Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 11
Title:
Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration
Description:
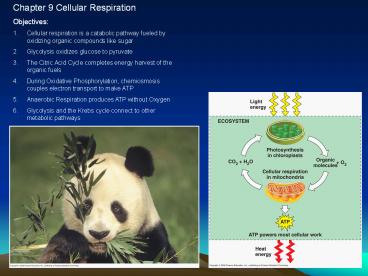
Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration Objectives: Cellular respiration is a catabolic pathway fueled by oxidizing organic compounds like sugar Glycolysis oxidizes glucose to ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:43
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration
1
- Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration
- Objectives
- Cellular respiration is a catabolic pathway
fueled by oxidizing organic compounds like sugar - Glycolysis oxidizes glucose to pyruvate
- The Citric Acid Cycle completes energy harvest of
the organic fuels - During Oxidative Phosphorylation, chemiosmosis
couples electron transport to make ATP - Anaerobic Respiration produces ATP without Oxygen
- Glycolysis and the Krebs cycle connect to other
metabolic pathways
2
- Catabolism
- The break down of C6H12O6 is highly exergonic
with a - Change in G -686 kcal/mol energy release
- Energy is transferred to ATP, which can be used
for Cellular Work
Redox Reactions -Energy is release through a
series of electron transfers. -Electrons are
transferred from one reactant to
another -Oxidation Loss of electrons
(LEO) -Reduction Gain of electrons
(GER) (net reduction in oxidation number)
-Oxygen is one of the greatest oxidizers -Oxygen
pulls electrons from sugar -Electrons travel with
hydrogens -The more hydrogen atoms the more
electrons that can be transfered the more
energy can be captured
3
Electrons are released to Oxygen slowly -Use of
NAD which is reduced to NADH (High potential
energy) -Travels to Electron Transport Chain
where ATP is produced
4
Cellular Respiration Overview -Think
Mitochondria -Think Plant and Animal Cells -Think
Production of ATP
5
Glycolysis Overview
Goal is to split one glucose in half See page 168
-169 for details
6
The Citric Acid Cycle Krebs Cycle
- Pyruvate enters and converts to Acetyl CoA, which
is a co enzyme - -Cycle goes twice per glucose molecule
- p. 171
- -Produces/cycle
- 4 NADH
- 2 FADH2
- 3 CO2
7
Oxidative Phosphorylation -Differs from
Substrate level phosphorylation -Protein
complexes are in the inner membrane of the
mitochondria -Electron carriers alternate
between oxidized and reduced forms -Each form is
oxidized by a more electronegative
neighbor -Oxygen is the final oxidizer
8
Electron Transport Powers Chemiosmosis -When
electron carrier is oxidized a proton is
tranfered to intermembrane space -Proton
gradient is used to run the ATP Synthase to
produce ATP
9
Most Energy Flows through Glucose -- NADH --
Electron Transport Chain -- Proton Motive Force
-- ATP
-Total ATP is not exact -About 40 efficient
based on energy available and energy released in
ATP
NADH 3 ATP FADH2 2 ATP
10
Fermentation -Most of the ATP is dependent on
Oxygen to pull electrons down the electron
Transport Chain -Fermentation is a way to harvest
chemical energy without an electron transport
chain -Glycolysis is the most wide spread
metabolic pathway in all species producing
Pyruvate --- is a juncture between aerobic
and anaerobic activity
11
Carbs, Proteins, and Lipids can enter the
Respiration cycle at various points
Respiration is governed by supply and demand