The Skeletal System - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
The Skeletal System
Description:
The human skeleton is made of individual or joined bones supported and supplemented by a structure of ligaments, tendons, muscles, cartilage and other organs. – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:170
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: The Skeletal System
1
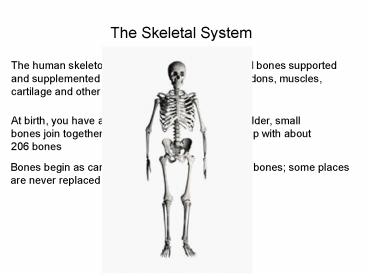
The Skeletal System
The human skeleton is made of individual or
joined bones supported and supplemented by a
structure of ligaments, tendons, muscles,
cartilage and other organs.
At birth, you have about 300 bones. As you grow
older, small bones join together to make big
ones. Adults end up with about 206 bones
Bones begin as cartilage and then are replaced by
bones some places are never replaced by bone
(tip of nose, ear, etc.
2
The skeletal system has five major functions.
1. Provides shape and support.
2. Enables you move in conjunction with the
muscle system
3. Provides protection to internal organs
4. Produces blood cells
5. Stores minerals and other materials
3
Shape and Support
Your skeleton determines the shape of your body
The vertebrae is the center of the skeleton.
The vertebrae is composed of 26 small bones
4
Movement
Most of the bodys bones are associated with
muscles
The muscles pull on the bones to make the body
move.
Joints a place where two bones come together and
allow bones to move in different ways
Joints are held together by ligaments
5
Immovable joints connect bones in a way that
allows little or no movement - skull
6
Movable joints allow the body to make a wide
range of movements
Gliding joint - Hand
Ball and socket joint - shoulders and hips
Hinge joint - knees and elbows
Pivot Joint - neck
7
(No Transcript)
8
Cartilage cushions place between two bones
arthritis cartilage is gone
9
Bones are living organs that undergo growth and
development
Bone Cells Osteocytes - Mature bone
cells Osteoblasts - Bone-forming
cells Osteoclasts - Bone-destroying cells (break
down bone matrix for remodeling and release of
calcium)Bone remodeling is a process by both
osteoblasts and osteoclasts
10
There are two types of bone tissue
1. Compact bone - layer of hard and dense bone
beneath the outer membrane called the periosteum.
Periosteum - fibrous connective tissue membrane
covering the compact bone
2. Spongy bone - porous, strong, lightweight
layer of bone tissue beneath the compact bone.
Found at the ends of bone that provides strength.
11
Bone marrow - soft connective tissue found within
the bone. Two Types
1. Red marrow - produces most of the bodys blood
cells
2. Yellow marrow - stores fat and is an energy
reserve
12
Review Questions
13
Are Bones Dead?
- NO!
14
Are Bones Organs?
- YES!
15
How many types of bone tissue are there?
- 2
- Compact
- Spongy
16
True or False Bones begin as cartilage.
- TRUE!
17
Where do even adults still have cartilage?
- TIPS OF EARS
- NOSE
- GROWTH PLATES (IN KIDS)
18
Place where two bones meet
- JOINT
19
Four types of joints and examples of each
- SLIDING / GLIDING (Hand)
- BALL SOCKET (Shoulder)
- HINGE (Knee)
- PIVOT (Neck)
20
Is the skull a fixed or moveable joint?
- FIXED
21
What connects bone to bone?
- LIGAMENTS
22
Why is cartilage important?
- Provides a cushion between bones
23
(No Transcript)