Types of Isomers - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
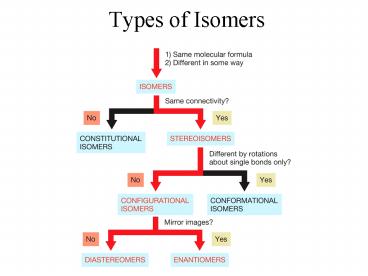
Types of Isomers
Description:
Optical Activity Chiral molecules interact with plane ... A polarizer generates plane-polarized light by filtering out light whose electric field oscillates in any ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:262
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Types of Isomers
1
Types of Isomers
2
Enantiomers
- Enantiomers are nonsuperimposable mirror images.
- Molecules are nonsuperimposable if there is no
orientation in which all atoms of both molecules
can be superimposed.
3
Ibuprofen
R form non-active side effects
S form active anti-inflammatory
4
Thalidomide is now being used to treat plasma
cell cancer, leprosy, and has shown anti-HIV
activity
5
Chirality
- A molecule is chiral if it has an enantiomer.
- Does NOT have mirror symmetry
- A molecule is achiral if it does not have an
enantiomer. - DOES have mirror symmetry
6
Terminology in Stereochemistry
- Stereocenter
- An atom about which exchange of 2 groups produces
a stereoisomer - Chiral Center
- Type of Stereocenter
- A tetrahedral atom that is bonded to four
different groups
7
(No Transcript)
8
Fischer Projections
- The Fischer projection is a convenient way to
depict complex molecules having more than one
stereocenter. - The intersection of a horizontal line and a
vertical line indicates a carbon stereocenter. - The substituents on the horizontal bonds are
understood to point toward you (like a bowtie),
whereas the substituents on the vertical bonds
are understood to point away from you.
9
Chirality and Conformational Isomers
- Rotation about single bonds can determine whether
a molecule is chiral or achiral. - If a molecule and its mirror image are rapidly
interconverting conformational isomers, then the
molecule is effectively achiral. - The mirror image of 1,2-dibromoethane in one of
its gauche conformations is its second gauche
conformation.
10
Haworth Projections
- Haworth projections are helpful in determining
the chirality of all cyclics. - Taking the chair conformation of cyclohexane to a
flat hexagon allows us to quickly and accurately
determine whether it is chiral or achiral.
11
Frozen Conformational Isomers
biphenyls
has been resolved half-life for racemization is
78 min at 118oC
12
Physical and Chemical Properties of Isomers
- Constitutional Isomers
- Due to different connectivities, these isomers
must have different physical and chemical
properties. - Enantiomers
- Have the same connectivities and precisely the
same polarities. - Diastereomers
- Have the same connectivities but different 3-D
arrangement, so they have different properties.
13
Optical Activity
- Chiral molecules interact with plane-polarized
light. - When all photons from a light source have their
electric fields oscillating in the same plane,
then the light is plane polarized.
14
The Polarizer
- Most light sources emit light that is
unpolarized. - A polarizer generates plane-polarized light by
filtering out light whose electric field
oscillates in any other plane. - If plane-polarized light passes through a sample
of a compound, the plane in which the light is
polarized can change, depending upon whether the
compound is chiral or achiral.
15
Enantiomers rotate Plane Polarized Light
- One enantiomer rotates polarized light in one
direction while the other enantiomer rotates it
in the opposite direction. - Enantiomers have identical physical and chemical
properties except the direction at which they
rotate polarized light.
16
(No Transcript)
17
Louis Pasteur
- Louis Pasteur was the first to isolate a pair of
enantiomers from each other. - Pasteur noted that the crystals appeared to grow
in one of two varietiesleft-handed crystals and
right-handed crystalsthat are mirror images of
each other - Pasteur physically separated the two types of
crystals using tweezers.
18
Separating (Resolving) Enantiomers
- Option for Separating Enantiomers
- Pasteur Method
- Conversion to Diastereomers
- Temporarily convert the enantiomers into a pair
of diastereomers (will now have different
physical properties). - Separate those diastereomers from each other by
exploiting their different physical and chemical
properties. - Regenerate the enantiomers from the separated
diastereomers. - Enzymes (version of 2)
- Chiral Chromatography (version of 2)
19
enantiomers to be separated
one enantiomer of a chiral amine
diastereomeric salts
one diastereomer
one pure enantiomer