More on Input Output - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
More on Input Output
Description:
More on Input Output Input Stream : A sequence of characters from an input device (like the keyboard) to the computer (the program running). Output Stream : A ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:89
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: More on Input Output
1
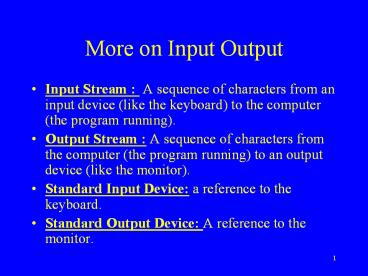
More on Input Output
- Input Stream A sequence of characters from an
input device (like the keyboard) to the computer
(the program running). - Output Stream A sequence of characters from the
computer (the program running) to an output
device (like the monitor). - Standard Input Device a reference to the
keyboard. - Standard Output Device A reference to the
monitor.
2
More on Input Output
- The include statements are also called headers
- The header include ltiostreamgt includes the
standard streams to the standard output and
standard input devices as long as we have the
statement - namespace std or the alternative
- stdcout
- stdcin
3
More on Input Output
- The symbol gtgt stands for extraction operator.
- It is a binary operator
- The left operand is a stream and the right
operand is a memory location. - i.e
- double payRate
- cingtgtpayRate
- The computer inputs the number typed on keyboard
and stores it in memory location identified as
payRate.
4
Selection (if-then-else)
- Programming Has 3 Types of Control
- Sequential (normal) Control of Execution
Proceeds One after the Other - Selection (if-then-else) Control Proceeds
Dependent on Conditions - Iteration (looping) Control Repeated until
Condition Met
5
C if Statement Syntax
- Syntax
- if (condition) statement
- If Condition Is True, Statement Is Executed
- If Condition Is False, Statement Is Not Executed
- If Multiple Actions Are Required for Statement, a
Compound Statement Must Be Used - if (condition)
- statement
- statement
6
Conditional Operators
- Relational Operators lt , gt , gt , lt
- Equality Operators , !
7
Selection Examples
- if (age lt 30)
- cout ltlt You are very very Young ltlt endl
- if (grade A)
- cout ltlt Congratulations! ltlt endl
- if (grade ! F)
- cout ltlt You passed! ltlt endl
8
else Statement
- Syntax
- if (condition)
- statement(s) //condition true
- else
- statement(s) //condition false
9
if-else Example
- if (myGrade gt 60)
- cout ltlt You passed! ltlt endl
- else
- cout ltlt How about them Cubs? ltlt endl
10
Compound Statements
- Compound Statement One or More Statements within
a Set of Curly Braces - Must Use Compound Statement if More than One
Statement Is Supposed to be under Control of if
or else Conditional - Include Curly Braces after if so if other
Statements Are Added in Future, Curly Braces Are
Already There
11
Nested if Statements
- if (myGrade gt 80)
- if (myGrade gt 90)
- cout ltlt You have an A! ltlt endl
- else
- cout ltlt You have a B! ltlt endl
- else
- cout ltlt Well give you a C. ltlt endl
12
if/else (Cascaded)
- Sequence of if/else Statements
- Example
- if (myGrade gt 90)
- cout ltlt A! ltlt endl
- else
- if (myGrade gt 80)
- cout ltlt B! ltlt endl
- else
- if (myGrade gt 70)
- cout ltlt C! ltlt endl
- else
- cout ltlt Oh-oh! ltlt endl
13
Boolean Type
- A Boolean Value Is One of Either True or
False - In C, Type bool
- Example
- bool done false
- . . .
- if (currentLetter Z)
- done true
- else
- done false
- if (done)
- return(0)
- . . .
14
Boolean Type
- if/else Conditionals Must Evaluate to True or
False, and Are Therefore Called Boolean
Expressions - In C, Any Non-Zero Value Is Considered True
Any Expression Evaluating to Zero Is Considered
False
15
Logical Operators
- A Logical Operator Is One Used to Further Specify
True or False in an Expression - Connects Two or More Expressions Together
- Is Logical AND
- Is Logical OR
- Both Operands Must Be True for Entire
Expression to Be True - Only One (or Both) of the Operands Must Be
True for Entire Expression to Be True
16
Logical Operators
- if (numStudents gt MIN numStudents lt MAX)
- classRun true
- if (numStudents gt MAX numInstructors 0)
- classRun false
17
Operator Precedence
- ()
- ! (not)
- , /,
- , -
- lt, lt, gt, gt (Relational Operators)
- , ! (Equality Operators)
- (Logical AND)
- (Logical OR)
- (ASSIGNMENT)
18
Order of Operations
- Precedence Level of Importance of Operations
- Multiplicative Operators Have Higher Precedence
than Additive Operators - , /, Higher
- , - Lower
- Associativity Order of Operation for Equal Level
Precedence - Most Operators Have Left-to-Right Associativity
- Use Parentheses to Force Differing Precedence of
Operations
19
Multiple Logical Operators
- if ( num1 gt MAX num2 0 num3 0)
- cout ltlt num1 is MAX or something is 0
- cout ltlt I think.. ltlt endl
20
Switch Statements
- Also Called Switch/Case Statement
- Just Case in Other Languages
- Selects Among Several Different Actions
- Can Only Select from Integer or Character
- If an Integer Value Is Matched, Statements under
Control of that Case Block Are Executed
21
Switch/Case Example
- int numPassengers
- cout ltlt Enter Passengers
- cin gtgt numPassengers
- switch(numPassengers)
- case 2
- rate BASERATE 0.80
- break
- case 4
- rate BASERATE 0.75
- break
- case 5
- rate BASERATE 0.55
- break
- default
- rate BASERATE
- break
22
Switch Case Example
- char menuItem
- cout ltlt "Enter Menu Selection "
- cin gtgt menuItem
- switch(menuItem)
- case 'O'
- / code to do ordering goes here/
- break
- case 'C'
- / code to do checkout goes here/
- break
- default
- cout ltlt Unknown option ltlt endl
- break
23
Announcements
- Exam 1 Tuesday July 14.
- 25 minutes
- 10 of Total Grade
- Covers Everything through Lectures 03 and o4
- All Terms (Underlined Items)
- Variable Declaration, Initialization, and
Assignment - Constant Declaration
- Expressions
- Operators
- Input (cin) and Output (cout)
- if/else and else if selections
- Logical Operators
- Switch