Throat and Thorax Injuries - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 28
Title:
Throat and Thorax Injuries
Description:
Throat and Thorax Injuries Chapter 7 Chapter 7 Objectives Understand the basic anatomy of the throat and thorax. Understand how to prevent injuries of the throat and ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:221
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Throat and Thorax Injuries
1
Throat and Thorax Injuries
Chapter 7
- Chapter 7
2
Objectives
- Understand the basic anatomy of the throat and
thorax. - Understand how to prevent injuries of the throat
and thorax. - Know the care necessary to treat an injury within
the throat or thorax. - Understand the implications of illness or injury
related to a specific organ in the thorax.
3
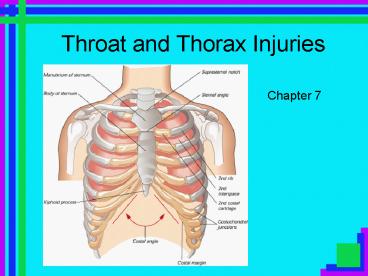
Throat Anatomy
- Carotid artery
- Jugular vein
- Larynx
- Trachea
- Esophagus
4
Throat Anatomy
- Esophagus
- Passageway for food
- In front of cervical vertebrae, behind trachea
and larynx - Trachea
- Made up of circular rings of cartilage
- Main passageway for air to get to and from lungs
- Larynx
- Modified portion of upper trachea, contains vocal
cords
5
Throat Anatomy
- Carotid artery
- One on each side of the trachea
- Carries oxygenated blood to the brain
- Jugular vein
- One on each side of the trachea
- Carries unoxygenated blood away from the brain
- Deadly if either are severed
6
Thorax Anatomy
- Thoracic Vertebrae
- 12 Ribs on each side (2 floating)
- Sternum
- These bones function to protect the organs
7
Thoracic organs
- Heart
- Lungs
- Diaphragm
8
Thorax Anatomy
- Heart
- Size of your fist
- Pumps blood to all parts of body
- Blood carries nutrients and oxygen to cells and
carbon dioxide and waste away from cells
9
Heart
- Chambers
- Left and right atrium
- Left and right ventricle
- Thicker due to function of pumping blood
throughout the body
10
Heart
- Function-pumps blood to lungs and entire body
- Path
- Right atrium(RA) fills with deoxygenated blood
from body - Goes to right ventricle (RV) and out to lungs to
receive oxygen
11
Heart
- Path (continued)
- Left atrium (LA) receives oxygenated blood from
the lungs - Goes to left ventricle (LV)largest chamber of
the heart and sends it to the rest of the body
through the aorta to other major arteries - Once oxygen is used, blood returns to heart
through veins
12
Lungs
- Function to exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide
and dissipate body heat
13
Lungs
- Bronchi
- Branches of the trachea
- Bronchioles
- Divisions of the bronchi
- Alveoli
- Ends of the bronchioles where oxygen-carbon
dioxide exchange occurs
14
Diaphragm
- Separates thorax and abdominal cavities
- Contracts and pulls down to assist inhalation and
moves up to push air out
15
Injury Prevention
- Protective equipment
- Rules
- Always buy best protective equipment
16
Treating throat injuries and conditions
- Most injuries to throat are contusions caused by
a blow from sticks, feet, or arms - Treat with ice
- Most response to throat injury is coughing,
spitting, difficulty breathing, and pain
17
Throat lacerations
- Superficial lacerations can be controlled with
direct pressure - Deep are medical emergencies
- Apply direct pressure, treat for shock
- Must respond quickly
18
Cartilage fracture
- Caused by severe blow to throat
- Can be life threatening
- Causes difficulty breathing, gasping, spitting
blood, pain, difficulty talking, appear anxious - May turn blue (lack of oxygen)
- Treat with extreme care due to possible cervical
spine injury - Treat as medical emergency (call 911) and
backboard to transport - Ice area, keep athlete calm, keep airway free of
blood
19
Pneumothorax
- Air in the pleural cavity (collapsed lung)
- Can occur with or without trauma
- Traumatic caused by punctured lung (rib fracture,
gunshot, severe laceration) - Non-traumatic caused by weakness of lung tissue
20
Pneumothorax
- When occurs, injured lung moves toward center of
chest, puts pressure on heart and other organs - Causes difficulty breathing and athlete will gasp
for air - Inhaled air escapes through hole and into chest
cavity which causes further compression on organs
21
Spontaneous pneumothorax
- Can happen in healthy athlete
- Caused by weakness in lung tissue
- Difficulty breathing, chest pain, possible blue
skin (cyanotic) - Place athlete on ground with injured lung closest
to ground, treat for shock and treat as medical
emergency (911) - Usually heals itself without surgery
22
Tension Pneumothorax
- Air leaking out forces lung into other lung and
heart - Tracheal deviation possible causing more
respiratory distress - Death can occur if not treated rapidly
- If there is an external puncture would, partially
cover it leaving one side unsealed to prevent
tension from getting worse
23
Tension Pneumothorax
- Sign/symptoms
- Respiratory distress
- Absent breath sounds on injured side
- Anxiety
- Bluish skin color
- Pulse rapid and weak
- Blood pressure will drop
- Injury requires physician to insert a chest tube
and possible surgical intervention
24
Flail chest
- Multiple ribs fractured in 2 or more places
- Occurs from direct impact
- Entire fractured portion moves in and out when
athlete breathes, but opposite normal - Very painful, possible other internal injuries
25
Flail chest
- Treatment- decrease movement of fracture
- Treat athlete for shock
- Call 911 immediately
26
Pulmonary contusions
- Bruised lung
- Direct impact (usually blunt object)
- Causes bleeding and swelling
- Difficulty breathing and bluish skin color
- Call 911, ice if athlete allows
27
Sucking chest wounds
- Puncture of chest wall, air from outside is drawn
noisily into cavity - Lung is not punctured
- Air coming in causes pressure on lungs causing
distress - Difficulty breathing, circulation impairment
(cyanotic) - Seal wound with cellophane or plastic bag
- Call EMS immediately
28
Hyperventilation
- Quick breathing gt24 breaths per min
- Causes abnormal loss of carbon dioxide from the
blood - Caused by becoming overly excited, anxiety, or
diabetes - Can become dizzy, experience numbness in
extremities, and/or loss of consciousness - Treat by encouraging athlete to breath slowly,
calming the athlete