Pre-Independence Laws: - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Pre-Independence Laws:
Description:
Title: PowerPoint Presentation Author: Vishnu Sudarsan Last modified by: amit Created Date: 11/19/2003 3:27:57 PM Document presentation format: On-screen Show – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:36
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Pre-Independence Laws:
1
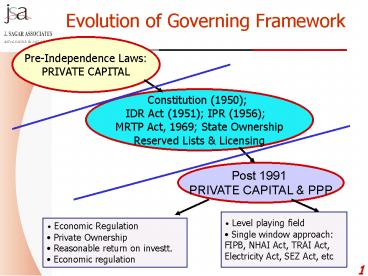
Evolution of Governing Framework
Pre-Independence Laws PRIVATE CAPITAL
Constitution (1950) IDR Act (1951) IPR (1956)
MRTP Act, 1969 State Ownership Reserved Lists
Licensing
Post 1991 PRIVATE CAPITAL PPP
- Level playing field
- Single window approach
- FIPB, NHAI Act, TRAI Act,
- Electricity Act, SEZ Act, etc
- Economic Regulation
- Private Ownership
- Reasonable return on investt.
- Economic regulation
2
MRTP Act vs Competition Act
MRTP Act Adjudicatory body Deeming provisions Pre-economic analysis a discretion Mergers are not within the domain Size of enterprises is frowned upon Complainants are limited International co-operation and Effects doctrine are not available Law could not be promoted Public interest Others Role of DG, absence of Leniency programme etc. Competition Act (CA) Market Regulator Rule of reason Pre-economic analysis is mandatory MA is one of the important functions Size is not bad but its abuse is Except Defence, Space Currency all commercial activities are within the ambit of the Law They are available Statutory advocacy role More filters Others enhanced role of DG, availability of Leniency etc.
3
Abuse of Dominance RULE OF REASON TARGET
ABUSE, NOT DOMINANCE
- Dominant position
- Ability to operate independent of competitive
forces prevailing in the relevant market - Affect its competitor/consumers/relevant market
- Abuse of dominant position
- Imposing unfair or discriminatory conditions
- Predatory pricing, limit production, deny market
access - Contracts contingent on supplementary obligation
- Use dominance in one market to move into or
protect other relevant market (product
geography)
4
Dominance FACTORS IN THE RELEVANT MARKET
- Market share of the enterprise
- Size or Resources of enterprise
- Size importance of competitors
- Economic power of enterprise
- Vertical integration of enterprises or their
network - Dependence of consumers
- Market structure size of market
- Entry barriers
- Monopoly/Dominance due to statute/govt. sanction
- Social obligation/costs
- Relative competitive advantage development vs
adverse effect on competition
5
Cartels
- Cartel
- Association of producers, sellers, distributors,
traders or service providers who - By inter-se agreement limit, control or attempt
to limit/control the production, sale or price of
or trade in goods /services