THROW Pattern PUSH Pattern - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
THROW Pattern PUSH Pattern
Description:
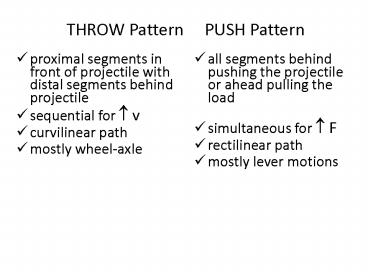
THROW Pattern PUSH Pattern proximal segments in front of projectile with distal segments behind projectile sequential for v curvilinear path – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:107
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: THROW Pattern PUSH Pattern
1
THROW Pattern PUSH Pattern
- proximal segments in front of projectile with
distal segments behind projectile - sequential for ? v
- curvilinear path
- mostly wheel-axle
- all segments behind pushing the projectile or
ahead pulling the load - simultaneous for ? F
- rectilinear path
- mostly lever motions
2
Preparation Phase 1. Rotate torso so that contra
lateral shoulder faces target 2. Step forward
with contra lateral leg
3
Hips Rotate whileupper torso and arm lag behind
4
1. HIPS are stopped while upper torso and
shoulders continue to rotate 2. Upper torso and
shoulders are stopped once they are aligned
with hips/lower torso
5
Wheel-Axle medial rotation of the shoulder
6
Wheel-Axle pronation during release phase
7
v r ? r is increased about both longitudinal
axis of torso via elbow extension
8
Release Point is beside torsonot in front of
torso
9
Mechanical Purposes of PUSH
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
10
Push Pattern for Force Activities
- maximum strength movements demand simultaneous
segmental rotations - move in a rectilinear path
- minimize acceleration in movements to avoid
injury and to comply with Force/Velocity principle
11
PUSH Pattern Power Activities
- Power movements require both F and v
- moving a resistance fast requires higher F max
- rapid acceleration in a short period of time
- strength-dominant P (e.g. shot putting)
- speed-dominant P (e.g. jump, start, strike, throw)
12
Power in Jumping
- PUSH body into space via segmental rotations
- large F required to achieve maximum vertical or
maximum horizontal distance - takeoff of a jump for maximum DistanceVERT
- bodys C of G has high VVERT moderate VHORZ
- takeoff of a jump for maximum DistanceHORZ
- bodys C of G has high VVERT high VHORZ
13
Jumping Motions Sequence
- 1. Massive segments/trunk _at_ open end of chain
- 2. Small segments/feet _at_ closed/fixed end
- 3. ideal direction of F is through bodys CG
- 4. initial shoulder flexion exerts downward F
- 5. stopping shld. flexion initiates trunk
extension - 6. Shld. flexion trunk extension loads legs
- 7. Loading of leg muscles increases ROM and
elicits elastic recoil in hip knee extensors
14
Jumping Motions Sequence
- 1. Massive segments/trunk _at_ open end of chain
- 2. Small segments/feet _at_ closed/fixed end
- 3. ideal direction of F is through bodys C of G
- 4. initial shoulder flexion exerts downward F
- 5. stopping shld. flexion initiates trunk
extension - 6. Shld. flexion trunk extension loads legs
- 7. Loading of leg muscles increases ROM and
elicits elastic recoil in hip knee extensors
15
Punch/Strike Power/Accuracy
- F v accuracy important in punch or strike
- Throw/Push Continuum involved in Punch/Strike
- v is initiated and increased using the kinetic
link and a curvilinear path v r? - F and accuracy is achieved by changing to a
rectilinear path near the end of the ROM, just
prior to contact/impact
16
Accuracy Accuracy with v
- Consistency in movements key to success
- straight line motion just prior to, during, and
just after release/impact - rectilinear path for projecting for short
distance - curvilinear then a flat space to a rectilinear
path just prior to and during release/impact
17
curvilinear path then a flat space to a
rectilinear path just prior to and during
release/impact