Unit 2: Cells - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Unit 2: Cells
Description:
Which of the graphs represents the effect of temperature on the rate of photosynthesis? III. Overview of Cellular Respiration (4.4) A. Cellular respiration makes ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:114
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Unit 2: Cells
1
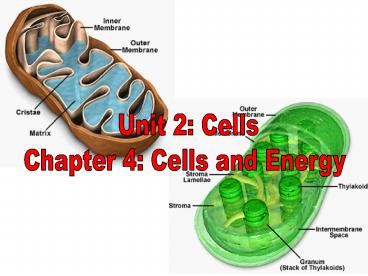
Unit 2 Cells Chapter 4 Cells and Energy
2
UNIT 2 Cells Chapter 4 Cells and Energy I.
Chemical Energy and ATP (4.1) A. The
________________used for most cell processes is
carried by _______ 1. All ________-based
molecules in _____ store chemical energy in
their ________
3
a. _________________ and _________ most
important energy sources. b. Energy comes from
food indirectly
4
2. All cells use energy carried by _________ a.
ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is molecule that
transfers energy from breakdown of food b. ATP
carries energy cells can use c. Used for
________________,__________ ____________ by
___________ transport, etc.
5
3. Energy of ATP released when ___________
__________ is removed a. Bond holding third
phosphate group is unstable and very easily
broken
6
b. When loses 3rd phosphate group, ATP become
_______ (adenosine diphosphate) 1). ADP is a
lower energy molecule than ATP 2). Can be
converted back into ATP with addition of
________ (adding phosphate group)
7
3). The breakdown of ATP to ADP and production
of ATP from ADP can be represented by
________. 4). This requires complex group of
proteins to help.
8
The most important energy storing compound is
______
A
P
P
P
ATP
9
B. Organisms break down _________-based molecules
to produce ________ 1. ________ you eat does not
contain _____ a. Food must first be __________
(break down into smaller molecules) b. Foods
provide different amounts of energy
(__________)
10
2. Number of ATP molecules depends on type of
molecule broken down (___________, _________,
__________) a. __________________ most commonly
broken down to make ATP b. Break down of
____________ yields _______ molecules of ATP
11
3. Fats store about 80 of energy in your
body a. When broken down, yield the most
ATP b. A typical triglyceride yields about
________ molecules of ATP
12
4. ____________ have about as much ATP as
carbohydrates a. Less likely to be broken
down b. ______________ needed to build new
proteins
13
5. _________ also need ATP a. Plants do not
eat to obtain energy b. Use energy produced by
_______________ (make sugars from
sunlight)
14
C. A few types of organisms do not need sunlight
and photosynthesis as a source of energy 1. Some
organisms use _________________ to produce
energy (sugars) 2. Used by organisms in
hydrothermal vents (deep ocean)
15
II. Overview of Photosynthesis (4.2) A.
Photosynthetic organisms are _________ 1.
Producers make their own source of
___________________
16
2. Plants use _______________ and are
producers
a. ______________ is process that captures
_________ from sunlight to make _________ that
store chemical energy
17
b. Uses __________ light made up of several
colors (wavelengths) of light.
18
1). Plants use molecule in _____________ called
__________________ 2). Two main types of
chlorophyll
19
a. Chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b b. Absorb
mostly ______ and ______ wavelengths.
c. Plants appear __________ because reflect green
light (not absorbed)
20
B. Photosynthesis in plants occurs in
____________ 1. Most of chloroplast are in
leaf cells
21
2. Two main parts of _______________ needed for
photosynthesis a. _______- stacks of
coin-shaped, membrane- enclosed compartments
called ____________. b. Membrane in thylakoids
contain _________________ c. _________ is the
fluid that surrounds grana
22
C. Photosynthesis occurs in two main stages 1.
_____________________ (capture energy from
sunlight)
a. Occurs within and across membrane of
_____________ b. ______ and _____________ are
needed.
23
c. Light dependent reactions 1).
_________________ absorbs energy from sunlight.
(photosystem)
24
2). ___________ transferred along thylakoid
membrane. 3). ________ molecules broken
down. 4).___________molecules produced
25
3). H2O molecules ______________. 4). Oxygen
molecules ____________
26
2. _____________________(uses energy produced
from light-dependent reactions) a. Occur in the
___________ of chloroplasts
27
b. ___________ needed 1). ________ added to
cycle to build larger molecules
(____________cycle) 2). _________ from light
dependent reactions is used 3). Molecule of
simple sugar is produced (usually
__________C6H12O6)
28
3. Equation for whole photosynthetic
process 6___ 6___ ? ????_______ 6___
____, _______
29
CO2
________________Reactions
______ cycle
O2
Glucose
30
D. Functions of Photosynthesis 1. Plant
produce ________ for themselves and other
organisms
2. Animals use ________ produced by
photosynthesis in __________________(released
stored energy)
31
3. It provides materials for plant growth and
development (simple sugars bonded together to
form carbohydrates like ________ and
____________)
32
4. Regulates Earths environment (removes
__________________from Earths atmosphere)
33
Which of the graphs represents the effect of
light intensity on the rate of photosynthesis?
34
Which of the graphs represents the effect of
temperature on the rate of photosynthesis?
35
III. Overview of Cellular Respiration (4.4) A.
Cellular respiration makes _______ by breaking
down _________ and other carbon- based molecules
to make ATP
1. Cellular respiration is ________ (requires
__________) 2. Takes place in _________________
(cellpowerhouse)
36
B. Process starts with _____________ (means
glucose breaking) 1. 6-carbon glucose broken
into two 3- carbon molecules of pyruvic
acid 2. Produces 2 molecules of _______ (makes
4, but uses 2 ATP net of 2 ATP)
37
3. anaerobic process (does not require
_________) 4. Takes place in _______________ 5.
Products of glycolysis used in respiration
process.
38
C. Cellular respiration is like mirror image of
_____________________ 1. Chemical equation for
cellular respiration is basically the
___________- of that for photosynthesis 2.
Structures in __________________ and
________________ are similar 6CO2 6H2O ?
????____________ 6_______
____________ ________ ? ???6CO2 6H2O
39
D. Cellular Respiration takes place in two main
stages
1. Krebs cycle- takes place in interior space of
______________.
40
a. 3-carbon molecules produced in glycolysis are
broken down in a cycle of chemical
reactions
b. _____________is given off (CO2) c. _______
produced is transferred to 2nd stage (energy in
the form of ATP and other charged molecules-
NADH and FADH2)
41
2. Electron Transport Chain-
a. Takes place in inner membrane b. Energy
transferred to electron transport chain
42
c. _________ enters process and picks up
electrons and hydrogen to make H2O (water) d.
________ produced (34 to 36 molecules) for a
total of 36 to 38 including glycolysis e. Many
___________ required for process
2
2
32
43
E. Overall equation of cellular respiration
_______ 6_____ ? ???6____ 6____
44
F. Comparing Photosynthesis and Cellular
Respiration (reactants of photosynthesis are same
as products of cellular respiration)
45
IV. Fermentation (4.6) A. Fermentation allows
_________ to continue 1. Fermentation allows
glycolysis to continue making _____ when
_________ is unavailable
46
2. Fermentation is an ___________ process
a. Occurs when oxygen not available for
cellular respiration b. Does not produce
ATP 3. NAD is recycled to glycolysis
47
B. ________________fermentation- occurs in muscle
cells 1. Glycolysis splits __________ into two
pyruvate molecules 2. Pyruvate and NADH enter
fermentation
48
3. Energy from NADH converts pyruvate into
lactic acid 4. NADH is changed back into
NAD
49
C. ___________ fermentation- similar to lactic
acid fermentation
1. Products of alcoholic fermentation include
______, ______, ______ 2. Glycolysis splits
glucose and products enter fermentation
50
3. Energy from NADH is used to spit pyruvate
into an alcohol and carbon dioxide 4. NADH is
changed back into NAD 5. NAD is recycled to
glycolysis
51
Energy and Exercise
Quick Energy
- Cells contain only enough ATP for a few seconds
of intense activity
- Then cells rely on _____________fermentation (can
supply for about 90 seconds)
- Lactic acid build-up causes ___________ in
muscles. Only way to get rid of lactic acid is
chemical pathway that requires oxygen (why you
breathe heavy after heavy excercise.)
52
Long Term Energy
- Cellular respiration only way to produce
continuous supply of_______
- Energy stored in muscles and other tissue in form
of carbohydrate ____________
- Enough glycogen for about 15 to 20 min.
- When glycogen used up, body breaks down other
stored molecules including _______, for energy.
53
A variety of organic molecules can be utilized to
produce energy. These molecules enter the Krebs
cycle different stages.