PowerPoint-Pr - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
PowerPoint-Pr
Description:
use of topical dessicant agent (hybenx ) as an adjunct to ultrasonic debridement in the initial treatment of chronic periodontitis: a clinical and microbiological ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:30
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: PowerPoint-Pr
1
USE OF TOPICAL DESSICANT AGENT (HYBENX) AS AN
ADJUNCT TO ULTRASONIC DEBRIDEMENT IN THE INITIAL
TREATMENT OF CHRONIC PERIODONTITIS A CLINICAL
AND MICROBIOLOGICAL PILOT STUDY IN HUMANS.
Lombardo G., Signoretto C., Pardo A., Flor C.,
Gelio V., Lubich S., Faccincani M.
The aim of the study was to clinically and
microbiologically evaluate if the ultrasonic
debridement efficacy can be enhanced by the
adjunctive topical administration of a liquid
with hygroscopic properties (HYBENX Oral Tissue
Decontaminant).
MATERIALS AND METHOD Twenty patients presenting
moderate to severe chronic periodontitis were
enrolled in a randomized 3-month, split-mouth,
single-blind, prospective study. At baseline
control and test sides were treated with supra
and subgingival ultrasonic debridement (UD) in
adjunction, for the test group, of a locally
delivered desiccant liquid (HYBENX). Treatments
were repeated after 6 weeks. Clinical (VPI, BoP,
GI, PPD, CAL, GM) and microbiological anaerobic
(ANAER) and aerobic (AER) bacterial loads were
assessed at baseline before treatment. Samples
were collected in the same session in test group
immediately after the topical administration
(T1b) to assess whether the topical agent had
some effectiveness if administered alone, and
then samples were repeated in both group after UD
treatment (T1c). Microbiological sampling and
Clinical measurements were repeated after 6 weeks
(T2) and after 3 months (T3).
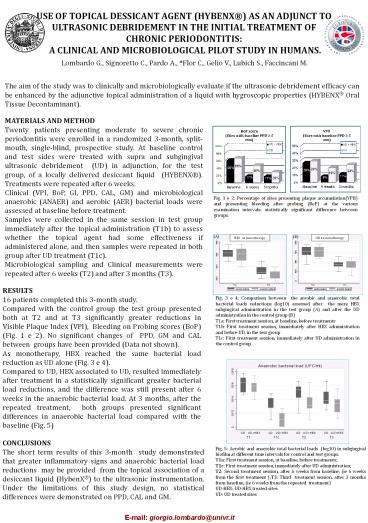
Fig. 1 e 2 Percentage of sites presenting plaque
accumulation(VPII) and presenting bleeding after
probing (BoP) at the various examination
intervals statistically significant difference
between groups.
(A)
(B)
UD as monotherapy
RESULTS 16 patients completed this 3-month study.
Compared with the control group the test group
presented both at T2 and at T3 significantly
greater reductions in Visible Plaque Index
(VPI), Bleeding on Probing scores (BoP) (Fig. 1
e 2). No significant changes of PPD, GM and CAL
between groups have been provided (Data not
shown). As monotherapy, HBX reached the same
bacterial load reduction as UD alone (Fig. 3 e
4). Compared to UD, HBX associated to UD,
resulted immediately after treatment in a
statistically significant greater bacterial load
reductions, and the difference was still present
after 6 weeks in the anaerobic bacterial load. At
3 months, after the repeated treatment, both
groups presented significant differences in
anaerobic bacterial load compared with the
baseline (Fig. 5)
Fig. 3 e 4 Comparison between the aerobic and
anaerobic total bacterial loads reductions
(log10) assessed after the mere HBX subgingival
administration in the test group (A) and after
the UD administration in the control group
(B) T1a First treatment session, at baseline,
before treatments T1b First treatment session,
immediately after HBX administration and before
UD, in the test group T1c First treatment
session, immediately after UD administration in
the control group
CONCLUSIONS The short term results of this
3-month study demonstrated that greater
inflammatory signs and anaerobic bacterial load
reductions may be provided from the topical
association of a desiccant liquid (HybenX) to
the ultrasonic instrumentation. Under the
limitations of this study design, no statistical
differences were demonstrated on PPD, CAL and GM.
Fig. 5 Aerobic and anaerobic total bacterial
loads (log10) in subgingival biofilm at
different time intervals for control and test
groups. T1a First treatment session, at
baseline, before treatments T1c First
treatment session, immediately after UD
administration T2 Second treatment session,
after 6 weeks from baseline, (ie 6 weeks from the
first treatment )T3 Third treatment session,
after 3 months from baseline, (ie 6 weeks from
the repeated treatment) UD-HBX UD-HBX treated
sites UD UD treated sites
E-mail giorgio.lombardo_at_univr.it