PowerPoint-Pr - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 1
Title:
PowerPoint-Pr
Description:
The Greifswald Blood Donor Study (GREBDOS): A tool for comparing blood donors with the general population Table 1: Distribution of gender and year of birth depending ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:37
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: PowerPoint-Pr
1
The Greifswald Blood Donor Study (GREBDOS) A
tool for comparing blood donors with the general
population
Lubenow N1, Konerding U2, Alpen U1, Bezold K2,
Hoffmann W2, Kohlmann T2, Greinacher A1
1Institute of Transfusion Medicine, 2Institute
for Community Medicine, University of Greifswald
Background Facing major demographic changes
(Greinacher et al. 2006), which will cause an
increased need for blood transfusion, strategies
to motivate donors will be of great importance to
secure blood supply. However, few data for
comparing blood donors with the general
population exist. This makes it difficult to
outline strategies for blood donor motivation. In
the region of Western Pomerania (north-east
Germany) the general population was well
characterised by the Study of Health in Pomerania
(SHIP, John et al. 2001). We report the design
and first results of a study comparing the
population of blood donors with the general
population within the same region The Greifswald
Blood Donor Study (GREBDOS).
Methods In GREBDOS over 12 months each 6th
person enrolling for blood donation was asked to
participate in the study. If this person refused
or had already participated, the next 6th person
was asked. Complete participation comprised 1) to
fill in a structured questionnaire which
contained a selection of questions posed in SHIP
(see questionnaire attached to poster) and 2) to
give a blood sample. To correct for multiple
donations the number of donations given within
the study interval was recorded for each
participant at the end of the study period.
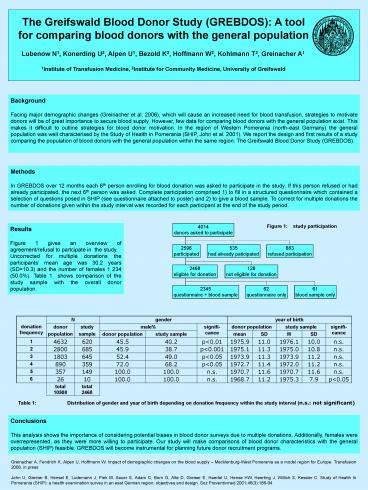
Results Figure 1 gives an overview of
agreement/refusal to partcipate in the
study. Uncorrected for multiple donations the
participants mean age was 30.2 years (SD10.3)
and the number of females 1 234 (50.0). Table 1
shows comparison of the study sample with the
overall donor population.
donation frequency N N gender gender gender year of birth year of birth year of birth year of birth year of birth
donation frequency donor population study sample male male signifi-cance donor population donor population study sample study sample signifi-cance
donation frequency donor population study sample donor population study sample signifi-cance mean SD M SD signifi-cance
1 4632 620 45.5 40.2 plt0.01 1975.9 11.0 1976.1 10.0 n.s.
2 2800 685 45.9 38.7 plt0.001 1975.1 11.3 1975.0 10.8 n.s.
3 1803 645 52.4 49.0 plt0.05 1973.9 11.3 1973.9 11.2 n.s.
4 890 359 72.0 68.2 plt0.05 1972.7 11.4 1972.0 11.2 n.s.
5 357 149 100.0 100.0 n.s. 1970.7 11.6 1970.7 11.6 n.s.
6 26 10 100.0 100.0 n.s. 1968.7 11.2 1975.3 7.9 plt0.05
total 10508 total 2468
Conclusions This analysis shows the importance
of considering potential biases in blood donor
surveys due to multiple donations. Additionally,
females were overrepresented, as they were more
willing to participate. Our study will make
comparisons of blood donor characteristics with
the general population (SHIP) feasible. GREBDOS
will become instrumental for planning future
donor recruitment programs.
Greinacher A, Fendrich K, Alpen U, Hoffmann W.
Impact of demographic changes on the blood supply
Mecklenburg-West Pomerania as a model region
for Europe. Transfusion 2006, in press John U,
Greiner B, Hensel E, Ludemann J, Piek M, Sauer S,
Adam C, Born G, Alte D, Greiser E, Haertel U,
Hense HW, Haerting J, Willich S, Kessler C. Study
of Health In Pomerania (SHIP) a health
examination survey in an east German region
objectives and design. Soz Praventivmed
200146(3)186-94