independence from the Sinhalese a Buddhist
majority
12
(No Transcript)
13
Who put the Balkan in Balkanization?
- Yugoslavia erupted into Civil War in the 1990s
- Background
- Thrown together after WW I with Serbia as the
core of The Land of the South Slavs - 7 major /17 minor ethnic groups, 3 religions 2
alphabets - North-Croats Slovenes Catholic
- South-Serbs are Orthodox
- Muslim enclaves
- Josip Broz Tito emerged as a communist leader
after WWII - Nationalism suppressed under his iron fist
14
- Tito dies communism collapses
- ? ethnic conflict
- Serb vs. Croat
- Everyone vs. Muslims
- Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia, Serbia, Montenegro
Macedonia became independent. - Bosnia-no clear majority-Muslims 44, Serbs 32
Croatians 17 - Dayton Accords partitioned Bosnia ended the
civil war
15
2.) Economic forces of devolution
16
- Poor regions can feel disadvantaged by
wealthier ones, or wealthier regions can feel put
upon by subsidies to poorer ones. - Examples include
- Italy the richer North pushed for autonomy from
poorer South - Brazil Wealthier provinces of southern Brazil
argue their tax money is being misspent by the
government for assistance to Amazonia. - Spain Catalonians have 6 of territory, 17 of
population, but 25 of exports, and 40 of
industrial product. Devolutionary demands by
Catalonian nationalists.
17
- Catalonia, Spain
- Barcelona is the center of banking and commerce
in Spain and the region is much wealthier than
the rest of Spain.
18
The Forces of Devolution
- EU and euro centrifugal or centripetal?
- Ironically, centrifugal
- Londons decision to join EU encouraged Scottish
nationalism. - 1990s Scottish National Party encouraged
devolution. - 1997 Labour Party gave Scots Welsh chance to
vote both voted to have their own parliaments
19
3.) Spatial/Territorial Forces of Devolution
20
- Spatial factors
- remote frontiers
- isolated villages
- rugged topography
- repeated historic invasions,
- islands, such as
- Corsica for France
- Sardinia for Italy
- Taiwan for China
- East Timor for Indonesians
- Jolo (Philippines)
- Puerto Rico for the U.S.
- 1997, native Hawaiians demanded return of rights
lost during occupation by the U.S.
21
Topic Spatial Characteristics of States
(Territorial Morphology)
- Aim In what ways can the shapes of states
influence them? - Do Now In what ways does the shape of your house
influence how you live?
22
The State of Shapes Activity
- Territorial morphology
- Relationship between a states geographic shape,
size, relative location, and its political
situation - For each of the following countries, try to
determine the relative advantages and
disadvantages that might be caused by the shape
of the state
23
Uruguay, Zimbabwe, Poland, Belgium, Rwanda
24
Shape Compact
- Distance from the center to any boundary does not
vary significantly - Often the political ideal because no one part
feels to far from the center of control - Most efficient form is a circle with a capital in
the center, and the shortest possible boundaries
to defend
25
Norway, Chile, Vietnam, Italy, Gambia
26
Shape Elongated
- Long and narrow shape
- Diversity of climate, resources, and cultures
- Can lead to loss of influence in areas far from
capital - May pose transportation problems because of
distances - National cohesion difficult may suffer from
poor internal communications
27
Namibia, Oklahoma (U.S. State), Thailand,
Afghanistan
28
Shape Prorupt (aka - protruded or panhandled)
- Has a piece that protrudes from its core area
- Like an arm or leg jutting off from the main body
- Proruption may be natural or artificial
- Proruptions can be built to gain access to
resources, or to separate areas from one another - The protruding piece may try to break away or may
be invaded
29
South Africa Lesotho / Rome Vatican City/
Senegal Gambia
30
Shape Perforated
- State that completely surrounds another one
- The surrounded state (Lesotho, e.g.) thus depends
heavily on the state surrounding it for
imports/exports - May cause tension
- http//www.youtube.com/watch?vVui-qGCfXuAlistUU
2C_jShtL725hvbm1arSV9w
Video - Countries Inside Countries Bizarre
Borders part 1 (YouTube - 2 minutes)
31
Indonesia, Azerbaijan, Russia, Denmark,
Philippines
32
Shape Fragmented
- Several discontinuous pieces of territory - 2
types - separated by water - (e.g. island nations such as
Indonesia, 13,677 islands, or Malaysia) - separated by an intervening state - (e.g. Angola
divided by Congo proruption or Russian territory
of Kaliningrad separated by Lithuania and
Belarus) - Also known as an exclave, e.g., Alaska
- Fragmentation weakens communication, fragments
culture, and makes centralized control difficult
33
(No Transcript)
34
Landlocked States
- Surrounded by other countries on all sides
- Lack a direct outlet to the seas
- In other words they have no coastline
- Must depend on neighbors for access to water
sources for trade and navigation - There are over 40 landlocked states in the world
35
What do you think?
- Which state shape would most exacerbate
centrifugal forces? Explain. - Which state shape would most support centripetal
forces? Explain.