Township and Range System in the U.S. - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Township and Range System in the U.S.
Description:
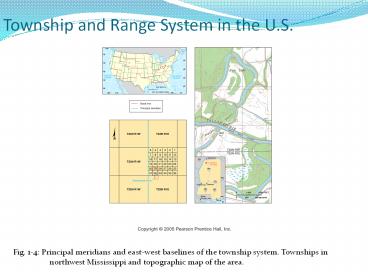
Township and Range System in the U.S. Fig. 1-4: Principal meridians and east-west baselines of the township system. Townships in northwest Mississippi and topographic ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:145
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Township and Range System in the U.S.
1
Township and Range System in the U.S.
Fig. 1-4 Principal meridians and east-west
baselines of the township system. Townships in
northwest Mississippi and topographic map of the
area.
2
Layers of a GIS
Fig. 1-5 A geographic information system (GIS)
stores information about a location in several
layers. Each layer represents a different
category of information.
3
Place Unique Location of a Feature
4
Place Names
- Toponym is the given name of a place
- Types of Toponyms
- For a person
- Religion
- Landscape/physical features
- Names can change
- Cincinnati, OH
- Truth or Consequence
5
Site
- Physical character of a place
- Climate, water sources, topography, soil,
vegetation, latitude, and elevation - Site factors have been essential in selecting
locations for settlements - Humans can modify the characteristics of a site
6
Site Lower Manhattan Island
Fig. 1-6 Site of lower Manhattan Island, New
York City. There have been many changes to the
area over the last 200 years.
7
(No Transcript)
8
Situation
- The location of a place relative to other places
- Can help us find unfamiliar places
- Helps us understand the importance of a location
9
Situation Singapore
Fig. 1-7 Singapore is situated at a key location
for international trade.
10
(No Transcript)
11
Mathematical Location
- Latitude (N/S)
- Parallels
- Equator
- Longitude (E/W)
- Meridians
- Prime Meridian runs through Greenwich, England
- Which is important in calculating time??
12
World Geographic Grid
Fig. 1-8 The world geographic grid consists of
meridians of longitude and parallels of latitude.
The prime meridian (0º) passes through Greenwich,
England.
13
World Time Zones
Fig. 1-9 The worlds 24 standard time zones are
often depicted using the Mercator projection.