Types of Isomers - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 9
Title:
Types of Isomers
Description:
Stereoisomers are very similar in characteristics and reactivity. ... smell receptor site will produce a different 'signal' or smell for two enantiomers ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:1348
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Types of Isomers
1
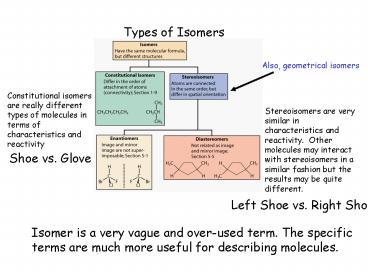
Types of Isomers
Also, geometrical isomers
Constitutional isomers are really different types
of molecules in terms of characteristics and
reactivity
Stereoisomers are very similar in characteristics
and reactivity. Other molecules may interact
with stereoisomers in a similar fashion but the
results may be quite different.
Shoe vs. Glove
Left Shoe vs. Right Shoe
Isomer is a very vague and over-used term. The
specific terms are much more useful for
describing molecules.
2
Stereoisomeric Definitions
Superimposable - spatially identical in 3D -
baseball hats Chiral - object whose mirror image
is nonsuperimposable - shoes, gloves Enantiomers
- pair of chiral molecules that are mirror images
of one another - enantiomer is one molecule of
the pair - pair of gloves Diastereomers - pair
of chiral molecules that have the same
connectivity, but are not superimposable and not
mirror images. - a pair of hands in which one of
the index fingers curves backwards. Asymmetric
atom or stereocenter - in most of organic
chemistry an atom with at least 4 different
substituents. For carbon, four different
substituents
3
Ramifications of Stereochemistry
Chiral objects distinguish between other chiral
objects - right hand fits the right
glove Chiral molecules distinguish between
enantiomeric molecules - smell receptor site
will produce a different signal or smell for
two enantiomers Enantiomers are identical except
in a chiral environment -same melting point,
boiling point, IR, polarity, solubility Diastereo
mers are different molecules, any similarities
are coincidental.
4
Chirality
Hands are Chiral
Hammers are not Chiral (Achiral)
5
Chiral Molecules and Reaction
Bromination of butane produces two molecules that
are -chiral -stereoisomers -enantiomers
6
Absolute Configuration R and S
R - rectus, Latin, right
S - sinister, Latin, left
Absolute configurations are a method of
nomenclature for stereogenic centers.
Steps to determine absolute configuration 1.
Assign a ranking to each of the four different
substituents -ranking is determined by atomic
number and then by multiplicity -the lower rank
is assigned a value of 4, while the highest rank
is assigned a value of 1. 2. Your right thumb is
placed pointing down the lowest ranking bond. 3.
If the curvature of your hand can pick-up the
substituents in decreasing order, e.g. 1-2-3,
then the stereogenic center is R. If you cannot
pick-up in 1-2-3 order than the assignment is S
7
Examples of R and S Determination
1
4
4
1
S
S
3
3
2
S
3
1
2
2
4
1
4
R
3
2
8
Comparing the R and S configurations is an
absolute method of determining diastereomers from
enantiomers
Mirror - enantiomers
enantiomers
S
R
RS SR
S
R
diastereomers
Not Mirror - diastereomers
R
RS RR
R
9
Polarization Change